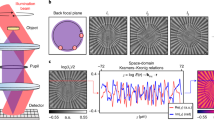
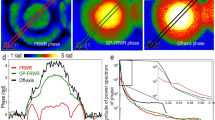
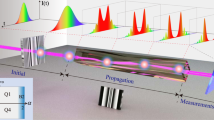
Abstract
It is well known that one cannot image directly through a nonlinear medium, as intensity-dependent phase changes distort signals as they propagate. Indirect methods can be used1,2,3,4,5,6, but none has allowed for the measurement of internal wave mixing and dynamics. Recently, the reconstruction of nonlinear pulse propagation in fibres was demonstrated by generalizing the techniques of digital holography7,8 to the nonlinear domain9. The method involves two steps: (1) recording the total field (both amplitude and phase) exiting a nonlinear medium and (2) numerically back-propagating the wavefunction. Here, we extend this process to two-dimensional spatial beams and experimentally demonstrate it in a self-defocusing photorefractive crystal, giving examples in soliton formation, dispersive radiation and imaging. For known nonlinearity, the technique enables reconstruction of wave dynamics within the medium and suggests new methods of super-resolved imaging, including subwavelength microscopy and lithography. For unknown nonlinearity, the method facilitates modelling and characterization of the optical response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yariv, A. Three-dimensional pictorial transmission in optical fibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 28, 88–89 (1976).
Yariv, A. Compensation for atmospheric degradation of optical beam transmission by nonlinear optical mixing. Opt. Commun. 21, 49–50 (1977).
Fischer, B., Cronin-Golomb, M., White, J. O. & Yariv, A. Real-time phase conjugate window for one-way optical field imaging through a distortion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 41, 141–143 (1982).
Khyzniak, A. et al. Phase conjugation by degenerate forward four-wave mixing. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1, 169–175 (1984).
Jones, D. C., Lyuksyutov, S. F. & Solymar, L. Three-wave and four-wave forward phase-conjugate imaging in photorefractive bismuth silicon oxide. Opt. Lett. 15, 935–937 (1990).
Kip, D., Anastassiou, C., Eugenieva, E., Christodoulides, D. & Segev, M. Transmission of images through highly nonlinear media by gradient-index lenses formed by incoherent solitons. Opt. Lett. 26, 524–526 (2001).
Schnars, U. & Jüptner, W. Direct recording of holograms by a CCD target and numerical reconstruction. Appl. Opt. 33, 179–181 (1994).
Schnars, U. & Jüptner, W. P. O. Digital recording and numerical reconstruction of holograms. J. Meas. Sci. Technol. 13, R85–R101 (2002).
Tsang, M., Psaltis, D. & Omenetto F. Reverse propagation of femtosecond pulses in optical fibers. Opt. Lett. 28, 1873–1875 (2003).
Yamaguchi, I. & Zhang, T. Phase-shifting digital holography. Opt. Lett. 22, 1268–1270 (1997).
Goldfarb, G. & Li, G. Demonstration of fibre impairment compensation using split-step infinite-impulse-response filtering method. Electron. Lett. 44, 814–815 (2008).
Mateo, E., Zhu, L. & Li, G. Impact of XPM and FWM on the digital implementation of impairment compensation for WDM transmission using backward propagation. Opt. Express 16, 16124–16137 (2008).
Segev, M., Valley, G. C., Crosignani, B., Diporto, P. & Yariv, A. Steady-state spatial screening solitons in photorefractive materials with external applied field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 3211–3214 (1994).
Christodoulides, D. N. & Carvalho, M. I. Bright, dark and gray spatial soliton states in photorefractive media. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 12, 1628–1633 (1995).
Wan, W., Jia, S. & Fleischer, J. W. Dispersive, superfluid-like shock waves in nonlinear optics. Nature Phys. 3, 46–51 (2007).
Ghofraniha, N., Conti, C., Ruocco, G. & Trillo, S. Shocks in nonlocal media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 043903 (2007).
Shih, M. et al. Two-dimensional steady-state photorefractive screening solitons. Opt. Lett. 21, 324–326 (1996).
Linzon, Y. et al. Near-field imaging of nonlinear pulse propagation in planar silica waveguides. Phys. Rev. E 72, 066607 (2005).
Krökel, D., Halas, N. J., Giuliani, G. & Grischkowsky, D. Dark-pulse propagation in optical fibers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 29–32 (1988).
Oppenheim, A. V. & Lim, J. S. The importance of phase in signals. Proc. IEEE 69, 529–541 (1981).
Agrawal, G. P. Modulation instability induced by cross-phase modulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 880–883 (1987).
Stentz, A. J., Kauranen, M., Maki, J. J., Agrawal, G. P. & Boyd, R. W. Induced focusing and spatial wave breaking from cross-phase modulation in a self-defocusing medium. Opt. Lett. 17, 19–21 (1992).
Hickmann, J. M., Gomes, A. S. L. & de Araújo, C. B. Observation of spatial cross-phase modulation effects in a self-defocusing nonlinear medium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3547–3550 (1992).
Jia, S., Wan, W. & Fleischer, J. W. Forward four-wave mixing with defocusing nonlinearity. Opt. Lett. 32, 1668–1670 (2007).
Goos, F. & Hänchen, H. Ein neuer und fundamentaler versuch zur totalreflexion. Ann. Phys. 1, 333–346 (1947).
Artmann, K. Berechnung der seitenversetzung des totalreflektierten strahles. Ann. Phys. 2, 87–102 (1947).
Tomlinson, W. J., Gordon, J. P., Smith, P. W. & Kaplan, A. E. Reflection of a Gaussian beam at a nonlinear interface. Appl. Opt. 21, 2041–2051 (1982).
Emile, O., Galstyan, T., Le Floch, A. & Bretenaker, F. Measurement of the nonlinear Goos–Hänchen effect for Gaussian optical beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 1511–1513 (1995).
Jost, B. M., Al-Rashed, A.-A. R. & Saleh, B. E. A. Observation of the Goos–Hänchen effect in a phase-conjugate mirror. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2233–2235 (1998).
Ash, E. A. & Nicholls, G. Super-resolution aperture scanning microscope. Nature 237, 510–512 (1972).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation, the Department of Energy and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research. C.B. would like to thank the Army Research Office for support through a National Defense Science and Engineering Graduate Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed to this paper and agree to its contents.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barsi, C., Wan, W. & Fleischer, J. Imaging through nonlinear media using digital holography. Nature Photon 3, 211–215 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.29
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.29
This article is cited by
-
Image encryption using spatial nonlinear optics
eLight (2022)
-
Dual-comb hyperspectral digital holography
Nature Photonics (2021)
-
Adaptive wavefront shaping for controlling nonlinear multimode interactions in optical fibres
Nature Photonics (2018)
-
Single-shot measurement of phase and amplitude by using a heterodyne time-lens system and ultrafast digital time-holography
Nature Photonics (2018)
-
Digital holographic high-speed 3D imaging for the vibrometry of fast-occurring phenomena
Scientific Reports (2017)