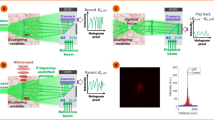
Abstract
Light scattering in inhomogeneous media induces wavefront distortions that pose an inherent limitation in many optical applications. Examples where this occurs include microscopy, nanosurgery and astronomy. In recent years, ongoing efforts have made the correction of spatial distortions possible using wavefront-shaping techniques. However, when ultrashort pulses are used, scattering also induces temporal distortions, which hinder the use of such pulses in nonlinear processes such as multiphoton microscopy and quantum control experiments. Here, we show that correction of both spatial and temporal distortions can be achieved by manipulating only the spatial degrees of freedom of the incident wavefront. By optimizing a nonlinear signal, we demonstrate spatiotemporal focusing and compression of chirped ultrashort pulses through scattering media, and refocusing in both space and time of 100 fs pulses through thick brain and bone samples. Our results open up new possibilities for optical manipulation and nonlinear imaging in scattering media.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sebbah, P. Waves and Imaging Through Complex Media (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2001).
Goodman, J. W. Speckle Phenomena in Optics: Theory and Applications (Roberts & Co., 2007).
Tal, E. & Silberberg, Y. Transformation from an ultrashort pulse to a spatiotemporal speckle by a thin scattering surface. Opt. Lett. 31, 3529–3531 (2006).
Bruce, N. C. et al. Investigation of the temporal spread of an ultrashort light pulse on transmission through a highly scattering medium. Appl. Opt. 34, 5823–5828 (1995).
Webster, M. A., Gerke, T. D., Weiner, A. M. & Webb, K. J. Spectral and temporal speckle field measurements of a random medium. Opt. Lett. 29, 1491–1493 (2004).
Johnson, P. M. et al. Time-resolved pulse propagation in a strongly scattering material. Phys. Rev. E 68, 016604 (2003).
Szmacinski, H., Gryczynski, I. & Lakowicz, J. R. Spatially localized ballistic two-photon excitation in scattering media. Biospectroscopy 4, 303–310 (1998).
Dela Cruz, J. M., Pastirk, I., Comstock, M., Lozovoy, V. V. & Dantus, M. Use of coherent control methods through scattering biological tissue to achieve functional imaging. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 16996–17001 (2004).
Tyson, R. K. Principles of Adaptive Optics 2nd edn (Academic Press, 1998).
Nature Photon. Technology focus: Adaptive optics. Nature Photon. 5, 15–28 (2011).
Booth, M. J. Adaptive optics in microscopy. Phil.Trans. R. Soc. A 365, 2829–2843 (2007).
Rueckel, M., Mack-Bucher, J. A. & Denk, W. Adaptive wavefront correction in two-photon microscopy using coherence-gated wavefront sensing. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 17137–17142 (2006).
Vellekoop, I. M. & Mosk, A. P. Focusing coherent light through opaque strongly scattering media. Opt. Lett. 32, 2309–2311 (2007).
Vellekoop, I. M., van Putten, E. G., Lagendijk, A. & Mosk, A. P. Demixing light paths inside disordered metamaterials. Opt. Express 16, 67–80 (2008).
Vellekoop, I. M., Lagendijk, A. & Mosk, A. P. Exploiting disorder for perfect focusing. Nature Photon. 4, 320–322 (2010).
Vellekoop, I. M. & Aegerter, C. M. Scattered light fluorescence microscopy: imaging through turbid layers. Opt. Lett. 35, 1245–1247 (2010).
Popoff, S. M. et al. Measuring the transmission matrix in optics: an approach to the study and control of light propagation in disordered media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 100601 (2010).
Popoff, S., Lerosey, G., Fink, M., Boccara, A. C. & Gigan, S. Image transmission through an opaque material. Nature Commun. 1, 81. doi:10.1038/ncomms1078 (2010).
Čižmár, T., Mazilu, M. & Dholakia, K. In situ wavefront correction and its application to micromanipulation. Nature Photon. 4, 388–394 (2010).
Yaqoob, Z., Psaltis, D., Feld, M. S. & Yang, C. Optical phase conjugation for turbidity suppression in biological samples. Nature Photon. 2, 110–115 (2008).
Denk, W., Strickler, J. H. & Webb, W. W. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science 248, 73–76 (1990).
Oheim, M., Beaurepaire, E., Chaigneau, E., Mertz, J. & Charpak, S. Two-photon microscopy in brain tissue: parameters influencing the imaging depth. J. Neurosci. Methods 111, 29–37 (2001).
Rabitz, H., de Vivie-Riedle, R., Motzkus, M. & Kompa, K. Whither the future of controlling quantum phenomena? Science 288, 824–828 (2000).
Assion, A. et al. Control of chemical reactions by feedback-optimized phase-shaped femtosecond laser pulses Science 30, 919–922 (1998).
Pearson, B. J., White, J. L., Weinacht, T. C. & Bucksbaum, P. H. Coherent control using adaptive learning algorithms. Phys. Rev. A 63, 063412 (2001).
Stockman, M. I., Faleev, S. V. & Bergman, D. J. Coherent control of femtosecond energy localization in nanosystems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 067402 (2002).
Aeschlimann, M. et al. Adaptive subwavelength control of nano-optical fields. Nature 446, 301–304 (2007).
Oron, D., Dudovich, N. & Silberberg, Y. All-optical processing in coherent nonlinear spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. A 70, 023415 (2004).
Fink, M. Time reversed acoustics. Phys. Today 50, 34–40 (1997).
Lerosey, G. et al. Time reversal of electromagnetic waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 193904 (2004).
Derode, A. et al. Taking advantage of multiple scattering to communicate with time-reversal antennas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 014301 (2003).
Weiner, A. M. Femtosecond pulse shaping using spatial light modulators. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71, 1929–1960 (2000).
McCabe, D. J. et al. Shaping speckles: spatio-temporal focussing of an ultrafast pulse through a multiply scattering medium. arXiv:1101.0976 (2011).
Jiang, Y., Narushima, T. & Okamoto, H. Nonlinear optical effects in trapping nanoparticles with femtosecond pulses. Nature Phys. 6, 1005–1009 (2010).
Andrasfalvy, B. K., Zemelman, B. V., Tang, J. & Vaziri, A. Two-photon single-cell optogenetic control of neuronal activity by sculpted light. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 11981–11986 (2010).
Vellekoop, I. M. & Mosk, A. P. Phase control algorithms for focusing light through turbid media. Opt. Commun. 281, 3071–3080 (2008).
Diels, J. C., Fontaine, J. J., McMichael, I. C. & Simoni, F. Control and measurement of ultrashort pulse shapes (in amplitude and phase) with femtosecond accuracy. Appl. Opt. 24, 1270–1282 (1985).
Yelin, D., Meshulach, D. & Silberberg, Y. Adaptive femtosecond pulse compression. Opt. Lett. 22, 1793–1795 (1997).
Lemoult, F., Lerosey, G., de Rosny, J. & Fink, M. Manipulating spatiotemporal degrees of freedom of waves in random media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 173902 (2009).
Aulbach, J., Gjonaj, B., Johnson, P. M., Mosk, A. P. & Lagendijk, A. Control of light transmission through opaque scattering media in space and time. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 103901 (2011).
Small, E., Katz, O., Eshel, Y., Silberberg, Y. & Oron, D. Spatio-temporal X-wave. Opt. Express 17, 18659–18668 (2009).
Oron, D., Tal, E. & Silberberg, Y. Scanningless depth-resolved microscopy. Opt. Express 13, 1468–1476 (2005).
Wilt, B. A. et al. Advances in light microscopy for neuroscience. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 32, 435–506 (2009).
Cui, M. A high speed wavefront determination method based on spatial frequency modulations for focusing light through random scattering media. Opt. Express 19, 2989–2995 (2011).
Hsieh, C.-L., Pu, Y., Grange, R. & Psaltis, D. Digital phase conjugation of second harmonic radiation emitted by nanoparticles in turbid media. Opt. Express 18, 12283–12290 (2010).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank E. Korkotian, G. Grigoryan and M. Segal for brain samples, N. Reznikov, J.M. Levitt and S. Weiner for the bone sample, R. Ozeri's group for the EMCCD camera, M. Covo for graphical design and D. Oron for fruitful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the Israel Science Foundation, the Israel Ministry of Science and the Crown Photonics Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
O.K. conceived the idea. O.K., Y.B., E.S. and Y.S. designed the experiments. O.K., E.S. and Y.B. performed the experiments, analysed the data and carried out numerical simulations. All authors contributed to the writing of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary movie (MOV 2794 kb)
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 221 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, O., Small, E., Bromberg, Y. et al. Focusing and compression of ultrashort pulses through scattering media. Nature Photon 5, 372–377 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.72
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.72
This article is cited by
-
Exploiting volumetric wave correlation for enhanced depth imaging in scattering medium
Nature Communications (2023)
-
High-gain and high-speed wavefront shaping through scattering media
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
Measuring the scattering tensor of a disordered nonlinear medium
Nature Physics (2023)
-
Spatiotemporal mode-locking and dissipative solitons in multimode fiber lasers
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Enhance the delivery of light energy ultra-deep into turbid medium by controlling multiple scattering photons to travel in open channels
Light: Science & Applications (2022)