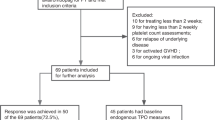
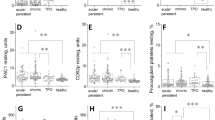
Abstract
Thrombocytopenia is commonly seen in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients, and bleeding complications are a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Thrombocytopenia is an independent factor for decreased survival and has been incorporated in newer prognostic scoring systems. The mechanisms of thrombocytopenia are multifactorial and involve a differentiation block of megakaryocytic progenitor cells, leading to dysplastic, hypolobated and microscopic appearing megakaryocytes or increased apoptosis of megakaryocytes and their precursors. Dysregulated thrombopoietin (TPO) signaling and increased platelet destruction through immune or nonimmune mechanisms are frequently observed in MDS. The clinical management of patients with low platelet counts remains challenging and approved chemotherapeutic agents such as lenalidomide and azacytidine can also lead to a transient worsening of thrombocytopenia. Platelet transfusion is the only supportive treatment option currently available for clinically significant thrombocytopenia. The TPO receptor agonists romiplostim and eltrombopag have shown clinical activity in clinical trials in MDS. In addition to thrombopoietic effects, eltrombopag can inhibit leukemic cell proliferation via TPO receptor-independent effects. Other approaches such as treatment with cytokines, immunomodulating drugs and signal transduction inhibitors have shown limited activity in selected groups of MDS patients. Combination trials of approved agents with TPO agonists are ongoing and hold promise for this important clinical problem.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heaney ML, Golde DW . Myelodysplasia. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: 1649–1660.
Hofmann WK, Koeffler HP . Myelodysplastic syndrome. Annu Rev Med 2005; 56: 1–16.
Sanz GF, Sanz MA, Greenberg PL . Prognostic factors and scoring systems in myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 1998; 83: 358–368.
Kantarjian H, Giles F, List A, Lyons R, Sekeres MA, Pierce S et al. The incidence and impact of thrombocytopenia in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer 2007; 109: 1705–1714.
Neukirchen J, Blum S, Kuendgen A, Strupp C, Aivado M, Haas R et al. Platelet counts and haemorrhagic diathesis in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Eur J Haematol 2009; 83: 477–482.
Steensma DP, Bennett JM . The myelodysplastic syndromes: diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc 2006; 81: 104–130.
Will B, Zhou L, Vogler TO, Ben-Neriah S, Schinke C, Tamari R et al. Stem and progenitor cells in myelodysplastic syndromes show aberrant stage-specific expansion and harbor genetic and epigenetic alterations. Blood 2012; 120: 2076–2086.
Hofmann WK, Kalina U, Koschmieder S, Seipelt G, Hoelzer D, Ottmann OG . Defective megakaryocytic development in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma 2000; 38: 13–19.
Bruno E, Hoffman R . Human megakaryocyte progenitor cells. Semin Hematol 1998; 35: 183–191.
Houwerzijl EJ, Blom NR, van der Want JJ, Vellenga E, de Wolf JT . Megakaryocytic dysfunction in myelodysplastic syndromes and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is in part due to different forms of cell death. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1937–1942.
Bhagat TD, Zhou L, Sokol L, Kessel R, Caceres G, Gundabolu K et al. miR-21 mediates hematopoietic suppression in MDS by activating TGF-beta signaling. Blood 2013; 121: 2875–2881.
Zhou L, McMahon C, Bhagat T, Alencar C, Yu Y, Fazzari M et al. Reduced SMAD7 leads to overactivation of TGF-beta signaling in MDS that can be reversed by a specific inhibitor of TGF-beta receptor I kinase. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 955–963.
Zhou L, Nguyen AN, Sohal D, Ying Ma J, Pahanish P, Gundabolu K et al. Inhibition of the TGF-beta receptor I kinase promotes hematopoiesis in MDS. Blood 2008; 112: 3434–3443.
Hatfill SJ, Fester ED, Steytler JG . Apoptotic megakaryocyte dysplasia in the myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematol Pathol 1992; 6: 87–93.
Yoshida Y . Hypothesis: apoptosis may be the mechanism responsible for the premature intramedullary cell death in the myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 1993; 7: 144–146.
Raza A, Yousuf N, Bokhari S, Abbas A, Lampkin B, Pancoast J et al. Cell-cycle characteristics - alterable determinants of remission duration in a study of 179 standard risk newly diagnosed patients with acute myeloid-leukemia. Int J Oncol 1993; 2: 301–307.
Raza A, Gezer S, Mundle S, Gao XZ, Alvi S, Borok R et al. Apoptosis in bone marrow biopsy samples involving stromal and hematopoietic cells in 50 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1995; 86: 268–276.
Raza A, Alvi S, Borok RZ, Span L, Parcharidou A, Alston D et al. Excessive proliferation matched by excessive apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndromes: the cause-effect relationship. Leuk Lymphoma 1997; 27: 111–118.
Bogdanovic AD, Jankovic GM, Colovic MD, Trpinac DP, Bumbasirevic VZ . Apoptosis in bone marrow of myelodysplastic syndrome patients. Blood 1996; 87: 3064.
Bogdanovic AD, Trpinac DP, Jankovic GM, Bumbasirevic VZ, Obradovic M, Colovic MD . Incidence and role of apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome: morphological and ultrastructural assessment. Leukemia 1997; 11: 656–659.
Shetty V, Hussaini S, Broady-Robinson L, Allampallam K, Mundle S, Borok R et al. Intramedullary apoptosis of hematopoietic cells in myelodysplastic syndrome patients can be massive: apoptotic cells recovered from high-density fraction of bone marrow aspirates. Blood 2000; 96: 1388–1392.
Kurotaki H, Tsushima Y, Nagai K, Yagihashi S . Apoptosis, bcl-2 expression and p53 accumulation in myelodysplastic syndrome, myelodysplastic-syndrome-derived acute myelogenous leukemia and de novo acute myelogenous leukemia. Acta Haematol 2000; 102: 115–123.
Houwerzijl EJ, Blom NR, van der Want JJ, Louwes H, Esselink MT, Smit JW et al. Increased peripheral platelet destruction and caspase-3-independent programmed cell death of bone marrow megakaryocytes in myelodysplastic patients. Blood 2005; 105: 3472–3479.
Kitagawa M, Yamaguchi S, Takahashi M, Tanizawa T, Hirokawa K, Kamiyama R . Localization of Fas and Fas ligand in bone marrow cells demonstrating myelodysplasia. Leukemia 1998; 12: 486–492.
Navas TA, Mohindru M, Estes M, Ma JY, Sokol L, Pahanish P et al. Inhibition of overactivated p38 MAPK can restore hematopoiesis in myelodysplastic syndrome progenitors. Blood 2006; 108: 4170–4177.
Verma A, Deb DK, Sassano A, Uddin S, Varga J, Wickrema A et al. Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates the suppressive effects of type I interferons and transforming growth factor-beta on normal hematopoiesis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 7726–7735.
Verma A, Deb DK, Sassano A, Kambhampati S, Wickrema A, Uddin S et al. Cutting edge: activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway mediates cytokine-induced hemopoietic suppression in aplastic anemia. J Immunol 2002; 168: 5984–5988.
Kaushansky K . Thrombopoietin: the primary regulator of megakaryocyte and platelet production. Thromb Haemost 1995; 74: 521–525.
Vigon I, Mornon JP, Cocault L, Mitjavila MT, Tambourin P, Gisselbrecht S et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of MPL, the human homolog of the v-mpl oncogene: identification of a member of the hematopoietic growth factor receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 5640–5644.
Sattler M, Durstin MA, Frank DA, Okuda K, Kaushansky K, Salgia R et al. The thrombopoietin receptor c-MPL activates JAK2 and TYK2 tyrosine kinases. Exp Hematol 1995; 23: 1040–1048.
Rojnuckarin P, Drachman JG, Kaushansky K . Thrombopoietin-induced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in normal megakaryocytes: role in endomitosis. Blood 1999; 94: 1273–1282.
de Sauvage FJ, Hass PE, Spencer SD, Malloy BE, Gurney AL, Spencer SA et al. Stimulation of megakaryocytopoiesis and thrombopoiesis by the c-Mpl ligand. Nature 1994; 369: 533–538.
Buza-Vidas N, Antonchuk J, Qian H, Mansson R, Luc S, Zandi S et al. Cytokines regulate postnatal hematopoietic stem cell expansion: opposing roles of thrombopoietin and LNK. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 2018–2023.
Adams JA, Liu Yin JA, Brereton ML, Briggs M, Burgess R, Hyde K . The in vitro effect of pegylated recombinant human megakaryocyte growth and development factor (PEG rHuMGDF) on megakaryopoiesis in normal subjects and patients with myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 1997; 99: 139–146.
Kalina U, Hofmann WK, Koschmieder S, Wagner S, Kauschat D, Hoelzer D et al. Alteration of c-mpl-mediated signal transduction in CD34(+) cells from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Exp Hematol 2000; 28: 1158–1163.
Tamura H, Ogata K, Luo S, Nakamura K, Yokose N, Dan K et al. Plasma thrombopoietin (TPO) levels and expression of TPO receptor on platelets in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1998; 103: 778–784.
Zwierzina H, Rollinger-Holzinger I, Nuessler V, Herold M, Meng YG . Endogenous serum thrombopoietin concentrations in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 1998; 12: 59–64.
Pellagatti A, Cazzola M, Giagounidis A, Perry J, Malcovati L, Della Porta MG et al. Deregulated gene expression pathways in myelodysplastic syndrome hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 2010; 24: 756–764.
List AF, Estes M, Williams A, Sekharam M, Ozawa U, Gao G et al. Lenalidomide (CC-5013); Revlimid (R)) promotes erythropoiesis in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) by CD45 protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) inhibition. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 2006; 108: 1360.
Billstrom R, Johansson H, Johansson B, Mitelman F . Immune-mediated complications in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes—clinical and cytogenetic features. Eur J Haematol 1995; 55: 42–48.
Marisavljevic D, Kraguljac N, Rolovic Z . Immunologic abnormalities in myelodysplastic syndromes: clinical features and characteristics of the lymphoid population. Med Oncol 2006; 23: 385–391.
Hall AG, Proctor SJ, Saunders PW . Increased platelet associated immunoglobulin in myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1987; 65: 245–246.
Bourgeois E, Caulier MT, Rose C, Dupriez B, Bauters F, Fenaux P . Role of splenectomy in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes with peripheral thrombocytopenia: a report on six cases. Leukemia 2001; 15: 950–953.
Passweg JR, Giagounidis AA, Simcock M, Aul C, Dobbelstein C, Stadler M et al. Immunosuppressive therapy for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a prospective randomized multicenter phase III trial comparing antithymocyte globulin plus cyclosporine with best supportive care–SAKK 33/99. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 303–309.
Saunthararajah Y, Nakamura R, Wesley R, Wang QJ, Barrett AJ . A simple method to predict response to immunosuppressive therapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2003; 102: 3025–3027.
Mittelman M, Zeidman A . Platelet function in the myelodysplastic syndromes. Int J Hematol 2000; 71: 95–98.
Rasi V, Lintula R . Platelet function in the myelodysplastic syndromes. Scand J Haematol Suppl 1986; 45: 71–73.
Girtovitis FI, Ntaios G, Papadopoulos A, Ioannidis G, Makris PE . Defective platelet aggregation in myelodysplastic syndromes. Acta Haematol 2007; 118: 117–122.
Frobel J, Cadeddu RP, Hartwig S, Bruns I, Wilk CM, Kundgen A et al. Platelet proteome analysis reveals integrin-dependent aggregation defects in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Mol Cell Proteomics 2013; 12: 1272–1280.
Bejar R, Stevenson K, Abdel-Wahab O, Galili N, Nilsson B, Garcia-Manero G et al. Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 2496–2506.
Pencovich N, Jaschek R, Tanay A, Groner Y . Dynamic combinatorial interactions of RUNX1 and cooperating partners regulates megakaryocytic differentiation in cell line models. Blood 2011; 117: e1–14.
Jongmans MC, Kuiper RP, Carmichael CL, Wilkins EJ, Dors N, Carmagnac A et al. Novel RUNX1 mutations in familial platelet disorder with enhanced risk for acute myeloid leukemia: clues for improved identification of the FPD/AML syndrome. Leukemia 2010; 24: 242–246.
Connelly JP, Kwon EM, Gao Y, Trivedi NS, Elkahloun AG, Horwitz MS et al. Targeted correction of RUNX1 mutation in FPD patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells rescues megakaryopoietic defects. Blood 2014; 124: 1926–1930.
Lordier L, Bluteau D, Jalil A, Legrand C, Pan J, Rameau P et al. RUNX1-induced silencing of non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIB contributes to megakaryocyte polyploidization. Nat Commun 2012; 3: 717.
Apostolidis PA, Woulfe DS, Chavez M, Miller WM, Papoutsakis ET . Role of tumor suppressor p53 in megakaryopoiesis and platelet function. Exp Hematol 2012; 40: 131–42 e4.
Horiike S, Kita-Sasai Y, Nakao M, Taniwaki M . Configuration of the TP53 gene as an independent prognostic parameter of myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma 2003; 44: 915–922.
Duarte FB, Goncalves RP, Barbosa MC, Rocha Filho FD, de Jesus Dos Santos TE, Dos Santos TN et al. Tumor suppressor p53 protein expression: prognostic significance in patients with low-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter 2014; 36: 196–201.
Kulasekararaj AG, Smith AE, Mian SA, Mohamedali AM, Krishnamurthy P, Lea NC et al. TP53 mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome are strongly correlated with aberrations of chromosome 5, and correlate with adverse prognosis. Br J Haematol 2013; 160: 660–672.
Kaushansky K . Determinants of platelet number and regulation of thrombopoiesis. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2009, 147–152.
Garcia J, de Gunzburg J, Eychene A, Gisselbrecht S, Porteu F . Thrombopoietin-mediated sustained activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in UT7-Mpl cells requires both Ras-Raf-1- and Rap1-B-Raf-dependent pathways. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 2659–2670.
Alessandrino EP, Amadori S, Barosi G, Cazzola M, Grossi A, Liberato LN et al. Evidence- and consensus-based practice guidelines for the therapy of primary myelodysplastic syndromes. A statement from the Italian Society of Hematology. Haematologica 2002; 87: 1286–1306.
Al Ameri A, Jabbour E, Garcia-Manero G, O'Brien S, Faderl S, Ravandi F et al. Significance of thrombocytopenia in myelodysplastic syndromes: associations and prognostic implications. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2011; 11: 237–241.
Kantarjian H, O'Brien S, Ravandi F, Cortes J, Shan J, Bennett JM et al. Proposal for a new risk model in myelodysplastic syndrome that accounts for events not considered in the original International Prognostic Scoring System. Cancer 2008; 113: 1351–1361.
Kao JM, McMillan A, Greenberg PL . International MDS risk analysis workshop (IMRAW)/IPSS reanalyzed: impact of cytopenias on clinical outcomes in myelodysplastic syndromes. Am J Hematol 2008; 83: 765–770.
Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Sole F et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012; 120: 2454–2465.
Sekeres MA, Schoonen WM, Kantarjian H, List A, Fryzek J, Paquette R et al. Characteristics of US patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: results of six cross-sectional physician surveys. J Natl Cancer Inst 2008; 100: 1542–1551.
Sloand EM, Olnes MJ, Shenoy A, Weinstein B, Boss C, Loeliger K et al. Alemtuzumab treatment of intermediate-1 myelodysplasia patients is associated with sustained improvement in blood counts and cytogenetic remissions. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 5166–5173.
Platzbecker U, Haase M, Herbst R, Hanel A, Voigtmann K, Thiede CH et al. Activity of sirolimus in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome—results of a pilot study. Br J Haematol 2005; 128: 625–630.
Tsimberidou AM, Giles FJ, Khouri I, Bueso-Ramos C, Pilat S, Thomas DA et al. Low-dose interleukin-11 in patients with bone marrow failure: update of the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center experience. Ann Oncol 2005; 16: 139–145.
Gordon MS, Nemunaitis J, Hoffman R, Paquette RL, Rosenfeld C, Manfreda S et al. A phase I trial of recombinant human interleukin-6 in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and thrombocytopenia. Blood 1995; 85: 3066–3076.
List A, Kurtin S, Roe DJ, Buresh A, Mahadevan D, Fuchs D et al. Efficacy of lenalidomide in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 549–557.
List A, Dewald G, Bennett J, Giagounidis A, Raza A, Feldman E et al. Lenalidomide in the myelodysplastic syndrome with chromosome 5q deletion. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1456–1465.
Raza A, Reeves JA, Feldman EJ, Dewald GW, Bennett JM, Deeg HJ et al. Phase 2 study of lenalidomide in transfusion-dependent, low-risk, and intermediate-1 risk myelodysplastic syndromes with karyotypes other than deletion 5q. Blood 2008; 111: 86–93.
Fenaux P, Giagounidis A, Selleslag D, Beyne-Rauzy O, Mufti G, Mittelman M et al. A randomized phase 3 study of lenalidomide versus placebo in RBC transfusion-dependent patients with Low-/Intermediate-1-risk myelodysplastic syndromes with del5q. Blood 2011; 118: 3765–3776.
Sekeres MA, Maciejewski JP, Giagounidis AA, Wride K, Knight R, Raza A et al. Relationship of treatment-related cytopenias and response to lenalidomide in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 5943–5949.
Silverman LR, Demakos EP, Peterson BL, Kornblith AB, Holland JC, Odchimar-Reissig R et al. Randomized controlled trial of azacitidine in patients with the myelodysplastic syndrome: a study of the cancer and leukemia group B. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 2429–2440.
Fenaux P, Mufti GJ, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Santini V, Finelli C, Giagounidis A et al. Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of conventional care regimens in the treatment of higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes: a randomised, open-label, phase III study. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: 223–232.
Kantarjian H, Issa JP, Rosenfeld CS, Bennett JM, Albitar M, DiPersio J et al. Decitabine improves patient outcomes in myelodysplastic syndromes: results of a phase III randomized study. Cancer 2006; 106: 1794–1803.
Zeidan AM, Lee JW, Prebet T, Greenberg P, Sun Z, Juckett M et al. Platelet count doubling after the first cycle of azacitidine therapy predicts eventual response and survival in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and oligoblastic acute myeloid leukaemia but does not add to prognostic utility of the revised IPSS. Br J Haematol 2014; 167: 62–68.
van der Helm LH, Alhan C, Wijermans PW, van Marwijk Kooy M, Schaafsma R, Biemond BJ et al. Platelet doubling after the first azacitidine cycle is a promising predictor for response in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia (CMML) and acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) patients in the Dutch azacitidine compassionate named patient programme. Br J Haematol 2011; 155: 599–606.
Kantarjian H, Fenaux P, Sekeres MA, Becker PS, Boruchov A, Bowen D et al. Safety and efficacy of romiplostim in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and thrombocytopenia. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 437–444.
Kantarjian HM, Giles FJ, Greenberg PL, Paquette RL, Wang ES, Gabrilove JL et al. Phase 2 study of romiplostim in patients with low- or intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndrome receiving azacitidine therapy. Blood 2010; 116: 3163–3170.
Giagounidis A, Mufti GJ, Fenaux P, Sekeres MA, Szer J, Platzbecker U et al. Results of a randomized, double-blind study of romiplostim versus placebo in patients with low/intermediate-1-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and thrombocytopenia. Cancer 2014; 120: 1838–1846.
Wang ES, Lyons RM, Larson RA, Gandhi S, Liu D, Matei C et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of romiplostim treatment of patients with low or intermediate-1 risk myelodysplastic syndrome receiving lenalidomide. J Hematol Oncol 2012; 5: 71.
Greenberg PL, Garcia-Manero G, Moore M, Damon L, Roboz G, Hu K et al. A randomized controlled trial of romiplostim in patients with low- or intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndrome receiving decitabine. Leuk Lymphoma 2013; 54: 321–328.
Prica A, Sholzberg M, Buckstein R . Safety and efficacy of thrombopoietin-receptor agonists in myelodysplastic syndromes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Br J Haematol 2014; 167: 626–638.
Erickson-Miller CL, Kirchner J, Aivado M, May R, Payne P, Chadderton A . Reduced proliferation of non-megakaryocytic acute myelogenous leukemia and other leukemia and lymphoma cell lines in response to eltrombopag. Leuk Res 2010; 34: 1224–1231.
Will B, Kawahara M, Luciano JP, Bruns I, Parekh S, Erickson-Miller CL et al. Effect of the nonpeptide thrombopoietin receptor agonist Eltrombopag on bone marrow cells from patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2009; 114: 3899–3908.
Roth M, Will B, Simkin G, Narayanagari S, Barreyro L, Bartholdy B et al. Eltrombopag inhibits the proliferation of leukemia cells via reduction of intracellular iron and induction of differentiation. Blood 2012; 120: 386–394.
Sugita M, Kalota A, Gewirtz AM, Carroll M . Eltrombopag inhibition of acute myeloid leukemia cell survival does not depend on c-Mpl expression. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1207–1210.
Tamari R, Schinke C, Bhagat T, Roth M, Braunschweig I, Will B et al. Eltrombopag can overcome the anti-megakaryopoietic effects of lenalidomide without increasing proliferation of the malignant myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myelogenous leukemia clone. Leuk Lymphoma 2014; 55: 2901–2906.
Kalota A, Selak MA, Garcia-Cid LA, Carroll M . Eltrombopag modulates reactive oxygen species and decreases acute myeloid leukemia cell survival. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0126691.
Svensson T, Chowdhury O, Garelius H, Lorenz F, Saft L, Jacobsen SE et al. A pilot phase I dose finding safety study of the thrombopoietin-receptor agonist, eltrombopag, in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome treated with azacitidine. Eur J Haematol 2014; 93: 439–445.
Mittelman M, Assouline S, Briasoulis E, Alonso A, Delgado RG, O'Gorman P et al. Eltrombopag treatment of thrombocytopenia in advanced myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia: results of the 8-week open-label part of an ongoing study. Blood 8-11 December 2012 54th ASH annual meeting: Atlanta, GA, USA, Abstract 3822.
Oliva EN, Santini V, Zini G, Palumbo GA, Poloni A, Cortelezzi A et al. Efficacy and safety of eltrombopag for the treatment of thrombocytopenia of low and intermediate-1 IPSS risk myelodysplastic syndromes: interim analysis of a prospective, randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial (EQoL-MDS). Blood 8-11 December 2012 54th ASH Annual Meeting: Atlanta, GA, USA, Abstract 923.
Platzbecker U, Wong RSM, Verma A, Abboud C, Araujo S, Chiou T-J . Placebo-controlled, randomized, phase I/II Trial of the thrombopoietin receptor agonist eltrombopag in thrombocytopenic patients with advanced myelodysplastic syndromes or acute myeloid leukemia. European Hematology Association 18th Congress; 13-16 June 2013. Stockholm, Sweden Haematologica 2013; 98 (Suppl 1): 445.
Platzbecker U, Sockel K, Schonefeldt C, Nowak D, Helas S, Rollig C et al. Induction of short-term remission with single agent eltrombopag in refractory nucleophosmin-1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2014; 99: e247–e248.
Hasle H, Kerndrup G, Jacobsen BB . Childhood myelodysplastic syndrome in Denmark: incidence and predisposing conditions. Leukemia 1995; 9: 1569–1572.
Wilson DB, Link DC, Mason PJ, Bessler M . Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes in adolescents and young adults. Ann Med 2014; 46: 353–363.
Smith AR, Christiansen EC, Wagner JE, Cao Q, MacMillan ML, Stefanski HE et al. Early hematopoietic stem cell transplant is associated with favorable outcomes in children with MDS. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2013; 60: 705–710.
Inoue A, Kawakami C, Takitani K, Tamai H . Azacitidine in the treatment of pediatric therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2014; 36: e322–e324.
Lubbert M, Suciu S, Baila L, Ruter BH, Platzbecker U, Giagounidis A et al. Low-dose decitabine versus best supportive care in elderly patients with intermediate- or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) ineligible for intensive chemotherapy: final results of the randomized phase III study of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Leukemia Group and the German MDS Study Group. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1987–1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Morrone, K., Kambhampati, S. et al. Thrombocytopenia in MDS: epidemiology, mechanisms, clinical consequences and novel therapeutic strategies. Leukemia 30, 536–544 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.297
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.297
This article is cited by
-
Utility of indium-111 platelet scintigraphy for understanding the mechanism of thrombocytopenia associated with myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
Excessive serine from the bone marrow microenvironment impairs megakaryopoiesis and thrombopoiesis in Multiple Myeloma
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Combination regimen of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and recombinant human thrombopoietin improves the curative effect on elderly patients with leukemia through inducing pyroptosis and ferroptosis of leukemia cells
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)
-
Effect of thrombopoietin receptor agonist on health-related quality of life and platelet transfusion burden for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Annals of Hematology (2022)
-
Eltrombopag in Immune Thrombocytopenia, Aplastic Anemia, and Myelodysplastic Syndrome: From Megakaryopoiesis to Immunomodulation
Drugs (2019)