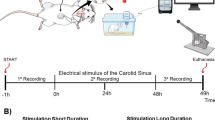
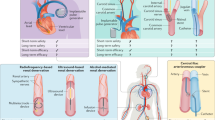
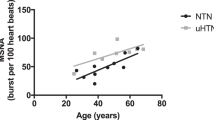
Abstract
The sympathetic nervous system is an effective homeostatic mechanism for modulating hemodynamics in times of stress and illness. Unfortunately, in some patients, this mechanism escapes physiologic control and through various mechanisms leads to resistant hypertension. Antihypertensive drug therapy is successful only to a point, leaving a significant percentage of patients nationwide with blood pressure measurements above guidelines despite being treated with at least three agents at maximally tolerated doses, consistent with a diagnosis of resistant hypertension. Novel methods of modifying the activity of the sympathetic nervous system have been studied in animals, and this review discusses the data in support of one of the techniques at the forefront of non-pharmacologic blood pressure therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff D, Murphy T, Toto R et al. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension 2008; 51: 1403–1419.
Egan B, Zhao Y, Axon RN, Brzezinski WA, Ferdinand KC . Uncontrolled and apparent treatment resistant hypertension in the United States, 1988 to 2008. Circulation 2011; 124: 1046–1058.
Balabanov A, Rossi MA . Epilepsy surgery and vagal nerve stimulation: what all neurologists should know. Semin Neurol 2008; 28: 355–363.
Thimmig RF, Smith MB, Sullivan JM . Lumbar sympathectomy in the treatment of arteriosclerotic peripheral vascular disease. Surg Clin North Am 1958; 38: 1081–1091.
Smithwick RH . Surgical treatment of Hypertension. Am J Med 1948; 4: 744–759.
Freyberg RH, Peet MM . The effect on the kidney of bilateral splanchnicectomy in patients with hypertension. J Clin Invest 1937; 16: 49–65.
Isenberg EM, Peet MM . The influence of supradiaphragmatic splanchnicectomy on the heart in hypertension. Am Heart J 1948; 35: 567–583.
Page IH, Heuer GJ . A surgical treatment of essential hypertension. J Clin Invest 1935; 14: 22–26.
Allen EV . Sympathectomy for essential hypertension. Circulation 1952; 6: 131–140.
Bisognano JD, Bakris G, Nadim MK, Sanchez L, Kroon AA, Schafer J et al. Baroreflex activation therapy lowers blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension: results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled rheos pivotal trial. JACC 2011; 58: 765–773.
Furlan R, Diedrich A, Rimoldi A, Palazzolo L, Porta C, Diedrich L et al. Effects of unilateral and bilateral carotid baroreflex stimulation on cardiac and neural sympathetic discharge oscillatory patterns. Circulation 2003; 108: 717–723.
Tafil-Klawe M, Raschke F, Hildebrandt G . Functional asymmetry in carotid sinus cardiac reflexes in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 1990; 60: 402–405.
Williamson JW, Raven PB . Unilateral carotid-cardiac baroreflex responses in humans. Am J Physiol 1993; 265: H1033–H1037.
Williamson JW, Muzi M, Ebert TJ . Unilateral carotid sinus stimulation and muscle sympathetic nerve activity in man. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1996; 28: 815–821.
Lohmeier TE, Irwin ED, Rossing MA, Sedar DJ, Kieval RS . Prolonged activation of the baroreflex produces sustained hypotension. Hypertension 2004; 43: 306–311.
Lohmeier TE, Dwyer TM, Hildebrandt DA, Irwin ED, Rossing MA, Sedar DJ et al. Influence of prolonged baroreflex activation on arterial pressure in angiotensin. Hypertension 2005; 46: 1194–1200.
Scheffers IJM, Kroon AA, Schmidli J, Jordan J, Tordoir JJM, Mohaupt MG et al. Novel baroreflex activation therapy in resistant hypertension: results of a European multi-center feasibility study. JACC 2010; 56: 1254–1258.
Bakris GL, Nadim MK, Haller H, Lovett EG, Schafer JE, Bisognano JD . Baroreflex activation therapy provides durable benefit in patients with resistant hypertension: results of long-term follow-up in the Rheos Pivotal Trial. J Am Soc Hypertens 2012; 6: 152–158.
Hoppe UC, Mathias-Christoph B, Wachter R, Beige J, Rump LC, Kroon AA et al. Minimally invasive system for baroreflex activation therapy chronically lowers blood pressure with pacemaker-like safety profile: results from the Barostim neo trial. J Am Soc Hypertens 2012; 6: 270–276.
Sica D, Bisognano J, Nadim M, Sanchez L, Bakris G . Individualized programming demonstrates feasibility of unilateral approach to delivery of baroreflex activation therapy. J Clin Hypertens 2011; 13 (suppl 1): A10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
John Gassler has received research support from CVRx. John Bisognano has received consultant fees and research support from CVRx.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gassler, J., Bisognano, J. Baroreflex activation therapy in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 28, 469–474 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.139
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.139
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vagus nerve stimulation using a miniaturized wirelessly powered stimulator in pigs
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Interventionelle Therapien bei Hypertonie – aktueller Stand
Der Internist (2021)
-
Device-based therapies for arterial hypertension
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2020)
-
Device-based Therapy for Hypertension
Current Hypertension Reports (2016)
-
Management of hypertension in chronic kidney disease
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2015)