Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate the safety of fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) and the reliability of both FEES and a videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) in identifying laryngeal penetration and tracheal aspiration in infants under 3 months old in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
Study Design:
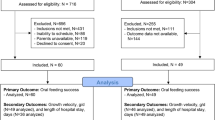
Twenty-five infants at least 37 weeks postmenstrual age suspected of aspirating were assessed with FEES and VFSS. Complications, autonomic instability and vital signs before endoscope insertion and following FEES were documented. Blinded video recordings were coded by two reviewers to determine reliability.
Results:
We found no major complications or significant differences between FEES prefeeding and postfeeding vital signs, including respiratory rate, heart rate or oxygen saturation. FEES interrater reliability was 80% for both penetration and aspiration, compared with 87 and 90%, respectively, for VFSS.
Conclusion:
FEES is safe and reliable in assessing laryngeal penetration and tracheal aspiration in NICU infants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvedson JC . Assessment of pediatric dysphagia and feeding disorders: Clinical and instrumental approaches. Dev Disabil Res Rev 2008; 14: 118–127.
Lefton-Greif MA . Pediatric dysphagia. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 2008; 19: 837–851, ix.
Dodrill P, Gosa MM . Pediatric dysphagia: Physiology, assessment, and management. Ann Nutr Metab 2015; 66 (Suppl 5): 24–31.
Reynolds J, Carroll S, Sturdivant C . Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing: a multidisciplinary alternative for assessment of infants with dysphagia in the neonatal intensive care unit. Adv Neonatal Care 2016; 16: 37–43.
Ekberg O, Nylander G, Fork FT, Sjöberg S, Birch-Iensen M, Hillarp B . Interobserver variability in cineradiographic assessment of pharyngeal function during swallow. Dysphagia 1988; 3: 46–48.
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL . A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 1996; 11: 93–98.
Wilcox F, Liss JM, Siegel GM . Interjudge agreement in videofluoroscopic studies of swallowing. J Speech Hear Res 1996; 39: 144–152.
Kuhlemeier KV, Yates P, Palmer JB . Intra- and interrater variation in the evaluation of videofluorographic swallowing studies. Dysphagia 1998; 13: 142–147.
Scott A, Perry A, Bench J . A study of interrater reliability when using videofluoroscopy as an assessment of swallowing. Dysphagia 1998; 13: 223–227.
Leder SB, Karas DE . Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in the pediatric population. Laryngoscope 2000; 110: 1132–1136.
McCullough GH, Wertz RT, Rosenbek JC, Mills RH, Webb WG, Ross KB . Inter- and intrajudge reliability for videofluoroscopic swallowing evaluation measures. Dysphagia 2001; 16: 110–118.
Newman LA, Keckley C, Petersen MC, Hamner A . Swallowing function and medical diagnoses in infants suspected of dysphagia. Pediatrics 2001; 108: E106–E106.
Rao N, Brady SL, Chaudhuri G, Donzelli, JJ, Wesling, M W . Gold-standard? analysis of the videofluoroscopic and fiberoptic endoscopic swallow examinations. J Appl Res 2003; 3: 89–96.
Stoeckli SJ, TAGM Huisman, Seifert B, Martin-Harris BJ . Interrater reliability of videofluoroscopic swallow evaluation. Dysphagia 2003; 18: 53–57.
Becker SS, McLeroy KE, Carpenter MA . Reliability of observations from modified barium swallow studies. J Med Speech-Lang Pathol 2005; 13: 97–109.
Kelly AM, Drinnan MJ, Leslie P . Assessing penetration and aspiration: how do videofluoroscopy and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing compare? Laryngoscope 2007; 117: 1723–1727.
Kim DH, Choi KH, Kim HM, Koo JH, Kim BR, Kim TW et al. Inter-rater reliability of videofluoroscopic dysphagia scale. Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 791–796.
Brady S, Donzelli J . The modified barium swallow and the functional endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2013; 46: 1009–1022.
Willette S, Molinaro LH, Thompson DM, Schroeder JW Jr . Fiberoptic examination of swallowing in the breastfeeding infant. Laryngoscope 2016; 126: 1681–1686.
Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olsen N . Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: a new procedure. Dysphagia 1988; 2: 216–219.
Aviv JE, Murry T, Zschommler A, Cohen M, Gartner C . Flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing: patient characteristics and analysis of safety in 1,340 consecutive examinations. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2005; 114: 173–176.
Tabaee A, Johnson PE, Gartner CJ, Kalwerisky K, Desloge RB, Stewart MG . Patient‐controlled comparison of flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing (FEESST) and videofluoroscopy. Laryngoscope 2006; 116: 821–825.
Warnecke T, Teismann I, Oelenberg S, Hamacher C, Ringelstein EB, Schäbitz WR et al. The safety of fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in acute stroke patients. Stroke 2009; 40: 482–486.
Leder SB, Acton LM, Lisitano HL, Murray JT . Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) with and without blue-dyed food. Dysphagia 2005; 20: 157–162.
Tohara H, Nakane A, Murata S, Mikushi S, Ouchi Y, Wakasugi Y et al. Inter- and intra-rater reliability in fibroptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. J Oral Rehabil 2010; 37: 884–891.
Hey C, Pluschinski P, Pajunk R, Almahameed A, Girth L, Sader R et al. Penetration–aspiration: is their detection in FEES® reliable without video recording? Dysphagia 2015; 30: 418–422.
Willging JP . Endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 1995; 32 (Suppl): S107–S108.
Hartnick CJ, Hartley BE, Miller C, Willging JP . Pediatric fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2000; 109: 996–999.
Link DT, Willging JP, Miller CK, Cotton RT, Rudolph CD . Pediatric laryngopharyngeal sensory testing during flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing: feasible and correlative. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2000; 109: 899–905.
da Silva AP, Lubianca Neto JF, Santoro PP . Comparison between videofluoroscopy and endoscopic evaluation of swallowing for the diagnosis of dysphagia in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010; 143: 204–209.
Leder SB, Baker KE, Goodman TR . Dysphagia testing and aspiration status in medically stable infants requiring mechanical ventilation via tracheotomy. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2010; 11: 484–487.
Sitton M, Arvedson J, Visotcky A, Braun N, Kerschner J, Tarima S et al. Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in children: feeding outcomes related to diagnostic groups and endoscopic findings. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2011; 75: 1024–1031.
Cichero JA, Nicholson TM, September C . Thickened milk for the management of feeding and swallowing issues in infants: a call for interdisciplinary professional guidelines. J Hum Lact 2013; 29: 132–135.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs. “Inactive” ingredients in pharmaceutical products: update (subject review). Pediatrics 1997; 99: 268–278.
Viera AJ, Garrett JM . Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Fam Med 2005; 37: 360–363.
Cichero J, Nicholson T, Dodrill P . Liquid barium is not representative of infant formula: characterisation of rheological and material properties. Dysphagia 2011; 26: 264–271.
Madhoun LL, Siler-Wurst KK, Sitaram S, Jadcherla SR . Feed-thickening practices in NICUs in the current era: variability in prescription and implementation patterns. J Neonatal Nurs 2015; 21: 255–262.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Monica Bennett, Gabriella Cantu, Elisa Priest, Simon Driver, Mary DeHaas, Rachel King, Misty Kyle, Jennifer Hendrikse, Lisa Tiltges and the Baylor Health Care System Foundation for their contributions to the study. Source of financial support/funding: Baylor Health Care System Foundation. ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT02003287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suterwala, M., Reynolds, J., Carroll, S. et al. Using fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing to detect laryngeal penetration and aspiration in infants in the neonatal intensive care unit. J Perinatol 37, 404–408 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2016.239
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2016.239
This article is cited by
-
Pediatric Dysphagia: Evaluation and Management for Otolaryngologists
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports (2023)
-
Position Statement of the Union of European Phoniatricians (UEP): Fees and Phoniatricians’ Role in Multidisciplinary and Multiprofessional Dysphagia Management Team
Dysphagia (2023)
-
Validation and Cultural Adaptation of an Arabic Version of Pediatric Eating Assessment Tool (Pedi-EAT-10Arabic)
Dysphagia (2022)
-
Instrumental Swallowing Assessments in the Neonatal and Pediatric Populations: A Systematic Review
Dysphagia (2022)
-
Pediatric Flexible Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing: Critical Analysis of Implementation and Future Perspectives
Dysphagia (2022)