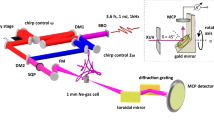
Abstract
Circular dichroism in the extreme ultraviolet range is broadly used as a sensitive structural probe of matter, from the molecular photoionization of chiral species1,2,3 to the magnetic properties of solids4. Extending such techniques to the dynamical regime has been a long-standing quest of solid-state physics and physical chemistry, and was only achieved very recently5 thanks to the development of femtosecond circular extreme ultraviolet sources. Only a few large facilities, such as femtosliced synchrotrons6,7 or free-electron lasers8, are currently able to produce such pulses. Here, we propose a new compact and accessible alternative solution: resonant high-order harmonic generation of an elliptical laser pulse. We show that this process, based on a simple optical set-up, delivers bright, coherent, ultrashort, quasi-circular pulses in the extreme ultraviolet. We use this source to measure photoelectron circular dichroism on chiral molecules, opening the route to table-top time-resolved femtosecond and attosecond chiroptical experiments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böwering, N. et al. Asymmetry in photoelectron emission from chiral molecules induced by circularly polarized light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 1187–1190 (2001).
Powis, I. Photoelectron circular dichroism in chiral molecules. Adv. Chem. Phys. 138, 267–329 (2008).
Garcia, G. A., Nahon, L., Daly, S. & Powis, I. Vibrationally induced inversion of photoelectron forward–backward asymmetry in chiral molecule photoionization by circularly polarized light. Nature Commun. 4, 2132 (2013).
Stohr, J. et al. Element-specific magnetic microscopy with circularly polarized X-rays. Science 259, 658–661 (1993).
Boeglin, C. et al. Distinguishing the ultrafast dynamics of spin and orbital moments in solids. Nature 465, 458–461 (2010).
Schoenlein, R. W. et al. Generation of femtosecond pulses of synchrotron radiation. Science 287, 2237–2240 (2000).
Čutić, N. et al. Vacuum ultraviolet circularly polarized coherent femtosecond pulses from laser seeded relativistic electrons. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 14, 030706 (2011).
Allaria, E. et al. Highly coherent and stable pulses from the FERMI seeded free-electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet. Nature Photon. 6, 699–704 (2012).
Le Déroff, L., Salières, P., Carré, B., Joyeux, D. & Phalippou, D. Measurement of the degree of spatial coherence of high-order harmonics using a Fresnel-mirror interferometer. Phys. Rev. A 61, 043802 (2000).
Hergott, J.-F. et al. Extreme-ultraviolet high-order harmonic pulses in the microjoule range. Phys. Rev. A 66, 021801 (2002).
Mahieu, B. et al. Full tunability of laser femtosecond high-order harmonics in the ultraviolet spectral range. Appl. Phys. B 108, 43–49 (2012).
Mairesse, Y. et al. High harmonic XUV spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 173903 (2005).
Chini, M., Zhao, K. & Chang, Z. The generation, characterization and applications of broadband isolated attosecond pulses. Nature Photon. 8, 178–186 (2014).
Klünder, K. et al. Probing single-photon ionization on the attosecond time scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 143002 (2011).
Haessler, S. et al. Phase-resolved attosecond near-threshold photoionization of molecular nitrogen. Phys. Rev. A 80, 011404(R) (2009).
Lépine, F., Ivanov, M. Y. & Vrakking, M. J. J. Attosecond molecular dynamics: fact or fiction? Nature Photon. 8, 195–204 (2014).
Bauer, M. Femtosecond ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy of ultra-fast surface processes. J. Phys. D 38, R253–R267 (2005).
Vodungbo, B. et al. Polarization control of high order harmonics in the EUV photon energy range. Opt. Express 19, 4346–4356 (2011).
Budil, K. S., Salières, P., Perry, M. D. & L'Huillier, A. Influence of ellipticity on harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. A 48, R3437–R3440 (1993).
Antoine, P., Carré, B., L'Huillier, A. & Lewenstein, M. Polarization of high-order harmonics. Phys. Rev. A 55, 1314–1324 (1997).
Milĕsević, D. B., Becker, W. & Kopold, R. Generation of circularly polarized high-order harmonics by two-color coplanar field mixing. Phys. Rev. A 61, 063403 (2000).
Yuan, K.-J. & Bandrauk, A. D. Single circularly polarized attosecond pulse generation by intense few cycle elliptically polarized laser pulses and terahertz fields from molecular media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 023003 (2013).
Fleischer, A., Kfir, O., Diskin, T., Sidorenko, P. & Cohen, O. Spin angular momentum and tunable polarization in high-harmonic generation. Nature Photon. 8, 543–549 (2014).
Smirnova, O. et al. Attosecond circular dichroism spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 063601 (2009).
Zhou, X. et al. Elliptically polarized high-order harmonic emission from molecules in linearly polarized laser fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 073902 (2009).
Mairesse, Y. et al. High harmonic spectroscopy of multichannel dynamics in strong-field ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 213601 (2010).
Yang, L. et al. Energy-dependent valence photoelectron spectra of SF6: ab initio calculations and measurements. J. Electron Spectrosc. Rel. Phenom. 94, 163–179 (1998).
Ferré, A. et al. Multi-channel static and dynamical resonant high-order harmonic generation. Nature Commun. 5, 5952 (2014).
Chini, M. et al. Coherent phase-matched VUV generation by field-controlled bound states. Nature Photon. 8, 437–441 (2014).
Rabinovitch, K., Canfield, L. R. & Madden, R. P. A method for measuring polarization in the vacuum ultraviolet. Appl. Opt. 4, 1005–1010 (1965).
Ferré, A. et al. High-harmonic transient grating spectroscopy of SF6 molecular vibrations. J. Phys. B 47, 124023 (2014).
Falcão-Filho, E. L. et al. Scaling of high-order harmonic efficiencies with visible wavelength drivers: a route to efficient extreme ultraviolet sources. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 061107 (2010).
Nahon, L., Garcia, G. A., Harding, C. J., Mikajlo, E. & Powis, I. Determination of chiral asymmetries in the valence photoionization of camphor enantiomers by photoelectron imaging using tunable circularly polarized light. J. Chem. Phys. 125, 114309 (2006).
Powis, I., Harding, C. J., Garcia, G. A. & Nahon, L. A valence photoelectron imaging investigation of chiral asymmetry in the photoionization of fenchone and camphor. Chem. Phys. Chem. 9, 475–483 (2008).
Pitzer, M. et al. Direct determination of absolute molecular stereochemistry in gas phase by Coulomb explosion imaging. Science 341, 1096–1100 (2013).
Lux, C. et al. Circular dichroism in the photoelectron angular distributions of camphor and fenchone from multiphoton ionization with femtosecond laser pulses. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 5001–5005 (2012).
Janssen, M. H. M. & Powis, I. Detecting chirality in molecules by imaging photoelectron circular dichroism. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 856–871 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank R. Bouillaud and L. Merzeau for technical assistance, and M. Mairesse for mechanical supplies. The authors acknowledge financial support from the Conseil Regional d'Aquitaine (20091304003 ATTOMOL and COLA 2 no. 2.1.3-09010502), l'Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR-14-CE32-0014 MISFITS and ANR-14-CE32-0010 XTASE), the European Union (Laserlab-Europe II no. 228334 and EU-FP7 284464) and the RTRA Triangle de la Physique (Attocontrol).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.H. built the VMIS. F.B., D.D. and S.P. operated the laser system. A.F., E.M., V.B. and Y.M. built the high-harmonic beamline. A.F., M.D., A.C., R.G., L.M., D.S., S.W., T.R., V.B. and Y.M. carried out the measurements. A.F. and Y.M. analysed the optical polarimetry measurements. G.A.G. and L.N. inverted the VMIS images and extracted and rationalized the PECD data. B.P. performed the theoretical calculations. Y.M. designed the manuscript. All authors contributed to the interpretation of the data and writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 527 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferré, A., Handschin, C., Dumergue, M. et al. A table-top ultrashort light source in the extreme ultraviolet for circular dichroism experiments. Nature Photon 9, 93–98 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.314
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.314
This article is cited by
-
Enabling elliptically polarized high harmonic generation with short cross polarized laser pulses
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Amplification of elliptically polarized sub-femtosecond pulses in neon-like X-ray laser modulated by an IR field
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Elliptically polarized high-harmonic radiation for production of isolated attosecond pulses
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Divergence and efficiency optimization in polarization-controlled two-color high-harmonic generation
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A theoretical model of high-harmonic generation from two-color relativistic circularly polarized laser pulse interacting with over-dense plasmas
Applied Physics B (2020)