Abstract
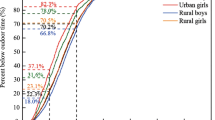
Information on time spent in microenvironments has a critical role for personal exposure to environmental pollutants. Unlike several large-scale studies in Western countries, no comprehensive research on time-activity patterns for exposure assessment has been conducted in Korea. We investigated determinants of residential indoor and transportation times of individuals over 10-years old in the Korean population. The population-based study collected time-activity patterns of 31,634 Koreans for two consecutive days. The residential indoor and transportation times were collected for a weekday and a weekend day. The impact of sociodemographic factors on time-activity was assessed using multiple linear regression models. The residential indoor times were 14.23 h for the weekday and 16.13 h for the weekend and shorter than those in Western countries. The transportation times were 1.75 h for the weekday and 1.68 h for the weekend day. The most significant factors in residential indoor time were employment status, age, monthly income, and gender for the weekday and employment status and gender for the weekend day. The factors in transportation were gender, employment status, and monthly income for the weekday and gender, employment status, age, and marriage status for the weekend day. Determinants of the time-activity pattern need to be taken into account in exposure assessment, epidemiological analyses, and exposure simulations, as well as in the development of preventive strategies. As Korean population activity patterns are substantially different from those in Western countries such as USA, Germany, and UK, this information could be critical for exposure assessment in Korea and other Asian countries.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brasche S., and Bischof W. Daily time spent indoor in German homes—baseline data for the assessment of indoor exposure of German occupants. Int J Hyg Environ Health 2005: 208: 247–253.
Briggs D.J., Denman A.R., Gulliver J., Marley R.F., Kennedy C.A., and Philips P.S., et al. Time activity modeling of domestic exposure to radon. J Environ Manage 2003: 67: 107–120.
Bruin Y.B.D., Hanninen O., Carrer P., Maroni M., Kephalopoulos S., and Marco G.S.D., et al. Simulation of working population exposures to carbon monoxide using EXOLIS-Milan microenvironment concentration time-activity data. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2004: 14: 154–163.
Chau C.K., Tu E.Y., Chan D.W.T., and Burnett J. Estimating the total exposure to air pollutants for different population age groups in Hong Kong. Environ Int 2002: 27: 617–630.
Dorre W.H. Time-activity patterns of some selected small groups as a basis for exposure estimation : a methodological study. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 1997: 7: 471–491.
Echols S.L., Macintosh D.L., Hammerstrom K.A., and Ryan P.B. Temporal variability of microenvironmental time budgets in Maryland. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 1999: 9: 502–512.
Freeman N.C., Lioy P.J., Pellizzari E., Zelon H., Thomas K., and Clayton A., et al. Responses to the region 5 NHEXAS time/activity diary. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 1999: 9: 414–426.
Freeman N.C., Waldman J.M., and Lioy P.J. Design evaluation a location activity log used for assessing personal exposure to air pollutants. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 1991: 1: 327–338.
Graham S.E., and McCurdy T. Developing meaningful cohorts for human exposure models. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2004: 14: 23–43.
Jenkins P.L., Philips T.J., Mulberg E.J., and Hui S.P. Activity patterns of Californians: use of proximity to indoor pollutants sources. Atmos Environ 1992: 26A: 2141–2148.
Klepeis N.E. An introduction to the indirect exposure assessment approach: modeling human exposure using microenvironmental measurements the recent national human activity pattern survey. Environ Health Perspect 1999: 107 (Suppl 2): 365–374.
Lai H.K., Kendall M., Ferrier H., Lindup I., Alm S., Hanninen O., Jantunen M., Mathys P., Colvile R., Ashmore M.R., Cullinan P. and Nieuwenhuijsen M.J. Personal exposures and microenvironment concentrations of PM2 5, VOC, NO2 and CO in Oxford, UK. Atm Environ 2004: 38: 6399–6410.
Leech J.A., Nelson W.C., Burnett R.T., Aaron S., and Raizenne M.E. It's about time: a comparison of Canadian and American time-activity patterns. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2002: 12: 427–432.
McCurdy T., and Graham S.E. Using human activity data in exposure models: analysis of discriminating factors. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2003: 13: 294–317.
Ministry of Environment (MEK). Korean Exposure Factor Handbook. Ministry of Environment of Korea, Incheon, 2007.
Rotko T., Oglesby L., Kunzli N., and Jantunen M.J. Population sampling in European air pollution exposure study, EXPOLIS: comparisons between the cities and representativeness of the samples. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2000: 10: 355–364.
Schwab M., Colome S.D., Spengler J.D., Ryan P.B., and Bullick I.H. Activity patterns applied to pollutant exposure assessment: data from a personal modeling study in Los Angeles. Toxicol Ind Health 1990: 6: 517–532.
Schweizer C., Edwards R.D., Bayer-oglesby L., Gauderman W.J., Ilacqua V., and Jantunen M.J., et al. Indoor time-microenvironment-activity patterns in seven regions of Europe. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 2007: 17: 170–181.
Sexton K., Mongin S.J., Adgate J.L., Pratt G.C., Ramachandran G., and Stock T.H., et al. Estimating volatile organic compound concentrations in selected microenvironments using time-activity and personal exposure data. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2007: 70: 465–476.
Wallace L.A., Pellizzari E.D., Hartwell T.D., Davis V., Michael L.C., and Whitmore R.W. The team study—personal exposures to toxic substances in air, drinking water, and breath of 400 residents of New Jersey, North Carolina, and North Dakota. Environ Res 1989: 43: 290–307.
Wang S.W., Majeed M.A., Chu P.L., and Lin H.C. Characterizing relationships between personal exposures to VOCs and socioeconomic, demographic, behavioral variables. Atmos Environ 2009: 43: 2296–2302.
WHO. Guideline for Air Quality. World Health Organization Document, WHO/SED/OEH/, WHO, Geneva,, 2000.
Yang W., Lee S., and Paek D. Exposure assessment and estimation of personal exposure for nitrogen dioxide using time weighted average model. J Korean Soc Atmos Environ 2001: 17: 251–258.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by National Institute of Environmental Research, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Lee, K., Yoon, C. et al. Determinants of residential indoor and transportation activity times in Korea. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 21, 310–316 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2010.23
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2010.23
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Temporal trend of microenvironmental time-activity patterns of the Seoul population from 2004 to 2022 and its potential impact on exposure assessment
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2024)
-
Updated general exposure factors for risk assessment in the Korean population
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2023)
-
Particulate matter generation in daily activities and removal effect by ventilation methods in residential building
Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health (2021)
-
Introducing DNA-based methods to compare fungal microbiota and concentrations in indoor, outdoor, and personal air
Aerobiologia (2018)
-
Characterization of urinary cotinine in non-smoking residents in smoke-free homes in the Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS)
BMC Public Health (2016)