Abstract
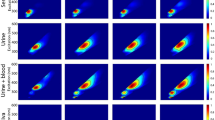
Human biomonitoring (analysis of biological fluids) is increasingly being used for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. Smoking tobacco is a significant source of indoor air pollution and is harmful to human health. The aim of this research was to find both the best non-invasive matrices (from among saliva, urine, semen and sweat) for evaluating environmental exposure to tobacco smoke and the relationships between thiocyanates (biomarkers of environmental tobacco smoke exposure) and other inorganic ions in these matrices collected from active and passive smokers and also non-smokers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilewicz R., and Kublik Z. The determination of traces of thiocyanate and copper (II) ions by cathodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1981: 123: 201–212.
Chen Z.F., Darvell B.W., and Leung V.W.H. Human salivary anionic analysis using ion chromatography. Arch. Oral Biol. 2004a: 49: 863–869.
Chen Z.F., Darvell B.W., and Leung V.W.H. Validation of ion chromatography for human salivary anionic analysis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2004b: 49: 855–862.
Chia S.E., et al. Comparison of zinc concentrations in blood and seminal plasma and the various sperm parameters between fertile and infertile men. J. Androl. 2000: 21: 53–57.
Chinaka S., et al. Simultaneous determination of cyanide and thiocyanate in blood by ion chromatography with fluorescence and ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. B. 1998: 713: 353–359.
Connolly D., Barron L., and Paull B. Determination of urinary thiocyanate and nitrate using fast ion-interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B. 2002: 767: 175–180.
Demkowska I., Polkowska Ż., and Namieśnik J Application of ion chromatography for the determination of inorganic ions, especially thiocyanates in human saliva samples as biomarkers of environmental tobacco smoke exposure. J. Chromatogr. B. 2008: 875: 419–426.
Demkowska I., Polkowska Ż., and Namieśnik J. Application of ion chromatography for the determination of inorganic ions, especially thiocyanates in human semen samples as biomarkers of environmental tobacco smoke exposure. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2010: 34 (9): 533–538.
Giraudi G., and Grillo C. Direct spectrophotometric determination of thiocyanate in serum and urine with continuous-flow analyzer. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1981: 128: 169–175.
Glatz Z., Nováková S., and Štěrbová H. Analysis of thiocyanate in biological fluids by capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A. 2001: 916: 273–277.
Hamamah S, and Gatti J.-L. Role of the ionic environment and internal pH on sperm activity. Hum. Reprod. 1998: 4: 20–30.
Huang YL, et al. Trace elements and lipid peroxidation in human seminal plasma. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2000: 76: 207–215.
LeGrys V.A. Sweat testing for the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: practical considerations. J. Pediatr. 1996: 129: 892–897.
LeGrys V.A., et al. Diagnostic sweat testing: the cystic fibrosis foundation guidelines. J Pediatr. 2007: 151: 85–89.
Pandy V.K., Parmeshwaran M., and Soman S.D. Concentrations of morphologically normal, motile spermatozoa : Mg, Ca and Zn in the semen of infertile men. Sci. Total Environ. 1983: 27: 49–57.
Sádecká J., and Polonský J. Determination of inorganic anions in saliva by capillary isotachophoresis. Talanta 2003: 59: 643–649.
Stanwell-Smith R, et al. A comparative study of zinc, copper, cadmium and lead levels in fertile and infertile men. Fertil. Steril. 1983: 40: 670–677.
Tamošiúnas V., Padarauskas A., and Pranaityté B. Thiocyanate determination by ion pair chromatography. Chemija. 2006: 17: 21–24.
Tanaka Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of nitrite, nitrate, thiocyanate and uric acid in human saliva by capillary zone electrophoresis and its application to the study of daily variations. J. Chromatogr. A. 2004: 1051: 193–197.
Themelis D.G., and Tzanavaras P.D. Solvent extraction flow-injection manifold for the simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of free cyanide and thiocyanate ions based upon on-line masking of cyanides by formaldehyde. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2002: 452: 295–302.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by a grant from the Committee on Scientific Research (Project N N523 454836).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demkowska, I., Polkowska, Ż. & Namieśnik, J. Non-invasive biological fluid matrices analysed to assess exposure to environmental tobacco smoke. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 21, 656–661 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2011.19
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2011.19
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Exposure to ultrafine particles in hospitality venues with partial smoking bans
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2013)