Abstract
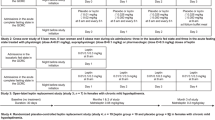
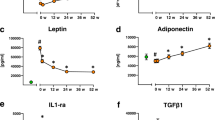
Leptin is an adipokine causing browning of adipose tissue, and it thus increases energy expenditure. The same is true for irisin. We studied whether exogenously administered metreleptin affects serum irisin concentrations in humans, which would suggest a direct interplay between leptin and irisin. We performed two studies: a dose-escalating 1-day-long study and a randomized placebo-controlled study. Study 1: 15 healthy, normal-weight and/or obese male and female individuals participated in three 1-day-long trials of metreleptin administration in the fed state. Metreleptin was administered once at physiological and pharmacological (0.01, 0.1 and 0.3 mg per kg body weight) doses. Study 2: 18 apparently healthy hypoleptinemic young women with hypoleptinemia and secondary amenorrhea took part in this study. Subjects received either metreleptin in replacement doses (0.08 and/or 0.12 mg kg−1) or placebo for 16 weeks. Blood samples were analyzed for leptin and irisin. We found no effect of metreleptin administration on irisin levels of subjects studied at either the fasting or the fed state either in the short or the long term. We provide evidence that leptin is not altering circulating irisin levels in humans.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bostrom P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC et al. A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012; 481: 463–468.
Roca-Rivada A, Castelao C, Senin LL, Landrove MO, Baltar J, Belen Crujeiras A et al. FNDC5/irisin is not only a myokine but also an adipokine. PLoS One 2013; 8: e60563.
Gutierrez-Repiso C, Garcia-Serrano S, Rodriguez-Pacheco F, Garcia-Escobar E, Haro-Mora JJ, Garcia-Arnes J et al. FNDC5 could be regulated by leptin in adipose tissue. Eur J Clin Invest 2014; 44: 918–925.
Swick AG, Orena S, O'Connor A . Irisin levels correlate with energy expenditure in a subgroup of humans with energy expenditure greater than predicted by fat free mass. Metabolism 2013; 62: 1070–1073.
Panagiotou G, Mu L, Na B, Mukamal KJ, Mantzoros CS . Circulating irisin, omentin-1, and lipoprotein subparticles in adults at higher cardiovascular risk. Metabolism 2014; 63: 1265–1271.
Rezai-Zadeh K, Yu S, Jiang Y, Laque A, Schwartzenburg C, Morrison CD et al. Leptin receptor neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus are key regulators of energy expenditure and body weight, but not food intake. Mol Metab 2014; 3: 681–693.
Zhang Y, Li R, Meng Y, Li S, Donelan W, Zhao Y et al. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes 2014; 63: 514–525.
Chan JL, Wong SL, Mantzoros CS . Pharmacokinetics of subcutaneous recombinant methionyl human leptin administration in healthy subjects in the fed and fasting states: regulation by gender and adiposity. Clin Pharm 2008; 47: 753–764.
Chou SH, Chamberland JP, Liu X, Matarese G, Gao C, Stefanakis R et al. Leptin is an effective treatment for hypothalamic amenorrhea. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 6585–6590.
Park KH, Zaichenko L, Brinkoetter M, Thakkar B, Sahin-Efe A, Joung KE et al. Circulating irisin in relation to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013; 98: 4899–4907.
Loffler D, Muller U, Scheuermann K, Friebe D, Gesing J, Bielitz J et al. Serum irisin levels are regulated by acute strenuous exercise. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015; 100: 1289–1299.
Mantzoros CS, Frederich RC, Qu D, Lowell BB, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS . Severe leptin resistance in brown fat-deficient uncoupling protein promoter-driven diphtheria toxin A mice despite suppression of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and circulating corticosterone concentrations. Diabetes 1998; 47: 230–238.
Elsen M, Raschke S, Eckel J . Browning of white fat: does irisin play a role in humans? J Endocrinol 2014; 222: R25–R38.
Lee P, Linderman JD, Smith S, Brychta RJ, Wang J, Idelson C et al. Irisin and FGF21 are cold-induced endocrine activators of brown fat function in humans. Cell Metab 2014; 19: 302–309.
Shan T, Liang X, Bi P, Kuang S . Myostatin knockout drives browning of white adipose tissue through activating the AMPK-PGC1alpha-Fndc5 pathway in muscle. FASEB J 2013; 27: 1981–1989.
Rodriguez A, Becerril S, Mendez-Gimenez L, Ramirez B, Sainz N, Catalan V et al. Leptin administration activates irisin-induced myogenesis via nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms, but reduces its effect on subcutaneous fat browning in mice. Int J Obes (Lond) 2015; 39: 397–407.
Palacios-Gonzalez B, Vadillo-Ortega F, Polo-Oteyza E, Sanchez T, Ancira-Moreno M, Romero-Hidalgo S et al. Irisin levels before and after physical activity among school-age children with different BMI: a direct relation with leptin. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2015; 23: 729–732.
Bluher S, Panagiotou G, Petroff D, Markert J, Wagner A, Klemm T et al. Effects of a 1-year exercise and lifestyle intervention on irisin, adipokines, and inflammatory markers in obese children. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014; 22: 1701–1708.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Institutional BIDMC. The project was also supported by Harvard Clinical and Translational Science Center Grant UL1 RR025758 from the National Center for Research Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavrieli, A., Panagiotou, G. & Mantzoros, C. Leptin administration in physiological or pharmacological doses does not alter circulating irisin levels in humans. Int J Obes 40, 1461–1463 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2016.99
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2016.99
This article is cited by
-
Serum asprosin levels and bariatric surgery outcomes in obese adults
International Journal of Obesity (2019)
-
Irisin in metabolic diseases
Endocrine (2018)
-
Physiology and role of irisin in glucose homeostasis
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2017)