Abstract
Objective:
To characterize the expression of the small leucine-rich glycoprotein decorin in adipose tissue.
Design:
Real-time PCR was used to measure decorin gene expression in adipose tissue from normal glucose tolerant (NGT), impaired glucose tolerant and type 2 diabetic (T2D) Psammomys obesus. Adipose tissue was fractionated to determine which cells were responsible for decorin expression. The location of decorin protein expression in adipose tissue was determined using immunohistochemistry. Real-time PCR was used to measure decorin mRNA levels in human adipose tissue from 16 insulin-sensitive, 16 insulin-resistant and 6 T2D human subjects. Circulating plasma decorin concentrations were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 145 NGT and 141 T2D human individuals from a large-scale epidemiological study in Mauritius.
Results:
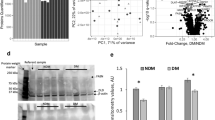
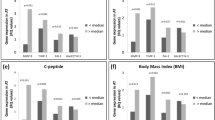
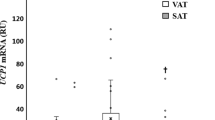
Decorin mRNA was found to be highly expressed in adipose tissue, and decorin gene expression was significantly higher in visceral than that in subcutaneous adipose tissue depots in both P. obesus and human subjects (P=0.002 and P=0.001, respectively). Decorin mRNA was predominantly expressed by stromal/vascular cells of adipose tissue, and decorin protein in adipose tissue was primarily detected adjacent to blood vessels. Circulating plasma decorin levels in humans were elevated by 12% in T2D (P=0.049) compared to NGT subjects. There was a significant independent correlation between plasma decorin levels and waist-to-hip ratio (WHR, P=0.024). In male subjects, plasma decorin levels were significantly correlated with WHR (P=0.006), and fasting and 2-h glucose levels in an oral glucose tolerance test (P=0.027 and P=0.001, respectively).
Conclusions:
Decorin expression in adipose tissue was markedly upregulated in the obese state and may therefore play a role in adipose tissue homeostasis or in pathophysiology associated with obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Rahilly S, Barroso I, Wareham NJ . Genetic factors in type 2 diabetes: the end of the beginning? Science 2005; 307: 370–373.
Taylor SI . Deconstructing type 2 diabetes. Cell 1999; 97: 9–12.
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994; 372: 425–432.
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K . Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999; 402: 656–660.
Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF . A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 26746–26749.
Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K et al. Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science 2005; 307: 426–430.
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2005; 436: 356–362.
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ . The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005; 365: 1415–1428.
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J . Metabolic syndrome—a new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med 2006; 23: 469–480.
Barnett M, Collier GR, Collier FM, Zimmet P, O’Dea K . A cross-sectional and short-term longitudinal characterisation of NIDDM in Psammomys obesus. Diabetologia 1994; 37: 671–676.
Bolton KA, Segal D, McMillan J, Sanigorski A, Todd S, Broz I et al. Identifying differentially expressed secreted novel peptides in diabetic skeletal muscle using a signal sequence trap (Abstract). Diabetologia 2005; 48: A196.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Zimmet P . Globalization, coca-colonization and the chronic disease epidemic: can the Doomsday scenario be averted? J Intern Med 2000; 247: 301–310.
Kopelman PG . Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000; 404: 635–643.
Hishikawa D, Hong YH, Roh SG, Miyahara H, Nishimura Y, Tomimatsu A et al. Identification of genes expressed differentially in subcutaneous and visceral fat of cattle, pig, and mouse. Physiol Genomics 2005; 21: 343–350.
Zhang J, Wright W, Bernlohr DA, Cushman SW, Chen X . Alterations of the classic pathway of complement in adipose tissue of obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007; 292: E1433–E1440.
Klein DJ, Cohen RM, Rymaszewski Z . Proteoglycan synthesis by bovine myocardial endothelial cells is increased by long-term exposure to high concentrations of glucose. J Cell Physiol 1995; 165: 493–502.
Nelimarkka L, Salminen H, Kuopio T, Nikkari S, Ekfors T, Laine J et al. Decorin is produced by capillary endothelial cells in inflammation-associated angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 2001; 158: 345–353.
Cao Y . Angiogenesis modulates adipogenesis and obesity. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2362–2368.
Hausman GJ, Richardson RL . Adipose tissue angiogenesis. J Anim Sci 2004; 82: 925–934.
Ruoslahti E . Structure and biology of proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1988; 4: 229–255.
Rupnick MA, Panigrahy D, Zhang CY, Dallabrida SM, Lowell BB, Langer R et al. Adipose tissue mass can be regulated through the vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 10730–10735.
Schonherr E, O’Connell BC, Schittny J, Robenek H, Fastermann D, Fisher LW et al. Paracrine or virus-mediated induction of decorin expression by endothelial cells contributes to tube formation and prevention of apoptosis in collagen lattices. Eur J Cell Biol 1999; 78: 44–55.
Jarvelainen HT, Iruela-Arispe ML, Kinsella MG, Sandell LJ, Sage EH, Wight TN . Expression of decorin by sprouting bovine aortic endothelial cells exhibiting angiogenesis in vitro. Exp Cell Res 1992; 203: 395–401.
Burke AP, Jarvelainen H, Kolodgie FD, Goel A, Wight TN, Virmani R . Superficial pseudoaneurysms: clinicopathologic aspects and involvement of extracellular matrix proteoglycans. Mod Pathol 2004; 17: 482–488.
Schonherr E, Sunderkotter C, Schaefer L, Thanos S, Grassel S, Oldberg A et al. Decorin deficiency leads to impaired angiogenesis in injured mouse cornea. J Vasc Res 2004; 41: 499–508.
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS . Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1111–1119.
Grant DS, Yenisey C, Rose RW, Tootell M, Santra M, Iozzo RV . Decorin suppresses tumor cell-mediated angiogenesis. Oncogene 2002; 21: 4765–4777.
Sulochana KN, Fan H, Jois S, Subramanian V, Sun F, Kini RM et al. Peptides derived from human decorin leucine-rich repeat 5 inhibit angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 27935–27948.
Kinsella MG, Fischer JW, Mason DP, Wight TN . Retrovirally mediated expression of decorin by macrovascular endothelial cells. Effects on cellular migration and fibronectin fibrillogenesis in vitro. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 13924–13932.
Davies Cde L, Melder RJ, Munn LL, Mouta-Carreira C, Jain RK, Boucher Y . Decorin inhibits endothelial migration and tube-like structure formation: role of thrombospondin-1. Microvasc Res 2001; 62: 26–42.
Nelimarkka L, Kainulainen V, Schonherr E, Moisander S, Jortikka M, Lammi M et al. Expression of small extracellular chondroitin/dermatan sulfate proteoglycans is differentially regulated in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 12730–12737.
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante Jr AW . Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1796–1808.
Curat CA, Miranville A, Sengenes C, Diehl M, Tonus C, Busse R et al. From blood monocytes to adipose tissue-resident macrophages: induction of diapedesis by human mature adipocytes. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1285–1292.
Curat CA, Wegner V, Sengenes C, Miranville A, Tonus C, Busse R et al. Macrophages in human visceral adipose tissue: increased accumulation in obesity and a source of resistin and visfatin. Diabetologia 2006; 49: 744–747.
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1821–1830.
Comalada M, Cardo M, Xaus J, Valledor AF, Lloberas J, Ventura F et al. Decorin reverses the repressive effect of autocrine-produced TGF-beta on mouse macrophage activation. J Immunol 2003; 170: 4450–4456.
Koninger J, Giese NA, Bartel M, di Mola FF, Berberat PO, di Sebastiano P et al. The ECM proteoglycan decorin links desmoplasia and inflammation in chronic pancreatitis. J Clin Pathol 2006; 59: 21–27.
Strazynski M, Eble JA, Kresse H, Schonherr E . Interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-10 induce decorin mRNA in endothelial cells, but interaction with fibrillar collagen is essential for its translation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 21266–21270.
Uhlin-Hansen L, Wik T, Kjellen L, Berg E, Forsdahl F, Kolset SO . Proteoglycan metabolism in normal and inflammatory human macrophages. Blood 1993; 82: 2880–2889.
Xaus J, Comalada M, Cardo M, Valledor AF, Celada A . Decorin inhibits macrophage colony-stimulating factor proliferation of macrophages and enhances cell survival through induction of p27(Kip1) and p21(Waf1). Blood 2001; 98: 2124–2133.
Groeneveld TW, Oroszlan M, Owens RT, Faber-Krol MC, Bakker AC, Arlaud GJ et al. Interactions of the extracellular matrix proteoglycans decorin and biglycan with C1q and collectins. J Immunol 2005; 175: 4715–4723.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Adrian Cooper and Jason Palmer for their valuable technical assistance. This work was financially supported by ChemGenex Pharmaceuticals (Geelong, VIC, Australia). Kristy Bolton is a recipient of a Deakin University postgraduate scholarship. This study was performed in collaboration with the Ministry of Health (Mauritius) and the International Diabetes Institute (Caulfield, Australia). The Mauritius field study was jointly funded by the US National Institutes of Health Grant DK-25446 and the International Diabetes Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Disclosure
PZ is chairman of the scientific advisor board of ChemGenex Pharmaceuticals. KW and GC are employees of ChemGenex Pharmaceuticals.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on International Journal of Obesity website (http://www.nature.com/ijo)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolton, K., Segal, D., McMillan, J. et al. Decorin is a secreted protein associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Obes 32, 1113–1121 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.41
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.41
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The effect of 8 weeks of circuit resistance training on serum levels of decorin and IGF-I in sedentary young men
Sport Sciences for Health (2023)
-
Breast cancer microenvironment and obesity: challenges for therapy
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2022)
-
Absence of the proteoglycan decorin reduces glucose tolerance in overfed male mice
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Adipose tissue loss and lipodystrophy in xylosyltransferase II deficient mice
International Journal of Obesity (2019)
-
Loss of periostin ameliorates adipose tissue inflammation and fibrosis in vivo
Scientific Reports (2018)