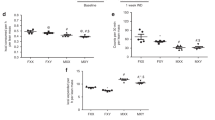
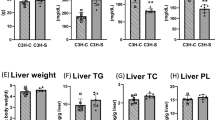
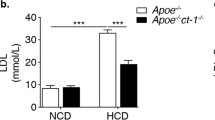
Abstract
High plasma concentrations of apolipoprotein (a) (apo(a)) have been implicated as a major independent risk factor for atherosclerosis in humans. Apo(a) is a large, evolutionary new gene (present primarily in primates) for which considerable controversy exists concerning the factors that regulate its expression. To investigate the in vivo regulation of apo(a), we have created several lines of YAC transgenic mice containing a 110–kb human apo(a) gene surrounded by greater than 60 kb of 5′ and 3′ flanking DNA. Studies in humans have suggested that acute–phase inducers increase and sex steroids decrease apo(a) concentrations, but these results are controversial. Analysis of the YAC transgenic mice conclusively supports the hypothesized role of sex steroids and refutes the suggested role of acute–phase inducers in regulating the apo(a) gene.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scanu, A.M., Lawn, R.M. & Berg, K. Lipoprotein (a) and atherosclerosis. in Davis Conference. Ann. intern. Med. 115, 209–218 (California, 1991).
Utermann, G. The mysteries of lipoprotein (a). Science 246, 904–910 (1989).
Chiesa, G. et al. Reconstitution of lipoprotein (a) by infusion of human low density lipoprotein into transgenic mice expressing human apolipoprotein (a). J. biol. Chem. 267, 24369–24374 (1992).
Lawn, R.M. et al. Atherogenesis in transgenic mice expressing human apolipoprotein (a). Nature 360, 670–672 (1992).
Lackner, C., Cohen, J.C. & Hobbs, H.H. Molecular definition of the extreme size polymorphism in apolipoprotein (a). Hum. molec. Gen. 2, 933–940 (1993).
McLean, J.W. et al. cDNA sequence of a human apolipoprotein (a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature 330, 132–137 (1987).
Grainger, D.J. et al. Proliferation of human smooth muscle cells promoted by lipoprotein (a). Science 260, 1656–1658 (1993).
Nachman, R.L. Thrombosis and atherogenesis: molecular connections. Blood 79, 1897–1906 (1992).
Magnaghi, P. et al. Molecular characterisation of the human apo (a)-plasminogen gene family clustered on the telomeric region of chromosome 6 (6q26–27). Hum. molec. Genet. 3, 437–442 (1994).
Byrne, C.D., Schwartz, K., Meer, K., Cheng, J.-F. & Lawn, R.M. The human apolipoprotein (a)/plasminogen gene cluster contains a novel homologue transcribed in liver. Arterioscler. Thromb. 14, 534–541 (1994).
Boerwinkle, E., et al. Apolipoprotein (a) gene accounts for greater than 90% of the variation in plasma lipoprotein (a) concentrations. J. clin. Invest. 90, 52–60 (1992).
Cohen, J.C., Chiesa, G. & Hobbs, H.H. Sequence polymorphisms in the apolipoprotein (a) gene. J. clin. Invest. 91, 1630–1636 (1993).
Perombelon, Y.F.N., Soutar, A.K. & Knight, B.L. Variation in lipoprotein (a) concentration associated with different apolipoprotein (a) alleles. J. clin. Invest. 93, 1481–1492 (1994).
Haffner, S.M., Mykkanen, L., Gruber, K.K., Rainwater, D.L. & Laakso, M. Lack of association between sex hormones and Lp (a) concentrations in American and Finnish. Arterioscler. Thromb. 14, 19–24 (1994).
Henriksson, P., Angelin, B. & Berglund, L. Hormonal regulation of serum Lp (a) levels. J. clin. Invest. 89, 116601171 (1992).
Soma, M.R. et al. Hormonal agents used in lowering lipoprotein (a). Chem. phys. Lipids 67–68, 345–350 (1994).
Slunga, L., Johnson, O., Dahlen, G.H. & Eriksson, S. Lipoprotein (a) and acute-phase proteins in acute myocardial infarction. Scand. J. clin. lab. Invest. 52, 95–101 (1992).
Maeda, S. et al. Transient changes of serum lipoprotein (a) as an acute phase protein. Atherosclerosis 78, 145–150 (1989).
Wade, D.P. et al. 5′ control regions of the apolipoprotein (a) gene and members of the related plasminogen gene family. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 1369–1373 (1993).
Tomlinson, J.E., McLean, J.W. & Lawn, R.M. Rhesus monkey apolipoprotein (a). J. biol. Chem. 264, 5957–5965 (1989).
Callow, M.J., Stoltzfus, L.J., Lawn, R.M. & Rubin, E.M. Expression of human apolipoprotein B and assembly of lipoprotein (a) in transgenic mice. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 21130–21136 (1994).
Linton, M.F. et al. Transgenic mice expressing high plasma concentrations of human apolipoprotein B100 and lipoprotein (a). J. clin. Invest. 92, 3029–3037 (1993).
Tang, J. et al. In vivo regulation of apolipoprotein A-l gene expression by estradiol and testosterone occurs by different mechanisms in inbred strains of mice. J. Lipid Res. 32, 1571–1585 (1991).
Utermann, G., Kraft, H.G., Menzel, H.J., Hopferwieser, T. & Seitz, C. Genetics of the quantitative Lp (a) lipoprotein trait. I. Relation of Lp (a) glycoprotein phenotypes to Lp (a) lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. Hum. Genet. 78, 41–46 (1988).
Utermann, G., Duba, C. & Menzel, H.J. Genetics of the quantitative Lp (a) lipoprotein trait. II. Inheritance of Lp (a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Hum. Genet. 78, 47–50 (1988).
Sandholzer, C. et al. Effects of the apolipoprotein (a) size polymorphism on the lipoprotein (a) concentration in 7 ethnic groups. Hum. Genet. 86, 607–614 (1991).
Boerwinkle, E., Menzel, H.G., Kraft, H.G. & Utermann, G. Genetics of the quantitative Lp (a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp (a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum. Genet. 82, 73–78 (1989).
Kraft, H.G., Menzel, H.J., Hoppichler, F., Vogel, W. & Utermann, G. Changes of genetic apolipoprotein phenotypes caused by livertransplantation. J. clin. Invest. 83, 137–142 (1989).
Schedl, A. et al. A method for the generation of YAC transgenic mice by pronuclear microinjection. Nucl. Acid Res. 21, 4783–4787 (1993).
Malgaretti, N. et al. Characterization by yeast artificial chromosome cloning of the linked apolipoprotein (a) and plasminogen genes and identification of the apolipoprotein (a) 5′ flanking region. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 11584–11588 (1992).
Burke, D.T., Carle, G.F. & Olson, M.V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science 236, 806–811 (1987).
Lackner, C., Boerwinkle, E., Leffert, C.C., Rahmig, T. & Hobbs, H.H. Molecular basis of apolipoprotein (a) isoform size heterogeneity as revealed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J. clin. Invest. 87, 2153–2161 (1991).
Yang, F. et al. Characterization of the mouse haptoglobin gene. Genomics 18, 374–380 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frazer, K., Narla, G., Zhang, J. et al. The apolipoprotein(a) gene is regulated by sex hormones and acute–phase inducers in YAC transgenic mice. Nat Genet 9, 424–431 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0495-424
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0495-424