Abstract
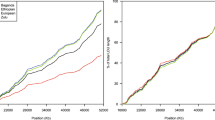
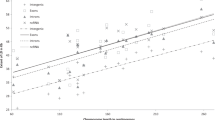
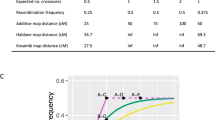
High resolution linkage maps have proven to be invaluable tools in genetic investigations. We have assembled a collection of genetic maps constructed from primary data collected from investigators performing genotyping using the Centre Etude Polymorphism Humain (CEPH) reference pedigree panel. These maps were constructed using a rigorous, semi–automated map construction algorithm that evaluates the integrity of the maps during construction. Two classes of maps were produced: a high confidence “skeletal” set composed of 544 PCR based markers, and a more highly annotated “framework” set containing maps of 1,123 markers. Genetic map locations within the framework maps are provided for an additional 1,758 loci without statistically unique interval assignments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dausset, J. et al. Centre d Etude du Polymorphisme Humain (CEPH): Collaborative Genetic Mapping of the Human Genome. Genomics 6, 575–577 (1990).
White, R.L. et al. The CEPH consortium primary linkage map of human chromosome 10. Genomics 6, 393–412 (1990).
Dracopoli, N.C. et al. The CEPH consortium linkage map of human chromosome 1. Genomics 9, 686–700 (1991).
NIH/CEPH Collaborative Mapping Group. A comprehensive genetic linkage map of the human genome. Science 258, 67–86 (1992).
Weissenbach, J. et al. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature 359, 794–801 (1992).
Keats, B.J.B. Linkage chromosome mapping in man. (University Press of Hawaii, Honolulu, 1981).
Donis-Keller, H. et al. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell 51, 319–337 (1987).
Buetow, K.H. Influence of aberrant observations on high resolution linkage analysis outcomes. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 985–994 (1991).
Morton, N.E. Sequential tests for the detectlon of linkage. Am. J. hum. Genet. 7, 277–318 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buetow, K., Weber, J., Ludwigsen, S. et al. Integrated human genome–wide maps constructed using the CEPH reference panel. Nat Genet 6, 391–393 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0494-391
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0494-391
This article is cited by
-
Optimizing the evidence for linkage by permuting marker order
BMC Genetics (2005)
-
Allelic structure and distribution of 103 STR loci in a Southern Tunisian population
Journal of Genetics (2004)
-
A common region of loss of heterozygosity in Wilms' tumor and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma distal to the D11S988 locus on chromosome 11p15.5
Human Genetics (1996)
-
An integrated genetic map of Chromosome 6
Mammalian Genome (1996)
-
Software for genetic linkage analysis
Molecular Biotechnology (1996)