Abstract
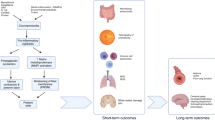
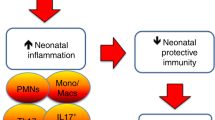
The bacterial infection of chorion and amnion is a common finding in premature delivery and is referred to as chorioamnionitis. As the mother rarely shows symptoms of a systemic inflammation, the course of chorioamnionitis is frequently asymptomatic and chronic. In contrast, the fetal inflammatory response syndrome represents a separate phenomenon, including umbilical inflammation and increased serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines in the fetus. Ascending maternal infections frequently lead to systemic fetal inflammatory reaction. Clinical studies have shown that antenatal exposure to inflammation puts the extremely immature neonates at a high risk for worsening pulmonary, neurological and other organ development. Interestingly, the presence of chorioamnionitis is associated with a lower rate of neonatal mortality in extremely immature newborns. In the following review, the pathogeneses of inflammation-associated perinatal morbidity are outlined. The concept of fetal multiorganic disease during intrauterine infection is introduced and discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldenberg RL, Culhane JF, Iams JD, Romero R . Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth. Lancet 2008; 371: 75–84.
Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC, Andrews WW . Intrauterine infection and preterm delivery. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 1500–1507.
Lahra MM, Beeby PJ, Jeffery HE . Intrauterine inflammation, neonatal sepsis, and chronic lung disease: a 13-year hospital cohort study. Pediatrics 2009; 123: 1314–1319.
Lahra MM, Beeby PJ, Jeffery HE . Maternal versus fetal inflammation and respiratory distress syndrome: a 10-year hospital cohort study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2009; 94: F13–F16.
Faye-Petersen OM . The placenta in preterm birth. J Clin Pathol 2008; 61: 1261–1275.
Annells MF, Hart PH, Mullighan CG, Heatley SL, Robinson JS, McDonald HM . Polymorphisms in immunoregulatory genes and the risk of histologic chorioamnionitis in Caucasoid women: a case control study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2005; 5: 4.
Holst D, Garnier Y . Preterm birth and inflammation-The role of genetic polymorphisms. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2008; 141: 3–9.
Been JV, Rours IG, Kornelisse RF, Lima Passos V, Kramer BW, Schneider TA et al. Histologic chorioamnionitis, fetal involvement, and antenatal steroids: effects on neonatal outcome in preterm infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 201 (6): 587.e1–587.e8.
Gotsch F, Romero R, Kusanovic JP, Mazaki-Tovi S, Pineles BL, Erez O et al. The fetal inflammatory response syndrome. Clin Obstet Gynecol 2007; 50: 652–683.
Been JV, Kramer BW, Zimmermann LJ . In utero and early-life conditions and adult health and disease. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1523–1524.
Berger R, Garnier Y . Pathophysiology of perinatal brain damage. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 1999; 30: 107–134.
Sarkar S, Kaplan C, Wiswell TE, Spitzer AR . Histological chorioamnionitis and the risk of early intraventricular hemorrhage in infants born < or =28 weeks gestation. J Perinatol 2005; 25: 749–752.
Woodward LJ, Anderson PJ, Austin NC, Howard K, Inder TE . Neonatal MRI to predict neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 685–694.
Wu YW, Colford Jr JM . Chorioamnionitis as a risk factor for cerebral palsy: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2000; 284: 1417–1424.
Leviton A, Paneth N, Reuss ML, Susser M, Allred EN, Dammann O et al. Maternal infection, fetal inflammatory response, and brain damage in very low birth weight infants. Developmental Epidemiology Network Investigators. Pediatr Res 1999; 46: 566–575.
Wu YW, Escobar GJ, Grether JK, Croen LA, Greene JD, Newman TB . Chorioamnionitis and cerebral palsy in term and near-term infants. JAMA 2003; 290: 2677–2684.
Back SA, Volpe JJ . Cellular and molecular pathogenesis of periventricular white matter damage. Ment Retard Dev 1997; 3: 96–107.
Gavilanes AW, Strackx E, Kramer BW, Gantert M, Van den Hove D, Steinbusch H et al. Chorioamnionitis induced by intraamniotic lipopolysaccharide resulted in an interval-dependent increase in central nervous system injury in the fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200: 437 e431–e438.
Garnier Y, Berger R, Alm S, von Duering MU, Coumans AB, Michetti F et al. Systemic endotoxin administration results in increased S100B protein blood levels and periventricular brain white matter injury in the preterm fetal sheep. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2006; 124: 15–22.
Malaeb S, Dammann O . Fetal inflammatory response and brain injury in the preterm newborn. J Child Neurol 2009; 24: 1119–1126.
Leviton A, Gressens P . Neuronal damage accompanies perinatal white-matter damage. Trends Neurosci 2007; 30: 473–478.
Kadhim H, Tabarki B, De Prez C, Sebire G . Cytokine immunoreactivity in cortical and subcortical neurons in periventricular leukomalacia: are cytokines implicated in neuronal dysfunction in cerebral palsy? Acta Neuropathol 2003; 105: 209–216.
Feldhaus B, Dietzel ID, Heumann R, Berger R . Effects of interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on survival and differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitors. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2004; 11: 89–96.
Haider S, Knofler M . Human tumour necrosis factor: physiological and pathological roles in placenta and endometrium. Placenta 2008; 30: 111–123.
Stolp HB, Dziegielewska KM, Ek CJ, Habgood MD, Lane MA, Potter AM et al. Breakdown of the blood-brain barrier to proteins in white matter of the developing brain following systemic inflammation. Cell Tissue Res 2005; 320: 369–378.
Feng SY, Phillips DJ, Stockx EM, Yu VY, Walker AM . Endotoxin has acute and chronic effects on the cerebral circulation of fetal sheep. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2009; 296: R640–R650.
Khwaja O, Volpe JJ . Pathogenesis of cerebral white matter injury of prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008; 93: F153–F161.
Dammann O, Kuban KC, Leviton A . Perinatal infection, fetal inflammatory response, white matter damage, and cognitive limitations in children born preterm. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2002; 8: 46–50.
Coumans AB, Middelanis JS, Garnier Y, Vaihinger HM, Leib SL, Von Duering MU et al. Intracisternal application of endotoxin enhances the susceptibility to subsequent hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res 2003; 53: 770–775.
Eklind S, Mallard C, Leverin AL, Gilland E, Blomgren K, Mattsby-Baltzer I et al. Bacterial endotoxin sensitizes the immature brain to hypoxic--ischaemic injury. Eur J Neurosci 2001; 13: 1101–1106.
Saha RN, Liu X, Pahan K . Up-regulation of BDNF in astrocytes by TNF-alpha: a case for the neuroprotective role of cytokine. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2006; 1: 212–222.
Cui Q, Yin Y, Benowitz LI . The role of macrophages in optic nerve regeneration. Neuroscience 2009; 158: 1039–1048.
Mallard C, Hagberg H . Inflammation-induced preconditioning in the immature brain. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2007; 12: 280–286.
Rocha G, Proenca E, Quintas C, Rodrigues T, Guimaraes H . [Chorioamnionitis and neonatal morbidity]. Acta Med Port 2006; 19: 207–212.
Polam S, Koons A, Anwar M, Shen-Schwarz S, Hegyi T . Effect of chorioamnionitis on neurodevelopmental outcome in preterm infants. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2005; 159: 1032–1035.
Ogunyemi D, Murillo M, Jackson U, Hunter N, Alperson B . The relationship between placental histopathology findings and perinatal outcome in preterm infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2003; 13: 102–109.
Fung G, Bawden K, Chow P, Yu V . Chorioamnionitis and outcome in extremely preterm infants. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2003; 32: 305–310.
Dammann O, Leviton A . Inflammation, brain damage and visual dysfunction in preterm infants. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2006; 11: 363–368.
Dammann O, Brinkhaus MJ, Bartels DB, Dordelmann M, Dressler F, Kerk J et al. Immaturity, perinatal inflammation, and retinopathy of prematurity: a multi-hit hypothesis. Early Hum Dev 2009; 85: 325–329.
Williams FL, Visser TJ, Hume R . Transient hypothyroxinaemia in preterm infants. Early Hum Dev 2006; 82: 797–802.
De Felice C, Bagnoli F, Toti P, Musaro MA, Peruzzi L, Paffetti P et al. Transient hypothyroxinemia of prematurity and histological chorioamnionitis. J Perinat Med 2005; 33: 514–518.
Yinon Y, Zalel Y, Weisz B, Mazaki-Tovi S, Sivan E, Schiff E et al. Fetal thymus size as a predictor of chorioamnionitis in women with preterm premature rupture of membranes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 29: 639–643.
De Felice C, Toti P, Santopietro R, Stumpo M, Pecciarini L, Bagnoli F . Small thymus in very low birth weight infants born to mothers with subclinical chorioamnionitis. J Pediatr 1999; 135: 384–386.
Di Naro E, Cromi A, Ghezzi F, Raio L, Uccella S, D’Addario V et al. Fetal thymic involution: a sonographic marker of the fetal inflammatory response syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006; 194: 153–159.
Toti P, De Felice C, Stumpo M, Schurfeld K, Di Leo L, Vatti R et al. Acute thymic involution in fetuses and neonates with chorioamnionitis. Hum Pathol 2000; 31: 1121–1128.
Kramer BW, Kallapur SG, Moss TJ, Nitsos I, Polglase GP, Newnham JP et al. Modulation of fetal inflammatory response on exposure to lipopolysaccharide by chorioamnion, lung, or gut in sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010; 202 (1): 77.e1–77.e9.
Been JV, Zimmermann LJ . Histological chorioamnionitis and respiratory outcome in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2009; 94: F218–F225.
Watterberg KL, Demers LM, Scott SM, Murphy S . Chorioamnionitis and early lung inflammation in infants in whom bronchopulmonary dysplasia develops. Pediatrics 1996; 97: 210–215.
Van Marter LJ, Dammann O, Allred EN, Leviton A, Pagano M, Moore M et al. Chorioamnionitis, mechanical ventilation, and postnatal sepsis as modulators of chronic lung disease in preterm infants. J Pediatr 2002; 140: 171–176.
Been JV, Zimmermann LJ . Chorioamnionitis and chronic lung disease in preterm infants. Pediatrics 2009, http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/eletters/123/5/1314.
Been JV, Zimmermann LJ, Debeer A, Kloosterboer N, Van Iwaarden JF . Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from preterm infants with chorioamnionitis inhibits alveolar epithelial repair. Respir Res 2009; 10: 116.
Been JV, Rours IG, Kornelisse RF, Jonkers F, de Krijger RR, Zimmermann LJ . Chorioamnionitis alters the response to surfactant in preterm infants. J Pediatr 2010; 156 (1): 10–15.e1.
Woldesenbet M, Rosenfeld CR, Ramilo O, Johnson-Welch S, Perlman JM . Severe neonatal hypoxic respiratory failure correlates with histologic chorioamnionitis and elevated concentrations of IL-6, IL-8 and CRP. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008; 93: F413–F417.
Watterberg KL, Shaffer ML, Mishefske MJ, Leach CL, Mammel MC, Couser RJ et al. Growth and neurodevelopmental outcomes after early low-dose hydrocortisone treatment in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2007; 120: 40–48.
Kumar R, Yu Y, Story RE, Pongracic JA, Gupta R, Pearson C et al. Prematurity, chorioamnionitis, and the development of recurrent wheezing: a prospective birth cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121: 878–884 e876.
Kramer BW, Kallapur S, Newnham J, Jobe AH . Prenatal inflammation and lung development. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2009; 14: 2–7.
Shimoya K, Taniguchi T, Matsuzaki N, Moriyama A, Murata Y, Kitajima H et al. Chorioamnionitis decreased incidence of respiratory distress syndrome by elevating fetal interleukin-6 serum concentration. Hum Reprod 2000; 15: 2234–2240.
Hannaford K, Todd DA, Jeffery H, John E, Blyth K, Gilbert GL . Role of ureaplasma urealyticum in lung disease of prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1999; 81: F162–F167.
Andrews WW, Goldenberg RL, Faye-Petersen O, Cliver S, Goepfert AR, Hauth JC . The Alabama Preterm Birth study: polymorphonuclear and mononuclear cell placental infiltrations, other markers of inflammation, and outcomes in 23- to 32-week preterm newborn infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006; 195: 803–808.
Bry K, Lappalainen U, Hallman M . Intraamniotic interleukin-1 accelerates surfactant protein synthesis in fetal rabbits and improves lung stability after premature birth. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 2992–2999.
Willet KE, Kramer BW, Kallapur SG, Ikegami M, Newnham JP, Moss TJ et al. Intra-amniotic injection of IL-1 induces inflammation and maturation in fetal sheep lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002; 282: L411–L420.
Kramer BW, Moss TJ, Willet KE, Newnham JP, Sly PD, Kallapur SG et al. Dose and time response after intraamniotic endotoxin in preterm lambs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 164: 982–988.
Kallapur SG, Willet KE, Jobe AH, Ikegami M, Bachurski CJ . Intra-amniotic endotoxin: chorioamnionitis precedes lung maturation in preterm lambs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2001; 280: L527–L536.
Kramer BW, Kramer S, Ikegami M, Jobe AH . Injury, inflammation, and remodeling in fetal sheep lung after intra-amniotic endotoxin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002; 283: L452–L459.
Jobe AH, Newnham JP, Willet KE, Moss TJ, Gore Ervin M, Padbury JF et al. Endotoxin-induced lung maturation in preterm lambs is not mediated by cortisol. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162: 1656–1661.
Willet KE, Jobe AH, Ikegami M, Newnham J, Brennan S, Sly PD . Antenatal endotoxin and glucocorticoid effects on lung morphometry in preterm lambs. Pediatr Res 2000; 48: 782–788.
Kallapur SG, Kramer BW, Moss TJ, Newnham JP, Jobe AH, Ikegami M et al. Maternal glucocorticoids increase endotoxin-induced lung inflammation in preterm lambs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2003; 284: L633–L642.
Sweet DG, Huggett MT, Warner JA, Moss TJ, Kloosterboer N, Halliday HL et al. Maternal betamethasone and chorioamnionitis induce different collagenases during lung maturation in fetal sheep. Neonatology 2008; 94: 79–86.
Ikegami M, Moss TJ, Kallapur SG, Mulrooney N, Kramer BW, Nitsos I et al. Minimal lung and systemic responses to TNF-alpha in preterm sheep. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2003; 285: L121–L129.
Kallapur SG, Moss TJ, Ikegami M, Jasman RL, Newnham JP, Jobe AH . Recruited inflammatory cells mediate endotoxin-induced lung maturation in preterm fetal lambs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 172: 1315–1321.
Newnham JP, Shub A, Jobe AH, Bird PS, Ikegami M, Nitsos I et al. The effects of intra-amniotic injection of periodontopathic lipopolysaccharides in sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005; 193: 313–321.
Hillman NH, Moss TJ, Nitsos I, Kramer BW, Bachurski CJ, Ikegami M et al. Toll-like receptors and agonist responses in the developing fetal sheep lung. Pediatr Res 2008; 63: 388–393.
Moss TJ, Newnham JP, Willett KE, Kramer BW, Jobe AH, Ikegami M . Early gestational intra-amniotic endotoxin: lung function, surfactant, and morphometry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: 805–811.
Kallapur SG, Bachurski CJ, Le Cras TD, Joshi SN, Ikegami M, Jobe AH . Vascular changes after intra-amniotic endotoxin in preterm lamb lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2004; 287: L1178–L1185.
Kunzmann S, Speer CP, Jobe AH, Kramer BW . Antenatal inflammation induced TGF-beta1 but suppressed CTGF in preterm lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2007; 292: L223–L231.
Sosenko IR, Kallapur SG, Nitsos I, Moss TJ, Newnham JP, Ikegami M et al. IL-1 alpha causes lung inflammation and maturation by direct effects on preterm fetal lamb lungs. Pediatr Res 2006; 60: 294–298.
Kramer BW, Jobe AH . The clever fetus: responding to inflammation to minimize lung injury. Biol Neonate 2005; 88: 202–207.
Kramer BW, Jobe AH, Ikegami M . Monocyte function in preterm, term, and adult sheep. Pediatr Res 2003; 54: 52–57.
Kramer BW, Joshi SN, Moss TJ, Newnham JP, Sindelar R, Jobe AH et al. Endotoxin-induced maturation of monocytes in preterm fetal sheep lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2007; 293: L345–L353.
Cheah FC, Pillow JJ, Kramer BW, Polglase GR, Nitsos I, Newnham JP et al. Airway inflammatory cell responses to intra-amniotic lipopolysaccharide in a sheep model of chorioamnionitis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2009; 296: L384–L393.
Kramer BW, Ikegami M, Moss TJ, Nitsos I, Newnham JP, Jobe AH . Endotoxin-induced chorioamnionitis modulates innate immunity of monocytes in preterm sheep. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171: 73–77.
Kramer BW, Kallapur SG, Moss TJ, Nitsos I, Newnham JP, Jobe AH . Intra-amniotic LPS modulation of TLR signaling in lung and blood monocytes of fetal sheep. Innate Immun 2009; 15: 101–107.
Kallapur SG, Jobe AH, Ball MK, Nitsos I, Moss TJ, Hillman NH et al. Pulmonary and systemic endotoxin tolerance in preterm fetal sheep exposed to chorioamnionitis. J Immunol 2007; 179: 8491–8499.
Yanowitz TD, Jordan JA, Gilmour CH, Towbin R, Bowen A, Roberts JM et al. Hemodynamic disturbances in premature infants born after chorioamnionitis: association with cord blood cytokine concentrations. Pediatr Res 2002; 51: 310–316.
Lee SY, Ng DK, Fung GP, Chow CB, Shek CC, Tang PM et al. Chorioamnionitis with or without funisitis increases the risk of hypotension in very low birthweight infants on the first postnatal day but not later. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2006; 91: F346–F348.
Furukawa S, Sameshima H, Ikenoue T . Circulatory disturbances during the first postnatal 24 hours in extremely premature infants 25 weeks or less of gestation with histological fetal inflammation. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2008; 34: 27–33.
Laughon M, Bose C, Allred E, O’Shea TM, Van Marter LJ, Bednarek F et al. Factors associated with treatment for hypotension in extremely low gestational age newborns during the first postnatal week. Pediatrics 2007; 119: 273–280.
Been JV, Kornelisse RF, Rours IG, Passos VL, De Krijger RR, Zimmermann LJ . Early postnatal blood pressure in preterm infants: effects of chorioamnionitis and timing of antenatal steroids. Pediatr Res 2009; 66: 571–576.
Coumans AB, Garnier Y, Supcun S, Jensen A, Berger R, Hasaart TH . The effects of low-dose endotoxin on the umbilicoplacental circulation in preterm sheep. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2004; 11: 289–293.
Garnier Y, Coumans A, Berger R, Jensen A, Hasaart TH . Endotoxemia severely affects circulation during normoxia and asphyxia in immature fetal sheep. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2001; 8: 134–142.
Klinger G, Levy I, Sirota L, Boyko V, Reichman B, Lerner-Geva L . Epidemiology and risk factors for early onset sepsis among very-low-birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 201: 38 e31–e36.
Park CW, Moon KC, Park JS, Jun JK, Romero R, Yoon BH . The involvement of human amnion in histologic chorioamnionitis is an indicator that a fetal and an intra-amniotic inflammatory response is more likely and severe: clinical implications. Placenta 2009; 30: 56–61.
Soraisham AS, Singhal N, McMillan DD, Sauve RS, Lee SK . A multicenter study on the clinical outcome of chorioamnionitis in preterm infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200: 372 e371–e376.
Mehta R, Nanjundaswamy S, Shen-Schwarz S, Petrova A . Neonatal morbidity and placental pathology. Indian J Pediatr 2006; 73: 25–28.
Falkenberg ER, Davis RO, DuBard M, Parker Jr CR . Effects of maternal infections on fetal adrenal steroid production. Endocr Res 1999; 25: 239–249.
Watterberg KL, Scott SM, Naeye RL . Chorioamnionitis, cortisol, and acute lung disease in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 1997; 99: E6.
Buhimschi CS, Turan OM, Funai EF, Azpurua H, Bahtiyar MO, Turan S et al. Fetal adrenal gland volume and cortisol/dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate ratio in inflammation-associated preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol 2008; 111: 715–722.
Yoon BH, Romero R, Jun JK, Maymon E, Gomez R, Mazor M et al. An increase in fetal plasma cortisol but not dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate is followed by the onset of preterm labor in patients with preterm premature rupture of the membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998; 179: 1107–1114.
Papadopoulos N, Simopoulos C, Sigalas J, Kotini A, Cheva A, Tamiolakis D . Induction of hepatic hematopoiesis with tenascin-C expression during the second trimester of development. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2004; 113: 56–60.
Pfisterer C, Faber R, Horn LC . Chorioamnionitis-induced changes of fetal extramedullar hematopoiesis in the second trimester of gestation. Is diagnosis from fetal autopsy possible? Virchows Arch 2005; 446: 150–156.
Stallmach T, Karolyi L . Augmentation of fetal granulopoiesis with chorioamnionitis during the second trimester of gestation. Hum Pathol 1994; 25: 244–247.
Wilson TC, Bachurski CJ, Ikegami M, Jobe AH, Kallapur SG . Pulmonary and systemic induction of SAA3 after ventilation and endotoxin in preterm lambs. Pediatr Res 2005; 58: 1204–1209.
Ragouilliaux CJ, Keeney SE, Hawkins HK, Rowen JL . Maternal factors in extremely low birth weight infants who develop spontaneous intestinal perforation. Pediatrics 2007; 120: e1458–e1464.
Neu J, Mshvildadze M, Mai V . A roadmap for understanding and preventing necrotizing enterocolitis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2008; 10: 450–457.
Wolfs TG, Buurman WA, Zoer B, Moonen RM, Derikx JP, Thuijls G et al. Endotoxin induced chorioamnionitis prevents intestinal development during gestation in fetal sheep. PLoS One 2009; 4: e5837.
Kim YM, Romero R, Chaiworapongsa T, Espinoza J, Mor G, Kim CJ . Dermatitis as a component of the fetal inflammatory response syndrome is associated with activation of Toll-like receptors in epidermal keratinocytes. Histopathology 2006; 49: 506–514.
Kenyon SL, Taylor DJ, Tarnow-Mordi W . Broad-spectrum antibiotics for spontaneous preterm labour: the ORACLE II randomised trial. ORACLE Collaborative Group. Lancet 2001; 357: 989–994.
Kenyon SL, Taylor DJ, Tarnow-Mordi W . Broad-spectrum antibiotics for preterm, prelabour rupture of fetal membranes: the ORACLE I randomised trial. ORACLE Collaborative Group. Lancet 2001; 357: 979–988.
Briggs GG, Freeman RK, Yaffe SJ . Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation, 8th edn. Lippincott: Philadelphia, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This paper resulted from the Evidence vs Experience in Neonatal Practices conference, 19 to 20 June 2009, sponsored by Dey, LP.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gantert, M., Been, J., Gavilanes, A. et al. Chorioamnionitis: a multiorgan disease of the fetus?. J Perinatol 30 (Suppl 1), S21–S30 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2010.96
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2010.96
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Risk factors and postnatal biomarkers for acute placental inflammatory lesions and intrauterine infections in preterm infants
European Journal of Pediatrics (2022)
-
Histological chorioamnionitis is associated with an increased risk of wheezing in preterm children less than 34 gestational weeks
BMC Pediatrics (2021)
-
Chorioamnionitis induces hepatic inflammation and time-dependent changes of the enterohepatic circulation in the ovine fetus
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Pathological staging of chorioamnionitis contributes to complications in preterm infants
Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2020)
-
Chorioamnionitis induces enteric nervous system injury: effects of timing and inflammation in the ovine fetus
Molecular Medicine (2020)