Abstract
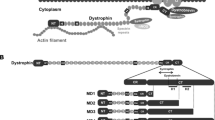
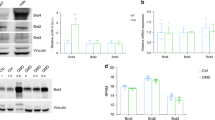
Dp71 is a non-muscle product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. It consists of the cysteine-rich and C-terminal domains of dystrophin. We have generated transgenic mdx mice which do not have dystrophin but express Dp71 in their muscle. In these mice, Dp71 was localized to the plasma membrane and restored normal levels of dystrophin associated protiens (DAPs), indicating that Dp71 is capable of interacting with the DAPs in a similar manner to dystrophin. However, the presence of Dp71 and DAPs in the muscle fibres of mdx mice was not sufficient to alleviate symptoms of muscle degeneration.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emery, A.E.H. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Oxford Monographs on Medical Genetics. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1987).
Ahn, A.H. & Kunkel, L.M. The structural and functional diversity of dystrophin. Nature Genet. 3, 283–291 (1993).
Ervasti, J.M., Ohlendieck, K., Kahl, S.D., Gaver, M.G. & Campbell, K.P. Deficiency of a glycoprotein component of the dystrophin complex in dystrophic muscle. Nature. 345, 315–319 (1990).
Ervasti, J.M. & Campbell, K.P. Membrane organization of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Cell. 66, 1121–1131 (1991).
Yoshida, M. & Ozawa, E. Glycoprotein complex anchoring dystrophin to the sarcolemma. J Biochem. (Tokyo) 108, 748–752 (1990).
Ohlendieck, K. & Campbell, K.P. Dystrophin-associated proteins are greatly reduced in skeletal muscle from mdx mice. J. cell Biol. 115, 1685–1694 (1990).
Matsumura, K. et al. Deficiency of the 50 K dystrophin associated glycoprotein in severe childhood autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy. Nature. 359, 320–322 (1992).
Lederfein, D., Yaffe, D. & Nudel, U. A housekeeping type promoter located in the 3′ region of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene controls the expression of Dp71 a major product of the gene. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 1883–1888( (1993).
Bar, S. et al. A novel product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene which differs greatly from the known isoforms in its structure and tissue distribution. Biochem. J. 272, 557–560 (1990).
Lederfein, D. et al. A 71-kDa protein is a major product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in brain and other nonmuscle tissues. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 5346–5350 (1992).
Hugnot, J.P. et al. Distal transcript of the dystrophin gene initiated from an alternative first exon and encoding a 75-kDa protein widely distributed in nonmuscle tissues. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7506–7510 (1992).
Blake, D.J. et al. Characterization of a 4.8 kb transcript from the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus expressed in Schwannoma cells. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 103–109 (1992).
Rapaport, D. et al. Characterization and cell type distribution of a novel major transcript of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Different. 49, 187–193 (1992).
Rapaport, D., Fuchs, O., Nudel, U. & Yaffe, D. Expression of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene products in embryonic stem cells and their differentiated derivatives. J. biol. Chem. 267, 21289–21292 (1992).
Rapaport, D., Greenberg, D.S., Tal, M., Yaffe, D. & Nudel, U. Dp71, the nonmuscle product of the Duchenne dystrophy gene is associated with the cell membrane. FEBS Lett. 328, 197–202 (1993).
Ellis, J.M. et al. Specificity of dystrophin analysis improved with monoclonal antibodies. Lancet 336, 881–882 (1990).
Pons, F. et al. A homologue of dystrophin is expressed at the neuromuscular junctions of normal individuals and DMD patients and of normal and mdx mice. Immunologigal evidence. FEBS Lett. 282, 161–165 (1991).
Suzuki, A., Yoshida, M., Yamamoto, H. & Ozawa, E. Glycoprotein-bindingsite of dystrophin is confined to the cysteine-rich domain and the first half of the carboxy-terminal domain. FEBS Lett. 308, 154–160 (1992).
Kramarcy, N.R., Vidal, A., Froehner, S.C. & Sealock, R. Association of utrophin and multiple dystrophin short forms with the mammalian M(r) 58,000 dystrophin-associated protein (syntrophin). J. biol. Chem. 269, 2870–2876 (1994).
Cox, G.A., Sunada, Y., Campbell, K.P. & Chamberlain, K.P. & Chamberlain, J.S. Dp71 can restore the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex in muscle but fails to prevent dystrophy. Nature Genet. 8, 334–340 (1994).
England, S.B. et al. Very mild muscular dystrophy associated with the deletion of 46% of dystrophin. Nature 343, 180–182 (1990).
Nicholson, L.V.B., Bushby, K.M.D., Johnson, M A, Gardner-Medwin, D. & Ginjaar, I.B. Dystrophin expression in Duchenne patients with “in frame” gene deletions. Neuroped. 24, 93–97 (1993).
Vainzof, M. et al. Is the maintenance of the C-terminus domain of dystrophin enough to ensure a milder Becker muscular dystrophy phenotype? Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 39–42 (1993).
Winnard, A.V. et al. Characterization of translational frame exception patients in Duchenne/Becker Muscular dystrophy. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 737–744 (1993).
Prior, T.W. et al. A missense mutation in the dystrophin gene in a Duchenne muscular dystrophy patient. Nature Genet. 4, 357–36024 (1993).
Ervasti, J.M. & Campbell, K.P. A role for the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex as a transmembrane linker between laminin and actin. J. cell Biol. 122, 809–823 (1993).
Sunada, Y., Bernier, S.M., Kozak, C.A., Yamada, Y. & Campbell, K.P. Deficiency of merosin in Dystrophic dy mice and genetic linkage of laminin M chain gene to dy locus. J. biol. chem. 269, 13729–13732 (1994).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual 2nd edn. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1992).
Hogan, B., Costantini, F. & Lacy, E. Manipulating the mouse embryo, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1986).
Ervasti, J.M., Kahl, S.D. & Campbell, K.P. Purification of dystrophin from skeletal muscle. J. biol. Chem. 266, 9161–9165 (1991).
Ohlendiek, K. et al. Dystrophin-related protein is localized to neuromuscular junctions of adult skeletal muscle. Neuron 7, 499–508 (1991).
Roberds, S.L. et al. Primary structure and muscle specific expression of the 50-kDa dystrophin-associated glycoprotein (adhalin). J. biol. Chem. 268, 23739–23742 (1993).
Matsumura, K., Ervasti, J.M., Ohlendieck, K., Kahl, S.D. & Campbell, K.P. Association of dystrophin-related protein with dystrophin-associated proteins in mdx muscle. Nature 360, 588–591 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greenberg, D., Sunada, Y., Campbell, K. et al. Exogenous Dp71 restores the levels of dystrophin associated proteins but does not alleviate muscle damage in mdx mice. Nat Genet 8, 340–344 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1294-340
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1294-340
This article is cited by
-
X-linked muscular dystrophy in a Labrador Retriever strain: phenotypic and molecular characterisation
Skeletal Muscle (2020)
-
Dystrophin Dp71: The Smallest but Multifunctional Product of the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Gene
Molecular Neurobiology (2012)
-
Transgenic overexpression of γ-cytoplasmic actin protects against eccentric contraction-induced force loss in mdx mice
Skeletal Muscle (2011)
-
Dystrophin associated proteins fail in filling dystrophin's shoes
Nature Genetics (1994)
-
Dp71 can restore the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex in muscle but fails to prevent dystrophy
Nature Genetics (1994)