Abstract
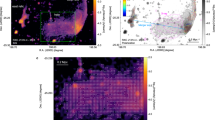
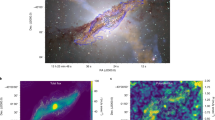
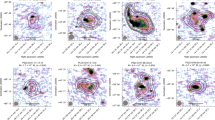
Clusters of galaxies, filled with hot magnetized plasma, are the largest bound objects in existence and an important touchstone in understanding the formation of structures in our Universe. In such clusters, thermal conduction follows field lines, so magnetic fields strongly shape the cluster’s thermal history; that some have not since cooled and collapsed is a mystery. In a seemingly unrelated puzzle, recent observations of Virgo cluster spiral galaxies imply ridges of strong, coherent magnetic fields offset from their centre. Here we demonstrate, using three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamical simulations, that such ridges are easily explained by galaxies sweeping up field lines as they orbit inside the cluster. This magnetic drape is then lit up with cosmic rays from the galaxies’ stars, generating coherent polarized emission at the galaxies’ leading edges. This immediately presents a technique for probing local orientations and characteristic length scales of cluster magnetic fields. The first application of this technique, mapping the field of the Virgo cluster, gives a startling result: outside a central region, the magnetic field is preferentially oriented radially as predicted by the magnetothermal instability. Our results strongly suggest a mechanism for maintaining some clusters in a ‘non-cooling-core’ state.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vollmer, B., Beck, R., Kenney, J. D. P. & van Gorkom, J. H. Radio continuum observations of the Virgo cluster spiral NGC 4522: The signature of ram pressure. Astron. J. 127, 3375–3381 (2004).
Vollmer, B. et al. The characteristic polarized radio continuum distribution of cluster spiral galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 464, L37–L40 (2007).
Weżgowiec, M. et al. The magnetic fields of large Virgo cluster spirals. Astron. Astrophys. 471, 93–102 (2007).
Vollmer, B. et al. The influence of the cluster environment on the large-scale radio continuum emission of 8 Virgo cluster spirals. Astron. Astrophys. 512, A36 (2010).
Beck, R. Galactic and extragalactic magnetic fields. Space Sci. Rev. 99, 243–260 (2001).
Voit, G. M. Tracing cosmic evolution with clusters of galaxies. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 207–258 (2005).
Winterhalter, D., Acuńa, M. & Zakharov, A. Mars’ Magnetism and its Interaction with the Solar Wind (Kluwer Academic, 2004).
Brandt, J. C. & Chapman, R. D. Introduction to Comets (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2004).
Bertucci, C., Mazelle, C., Acuña, M. H., Russell, C. T. & Slavin, J. A. Structure of the magnetic pileup boundary at Mars and Venus. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A01209 (2005).
Coleman, I. J. A multi-spacecraft survey of magnetic field line draping in the dayside magnetosheath. Ann. Geophys. 23, 885–900 (2005).
Neubauer, F. M. et al. Titan’s near magnetotail from magnetic field and electron plasma observations and modeling: Cassini flybys TA, TB, and T3. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A10220 (2006).
Liu, Y., Richardson, J. D., Belcher, J. W., Kasper, J. C. & Skoug, R. M. Plasma depletion and mirror waves ahead of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A09108 (2006).
Lyutikov, M. Magnetic draping of merging cores and radio bubbles in clusters of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 373, 73–78 (2006).
Dursi, L. J. & Pfrommer, C. Draping of cluster magnetic fields over bullets and bubbles-morphology and dynamic effects. Astrophys. J. 677, 993–1018 (2008).
Dursi, L. J. Bubble wrap for bullets: The stability imparted by a thin magnetic layer. Astrophys. J. 670, 221–230 (2007).
Slane, P. et al. Nonthermal X-ray emission from the shell-type supernova remnant G347.3–0.5. Astrophys. J. 525, 357–367 (1999).
Vink, J. et al. The X-ray synchrotron emission of RCW 86 and the implications for its age. Astrophys. J. Lett. 648, L33–L37 (2006).
Gold, B. et al. Five-year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe observations: Galactic foreground emission. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 180, 265–282 (2009).
Vollmer, B. et al. Pre-peak ram pressure stripping in the Virgo cluster spiral galaxy NGC 4501. Astron. Astrophys. 483, 89–106 (2008).
de Jong, T., Klein, U., Wielebinski, R. & Wunderlich, E. Radio continuum and far-infrared emission from spiral galaxies—A close correlation. Astron. Astrophys. 147, L6–L9 (1985).
Helou, G., Soifer, B. T. & Rowan-Robinson, M. Thermal infrared and nonthermal radio—Remarkable correlation in disks of galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 298, L7–L11 (1985).
Murphy, E. J., Kenney, J. D. P., Helou, G., Chung, A. & Howell, J. H. Environmental effects in clusters: Modified far-infrared-radio relations within Virgo cluster galaxies. Astrophys. J. 694, 1435–1451 (2009).
Balbus, S. A. Stability, instability, and backward transport in stratified fluids. Astrophys. J. 534, 420–427 (2000).
Braginskii, S. I. Transport processes in a plasma. Rev. Plasma Phys. 1, 205–311 (1965).
Parrish, I. J. & Stone, J. M. Saturation of the magnetothermal instability in three dimensions. Astrophys. J. 664, 135–148 (2007).
Parrish, I. J., Stone, J. M. & Lemaster, N. The magnetothermal instability in the intracluster medium. Astrophys. J. 688, 905–917 (2008).
Pfrommer, C., Springel, V., Enßlin, T. A. & Jubelgas, M. Detecting shock waves in cosmological smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 367, 113–131 (2006).
Jubelgas, M., Springel, V. & Dolag, K. Thermal conduction in cosmological SPH simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 351, 423–435 (2004).
Dolag, K., Jubelgas, M., Springel, V., Borgani, S. & Rasia, E. Thermal conduction in simulated galaxy clusters. Astrophys. J. Lett. 606, L97–L100 (2004).
Allen, S. W., Schmidt, R. W. & Fabian, A. C. The X-ray virial relations for relaxed lensing clusters observed with Chandra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 328, L37–L41 (2001).
Quataert, E. Buoyancy instabilities in weakly magnetized low-collisionality plasmas. Astrophys. J. 673, 758–762 (2008).
Parrish, I. J. & Quataert, E. Nonlinear simulations of the heat-flux-driven buoyancy instability and its implications for galaxy clusters. Astrophys. J. Lett. 677, L9–L12 (2008).
Randall, S. et al. Chandra’s view of the Ram pressure stripped galaxy M86. Astrophys. J. 688, 208–223 (2008).
Cavagnolo, K. W., Donahue, M., Voit, G. M. & Sun, M. Intracluster medium entropy profiles for a Chandra archival sample of galaxy clusters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 182, 12–32 (2009).
Sanderson, A. J. R., O’Sullivan, E. & Ponman, T. J. A statistically selected Chandra sample of 20 galaxy clusters—II. Gas properties and cool core/non-cool core bimodality. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 395, 764–776 (2009).
Voit, G. M. et al. Conduction and the star formation threshold in brightest cluster galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 681, L5–L8 (2008).
Guo, F., Oh, S. P. & Ruszkowski, M. A Global stability analysis of clusters of galaxies with conduction and AGN feedback heating. Astrophys. J. 688, 859–874 (2008).
Churazov, E., Brüggen, M., Kaiser, C. R., Böhringer, H. & Forman, W. Evolution of buoyant bubbles in M87. Astrophys. J. 554, 261–273 (2001).
Pfrommer, C., Enßlin, T. A., Springel, V., Jubelgas, M. & Dolag, K. Simulating cosmic rays in clusters of galaxies—I. Effects on the Sunyaev–Zel’dovich effect and the X-ray emission. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 378, 385–408 (2007).
Nagai, D., Kravtsov, A. V. & Vikhlinin, A. Effects of galaxy formation on thermodynamics of the intracluster medium. Astrophys. J. 668, 1–14 (2007).
Chung, A., van Gorkom, J. H., Kenney, J. D. P., Crowl, H. & Vollmer, B. VLA imaging of Virgo spirals in atomic gas (VIVA). I. The Atlas and the H I properties. Astron. J. 138, 1741–1816 (2009).
Stone, J. M., Gardiner, T. A., Teuben, P., Hawley, J. F. & Simon, J. B. Athena: A new code for astrophysical MHD. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 178, 137–177 (2008).
Gardiner, T. A. & Stone, J. M. An unsplit Godunov method for ideal MHD via constrained transport. J. Comput. Phys. 205, 509–539 (2005).
Gardiner, T. A. & Stone, J. M. An unsplit Godunov method for ideal MHD via constrained transport in three dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 4123–4141 (2008).
Böhringer, H. et al. The structure of the Virgo cluster of galaxies from Rosat X-ray images. Nature 368, 828–831 (1994).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank A. Chung, B. Vollmer and M. Weżgowiec for providing observational data and acknowledge C. Thompson, Y. Lithwick, J. Sievers and M. Ruszkowski for discussions during the preparation of this manuscript. C.P. gratefully acknowledges the financial support of the National Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada. Computations were carried out on the GPC supercomputer at the SciNet HPC Consortium. SciNet is funded by: the Canada Foundation for Innovation under the auspices of Compute Canada; the Government of Ontario; Ontario Research Fund—Research Excellence; and the University of Toronto. 3D renderings were carried out with Paraview.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.P. initiated this project, carried out the analytic estimates, developed an approach for comparing to observations, presented and analysed the observational data, measured magnetic field angles and discussed their uncertainties and explored consequences for cluster physics. L.J.D. carried out magnetohydrodynamical simulations with Athena, explored the parameter space and visualized the simulations. Both authors contributed to the exploratory simulations with Flash, the development of the synchrotron polarization model and post-processing, the statistical analysis, the interpretation of the results and writing of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1069 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfrommer, C., Dursi, J. Detecting the orientation of magnetic fields in galaxy clusters. Nature Phys 6, 520–526 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1657
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1657
This article is cited by
-
Cosmic ray feedback in galaxies and galaxy clusters
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (2023)
-
Highly ordered magnetic fields in the tail of the jellyfish galaxy JO206
Nature Astronomy (2020)
-
Magnetic bubble wrap
Nature Physics (2010)