Abstract
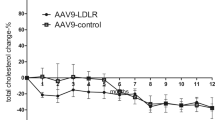
Liver directed gene transfer with adenoviral vectors is being considered for the treatment of several metabolic diseases, including familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH). Gene replacement therapy of human low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene into the murine model of FH transiently corrected the dyslipidaemia; however, humoral and cellular immune responses to LDL receptor developed — possibly contributing to the associated hepatitis and extinguishing of transgene expression. We evaluated an alternative strategy of ectopic expression in the liver of the very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptor, which is homologous to the LDL receptor but has a different pattern of expression. Infusion of recombinant adenoviruses containing the VLDL receptor gene corrected the dyslipidaemia in the FH mouse and circumvented immune responses to the transgene leading to a more prolonged metabolic correction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldstein, J.L., Hobbs, H.H. & Brown, M.S. Familial hypercholesterolemia. in The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease(eds Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S. & Valle, D.) 1981–2030 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1995).
Chowdhury, J. et al. Long-term improvement of hypercholesterolemia after ex vivo gene therapy in LDLR deficient rabbits. Science 254, 1802–1805 (1991).
Grossman, M., Raper, S. & Wilson, J. Transplantation of genetically-modified autologus hepatocytes into nonhuman primates: feasibility and short-term toxicity. Hum. Gene Ther. 3, 501–510 (1992).
Grossman, M. et al. Successful Ex Vivo Gene Therapy Directed to Liver Patient with Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Nature Genet. 6, 335–341 (1994).
Grossman, M. et al. A pilot study of ex vivo gene therapy for homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Nature Med. 1148–1154 (1995).
Kozarsky, K. et al. In vivo correction of LDL receptor deficiency in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit with recombinant adenoviruses. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 13695–13702 (1994).
Li, J. et al. In vivo gene therapy for hyperlipidemia: phenotypic correction in Watanabe rabbits by hepatic delivery of the rabbit LDL receptor gene. J. Clin. Invest. 95, 768–773 (1995).
Ishibashi, S. et al. Hypercholesterolemia in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice and its reversal by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. J. Clin. Invest. 92, 883–893 (1993).
Yang, Y. et al. Cellular immunity to viral antigens limits E1-deleted adenoviruses for gene therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 4407–4411 (1994).
Barr, D. et al. Strain related variations in adenovirally mediated transgene expression from mouse hepatocytes in vivo: comparisons between immunocompetent and immunodeficient inbred strains. Gene. Therapy 2, 151–155 (1995).
Yang, Y., Li, Q., Ertl, H. & Wilson, J. Cellular and humoral immune responses to viral antigens create barriers to lung-directed gene therapy with recombinant adenoviruses. J. Virol. 69, 2004–2015 (1995).
Engelhardt, J., Litzky, L. & Wilson, J. Prolonged transgene expression in cotton rat lung with recombinant adenoviruses defective in E2a. Hum. Gene Therapy 5, 1217–1229 (1994).
Yang, Y., Ertl, H. & Wilson, J. MHC class 1 restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes to viral antigens destroy hepatocytes in mice infected with E1 deleted recombinant adenoviruses. Immunity 1, 433–442 (1994).
Takahashi, S., Kawarabayasi, Y., Nakai, T., Sakai, J. & Yamamoto, T. Rabbit very low density lipoprotein receptor: a low density lipoprotein receptor-like protein with distinct ligand specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 9252–9256 (1992).
Gafvels, M.E. et al. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a putative human very low density lipoprotein/apolipoprotein E receptor and assignment of the gene to chromosome 9pter–p23. Som. Cell Mol. Genet. 19, 557–569 (1993).
Gafvels, M.E. et al. Cloning of a complementary deoxyribonucleic acid encoding the murine homolog of the very low density lipoprotein/ apolipoprotein-E receptor: expression pattern and assignment of the gene to mouse chromosome 19. Endocrinol. 135, 387–394 (1994).
Oka, K. et al. Mouse very-low-density-lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) cDNA cloning, tissue-specific expression and evolutionary relationship with the low-density-lipoprotein receptor. J. Biochem. 224, 975, 982 (1994).
Frykman, P., Brown, M., Yamamoto, T., Goldstein, J. & Herz, J. Normal plasma lipoproteins and fertility in gene-targeted mice homozygous for a disruption in the gene encoding very low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8453–8457 (1995).
Yamamoto, T., Takahashi, S., Sakai, J. & Kawarabayasi, Y. The very low density lipoprotein receptor, a seond lipoprotein receptor that may mediate uptake of fatty acids into muscle and fat cells. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 3, 144–148 (1993).
Kass-Eisler, A. et al. The impact of developmental stage, route of administration and the immune system on adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. Gene Tnerapy 1, 395–402 (1994).
Dai, Y. et al. Cellular and humoral immune responses to adenoviral vectors containing factor IX gene: Tolerization of factor IX and vector antigens allows for long-term expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 1401–1405 (1995).
Battey, F. et al. The 39-kDa receptor-associated protein regulates ligand binding by the very low density lipoprotein receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 23268–23273 (1994).
Van Ginkel, F. et al. Intratracheal gene delivery with adenoviral vector induces elevated systemic IgG and mucosal IgA antibodies to adenovirus and β-galactosidase. Hum. Gene Therapy 6, 895–903 (1995).
Yang, Y., Jooss, K.U., Su, Q., Ertl, H.C.J. & Wilson, J.M. Immune responses to viral antigens vs. transgene product in the elimination of recombinant adenovirus infected hepatocytesin vivo. Gene Therapy(in the press).
Jokinen, E.V. et al. Regulation of the very low density lipoprotein receptor by thyroid hormone in rat skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 26411–26418 (1994).
Willnow, T. & Herz, J. Animal models for disorders of hepatic lipoprotein metabolism. J. Mol. Med. 73, 213–20 (1995).
Shimano, H. et al. Secretion-recapture process of apolipoprotein E in hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants in transgenic mice. J. Clin. Invest. 93, 2215–2223 (1994).
Mokuno, H., Brady, S., Kotite, L., Herz, J. & Havel, R. Effect of the 39-kDa receptor-associated protein on the hepatic uptake and endocytosis of chylomicron remnants and low density lipoproteins in the rat. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 13238–13243 (1994).
Bu, G., Geuze, H., Strous, G. & Schwartz, A. 39 kDa receptor-associated protein is an ER resident protein and molecular chaperone for LDL receptor-related protein. EMBO J. 14, 2269–2280 (1995).
Polvino, W.J., Dichek, D.A., Mason, J. & Anderson, W.F. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding a functional murine low-density-lipoprotein receptor. Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 18, 443–450 (1992).
Hoffer, M.J.V. et al. The mouse low density lipoprotein receptor gene: cDNA sequence and exon–intron structure. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 191, 880–886 (1993).
Kozarsky, K., Grossman, M. & Wilson, J. Adenovirus-mediated correction of the genetic defect in hepatocytes from patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Somat. Cell Molec. Genet. 19, 449–458 (1993).
Engelhardt, J. et al. Direct gene transfer of human CFTR into human bronchial epithelia of xenografts with E1 -deleted adenoviruses. Nature Genet. 4, 27–34 (1993).
Yamamoto, T. et al. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell 39, 27–38 (1984).
Chakrabarti, S., Brechling, K. & Moss, B. Moss, B. vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of β-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol. Cell. Biol. 5, 3403–3409 (1985).
Wiktor, T. et al. Protection from rabies by a vaccinia virus recombinant containing the rabies virus glycoprotein gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 7194–7198 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozarsky, K., Jooss, K., Donahee, M. et al. Effective treatment of familial hypercholesterolaemia in the mouse model using adenovirus–mediated transfer of the VLDL receptor gene. Nat Genet 13, 54–62 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0596-54
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0596-54
This article is cited by
-
A viral biomolecular condensate coordinates assembly of progeny particles
Nature (2023)
-
Adenovirus-mediated ubiquitination alters protein–RNA binding and aids viral RNA processing
Nature Microbiology (2020)
-
Sleeping Beauty Transposon Vectors in Liver-directed Gene Delivery of LDLR and VLDLR for Gene Therapy of Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Molecular Therapy (2016)
-
A core viral protein binds host nucleosomes to sequester immune danger signals
Nature (2016)
-
RNAi-mediated knockdown of HMG CoA reductase enhances gene expression from physiologically regulated low-density lipoprotein receptor therapeutic vectors in vivo
Gene Therapy (2012)