Abstract
Objective:
The mechanisms underlying the association of the increased albumin excretion rate (AER) with adiposity have yet to be clarified. We therefore investigated (1) the predictors of AER after 3 months of lifestyle intervention in a large cohort of nondiabetic obese women and (2) the relationships between AER and the adipose tissue gene expression of adipokines linked to inflammation and insulin resistance.
Subjects:
A total of 269 obese nondiabetic women (age 49.9±13.1 years, body mass index (BMI) 36.8±4.6 kg m−2) participated in this program. Measurements used were anthropometrics parameters, blood pressure, oral glucose tolerance test, lipids, creatinine, AER, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and glomerular filtration rate at baseline and after 3 months of lifestyle intervention. At baseline, in a subgroup of 34 women, subcutaneous adipose tissue biopsy was carried out for the analysis of mRNA expression levels of adiponectin, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS-3), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), pentraxine 3 (PTX-3), angiotensinogen and angiotensin-converting enzyme, and a blood sample was also taken from this group for the measurement of circulating adiponectin, interleukin-6, TNF-α and PTX-3. Microalbuminuria was defined as albumin/creatinine ratio ⩾3.5 mg mmol−1. Real-time PCR was used to quantify mRNA.
Results:
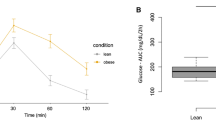
Six percent of obese women had microalbuminuria. When dividing the whole cohort into three groups according to AER changes (decrease, stability and increase), we noted that 2 h glucose, insulin and HOMA-IR significantly decreased (P<0.05 for all) only in women who had a decrease in AER, whereas BMI and waist circumference significantly decreased in all the three groups (P<0.05). At baseline, higher AER was associated to significantly higher adipose tissue mRNA expression levels of SOCS-3 and PTX-3 (P<0.05) and to higher TNF-α and angiotensinogen expression.
Conclusions:
In obese women, weight loss alone is not sufficient to induce the AER decrease that occurs only with a concomitant improvement in glucose homeostasis. The adipose tissue gene expression profile seems to favor the early renal impairment often seen in obese subjects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valensi P, Assayag M, Busby M, Pariès J, Lormeau B, Attali JR . Microalbuminuria in obese patients with or without hypertension. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996; 20: 574–579.
Verhave JC, Gansevoort RT, Hillege HL, Bakker SJ, De Zeeuw D, de Jong PE, PREVEND Study Group. An elevated urinary albumin excretion predicts de novo development of renal function impairment in the general population. Kidney Int Suppl 2004; 92: S18–S21.
Wachtell K, Ibsen H, Olsen MH, Borch-Johnsen K, Lindholm LH, Mogensen CE et al. Albuminuria and cardiovascular risk in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: the LIFE study. Ann Intern Med 2003; 139: 901–906.
Arnlöv J, Evans JC, Meigs JB, Wang TJ, Fox CS, Levy D et al. Low-grade albuminuria and incidence of cardiovascular disease events in nonhypertensive and nondiabetic individuals: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2005; 112: 969–975.
Liese AD, Hense HW, Döring A, Stieber J, Keil U . Microalbuminuria, central adiposity and hypertension in the non-diabetic urban population of the MONICA Augsburg survey 1994/95. J Hum Hypertens 2001; 15: 799–804.
Solbu MD, Kronborg J, Eriksen BO, Jenssen TG, Toft I . Cardiovascular risk-factors predict progression of urinary albumin-excretion in a general, non-diabetic population: a gender-specific follow-up study. Atherosclerosis 2008; 201: 398–406.
Bonnet F, Marre M, Halimi JM, Stengel B, Lange C, Laville M et al. Waist circumference and the metabolic syndrome predict the development of elevated albuminuria in non-diabetic subjects: the DESIR Study. J Hypertens 2006; 24: 1157–1163.
Bello AK, de Zeeuw D, El Nahas M, Brantsma AH, Bakker SJ, de Jong PE et al. Impact of weight change on albuminuria in the general population. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2007; 22: 1619–1627.
Prospective Studies Collaboration, Whitlock G, Lewington S, Sherliker P, Clarke R, Emberson J, Halsey J et al. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 2009; 373: 1083–1096.
Chagnac A, Weinstein T, Korzets A, Ramadan E, Hirsch J, Gafter U . Glomerular hemodynamics in severe obesity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2000; 278: F817–F822.
Chagnac A, Weinstein T, Herman M, Hirsh J, Gafter U, Ori Y . The effects of weight loss on renal function in patients with severe obesity. J Am Soc Nephrol 2003; 14: 1480–1486.
Cubeddu LX, Alfieri AB, Hoffmann IS . Lowering the threshold for defining microalbuminuria: effects of a lifestyle-metformin intervention in obese ‘normoalbuminuric’ non-diabetic subjects. Am J Hypertens 2008; 21: 1005–1010.
Shikano M, Sobajima H, Yoshikawa H, Toba T, Kushimoto H, Katsumata H et al. Usefulness of a highly sensitive urinary and serum IL-6 assay in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Nephron 2000; 85: 81–85.
Moriwaki Y, Inokuchi T, Yamamoto A, Ka T, Tsutsumi Z, Takahashi S et al. Effect of TNF-alpha inhibition on urinary albumin excretion in experimental diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol 2007; 44: 215–218.
Hayakawa K, Ohashi H, Yokoyama H, Yoshida G, Okada M, Minatoguchi S . Adiponectin is increased and correlated with the degree of proteinuria, but plasma leptin is not changed in patients with chronic glomerulonephritis. Nephrology 2009; 14: 327–331.
Norata GD, Baragetti I, Raselli S, Stucchi A, Garlaschelli K, Vettoretti S et al. Plasma adiponectin levels in chronic kidney disease patients: relation with molecular inflammatory profile and metabolic status. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2009. e-pub ahead of print 8 April 2009; doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2009.01.011.
Yano Y, Hoshide S, Ishikawa J, Hashimoto T, Eguchi K, Shimada K et al. Differential impacts of adiponectin on low-grade albuminuria between obese and nonobese persons without diabetes. J Clin Hypertens 2007; 9: 775–782.
Sharma K, Ramachandrarao S, Qiu G, Usui HK, Zhu Y, Dunn SR et al. Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 1645–1656.
Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, Marsh J, Stevens LA, Kusek JW et al. Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration. Expressing the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate with standardized serum creatinine values. Clin Chem 2007; 53: 766–772.
Muller B, Peri G, Doni A, Torri V, Landmann R, Bottazzi B et al. Circulating levels of the long pentraxin PTX3 correlate with severity of infection in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 2001; 29: 1404–1407.
Brantsma AH, Atthobari J, Bakker SJ, de Zeeuw D, de Jong PE, Gansevoort RT . What predicts progression and regression of urinary albumin excretion in the nondiabetic population? J Am Soc Nephrol 2007; 18: 637–645.
Morales E, Valero MA, León M, Hernández E, Praga M . Beneficial effects of weight loss in overweight patients with chronic proteinuric nephropathies. Am J Kidney Dis 2003; 41: 319–327.
Solerte SB, Fioravanti M, Schifino N, Ferrari E . Effects of diet-therapy on urinary protein excretion albuminuria and renal haemodynamic function in obese diabetic patients with overt nephropathy. Int J Obes 1989; 13: 203–211.
Serra A, Granada ML, Romero R, Bayés B, Cantón A, Bonet J et al. The effect of bariatric surgery on adipocytokines, renal parameters and other cardiovascular risk factors in severe and very severe obesity: 1-year follow-up. Clin Nutr 2006; 25: 400–408.
Cirillo M, Lanti MP, Menotti A, Laurenzi M, Mancini M, Zanchetti A et al. Definition of kidney dysfunction as a cardiovascular risk factor: use of urinary albumin excretion and estimated glomerular filtration rate. Arch Intern Med 2008; 168: 617–624.
Karelis AD . Metabolically healthy but obese individuals. Lancet 2008; 372: 1281–1283.
Goossens GH . The role of adipose tissue dysfunction in the pathogenesis of obesity-related insulin resistance. Physiol Behav 2008; 94: 206–218.
Sarafidis PA . Obesity, insulin resistance and kidney disease risk: insights into the relationship. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2008; 17: 450–456.
Krebs DL, Hilton DJ . SOCS: physiological suppressors of cytokine signaling. J Cell Sci 2000; 113: 2813–2819.
Lebrun P, Van Obberghen E . SOCS proteins causing trouble in insulin action. Acta Physiol 2008; 192: 29–36.
Shi H, Cave B, Inouye K, Bjørbaek C, Flier JS . Overexpression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in adipose tissue causes local but not systemic insulin resistance. Diabetes 2006; 55: 699–707.
Emanuelli B, Peraldi P, Filloux C, Chavey C, Freidinger K, Hilton DJ et al. SOCS-3 inhibits insulin signaling and is up-regulated in response to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the adipose tissue of obese mice. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 47944–47949.
Ueki K, Kondo T, Kahn CR . Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1) and SOCS-3 cause insulin resistance through inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins by discrete mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 5434–5446.
Rieusset J, Bouzakri K, Chevillotte E, Ricard N, Jacquet D, Bastard JP et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 expression and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of obese and type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 2004; 53: 2232–2241.
Séron K, Corset L, Vasseur F, Boutin P, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Salvador J et al. Distinct impaired regulation of SOCS3 and long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor in visceral and subcutaneous fat of lean and obese women. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 348: 1232–1238.
Lagathu C, Bastard JP, Auclair M, Maachi M, Capeau J, Caron M . Chronic interleukin-6 (IL-6) treatment increased IL-6 secretion and induced insulin resistance in adipocyte: prevention by rosiglitazone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 311: 372–379.
Mantovani A, Garlanda C, Bottazzi B, Peri G, Doni A, Martinez de la Torre Y et al. The long pentraxin PTX3 in vascular pathology. Vascul Pharmacol 2006; 45: 326–330.
Alberti L, Gilardini L, Zulian A, Micheletto G, Peri G, Doni A et al. Expression of long pentraxin PTX3 in human adipose tissue and its relation with cardiovascular risk factors. Atherosclerosis 2009; 202: 455–460.
Abderrahim-Ferkoune A, Bezy O, Chiellini C, Maffei M, Grimaldi P, Bonino F et al. Characterization of the long pentraxin PTX3 as a TNFα-induced secreted protein of adipose cells. J Lipid Res 2003; 44: 994–1000.
Suliman ME, Yilmaz MI, Carrero JJ, Qureshi AR, Saglam M, Ipcioglu OM et al. Novel links between the long pentraxin 3, endothelial dysfunction, and albuminuria in early and advanced chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2008; 3: 976–985.
Yilmaz MI, Axelsson J, Sonmez A, Carrero JJ, Saglam M, Eyileten T et al. Effect of renin angiotensin system blockade on pentraxin 3 levels in type-2 diabetic patients with proteinuria. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2009; 4: 535–541.
Ye J . Emerging role of adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and insulin resistance. Int J Obesity 2009; 33: 54–66.
Drevon CA . Fatty acids and expression of adipokines. Biochim Biophys Acta 2005; 1740: 287–292.
Berndt J, Kovacs P, Ruschke K, Klöting N, Fasshauer M, Schön MR et al. Fatty acid synthase gene expression in human adipose tissue: association with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007; 50: 1472–1480.
Korczynska J, Stelmanska E, Nogalska A, Szolkiewicz M, Goyke E, Swierczynski J et al. Upregulation of lipogenic enzymes genes expression in white adipose tissue of rats with chronic renal failure is associated with higher level of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1. Metabolism 2004; 53: 1060–1065.
Szolkiewicz M, Nieweglowski T, Korczynska J, Sucajtys E, Stelmanska E, Goyke E et al. Upregulation of fatty acid synthase gene expression in experimental chronic renal failure. Metabolism 2002; 51: 1605–1610.
Looker HC, Krakoff J, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Tanaka S, Nelson RG et al. Adiponectin concentrations are influenced by renal function and diabetes duration in Pima Indians with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 4010–4017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilardini, L., Zulian, A., Girola, A. et al. Predictors of the early impairment of renal disease in human obesity. Int J Obes 34, 287–294 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.227
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.227
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) and type 2 diabetes
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)