Abstract
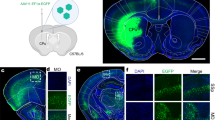
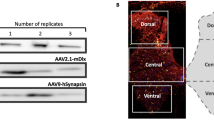
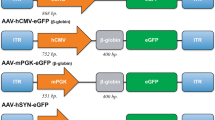
Adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors are one of the most promising gene delivery systems to the central nervous system. We now report, that AAV1 can be used to express transgenes trans-neuronally in neurons distant from the injection site. Specifically, intracortical injection of a bicistronic AAV1 vector trans-neuronally transduced spinal neurons as shown by fluorescence microscopy, the presence of AAV genome and AAV transcript in the contralateral spinal cord. Prior pyramidotomy abolished spinal transduction, confirming anterograde axonal transport of AAV1 in the corticospinal tract. These observations demonstrate the potential of bicistronic AAV1 for trans-neuronal expression of therapeutic transgenes in neurological disorders or reporter genes in connectivity studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Callaway EM . Transneuronal circuit tracing with neurotropic viruses. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2008; 18: 617–623.
Wall NR, Wickersham IR, Cetin A, De La Parra M, Callaway EM . Monosynaptic circuit tracing in vivo through Cre-dependent targeting and complementation of modified rabies virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 21848–21853.
McCown TJ . Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors in the CNS. Curr Gene Ther 2005; 5: 333–338.
Bucher T, Colle MA, Wakeling E, Dubreil L, Fyfe J, Briot-Nivard D et al. scAAV9 intracisternal delivery results in efficient gene transfer to the central nervous system of a feline model of motor neuron disease. Human Gene Ther 2013; 24: 670–682.
Castle MJ, Gershenson ZT, Giles AR, Holzbaur EL, Wolfe JH . Adeno-associated virus serotypes 1, 8, and 9 share conserved mechanisms for anterograde and retrograde axonal transport. Human Gene Ther 2014; 25: 705–720.
Cearley CN, Wolfe JH . A single injection of an adeno-associated virus vector into nuclei with divergent connections results in widespread vector distribution in the brain and global correction of a neurogenetic disease. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 9928–9940.
Ciron C, Cressant A, Roux F, Raoul S, Cherel Y, Hantraye P et al. Human alpha-iduronidase gene transfer mediated by adeno-associated virus types 1, 2, and 5 in the brain of nonhuman primates: vector diffusion and biodistribution. Human Gene Ther 2009; 20: 350–360.
Dodge JC, Haidet AM, Yang W, Passini MA, Hester M, Clarke J et al. Delivery of AAV-IGF-1 to the CNS extends survival in ALS mice through modification of aberrant glial cell activity. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 1056–1064.
Hadaczek P, Mirek H, Bringas J, Cunningham J, Bankiewicz K . Basic fibroblast growth factor enhances transduction, distribution, and axonal transport of adeno-associated virus type 2 vector in rat brain. Human Gene Ther 2004; 15: 469–479.
Kells AP, Hadaczek P, Yin D, Bringas J, Varenika V, Forsayeth J et al. Efficient gene therapy-based method for the delivery of therapeutics to primate cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 2407–2411.
Salegio EA, Samaranch L, Kells AP, Mittermeyer G, San Sebastian W, Zhou S et al. Axonal transport of adeno-associated viral vectors is serotype-dependent. Gene Therapy 2013; 20: 348–352.
Burger C, Nash K, Mandel RJ . Recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors in the nervous system. Human Gene Ther 2005; 16: 781–791.
Cearley CN, Wolfe JH . Transduction characteristics of adeno-associated virus vectors expressing cap serotypes 7, 8, 9, and Rh10 in the mouse brain. Mol Ther 2006; 13: 528–537.
Rabinowitz JE, Rolling F, Li C, Conrath H, Xiao W, Xiao X et al. Cross-packaging of a single adeno-associated virus (AAV) type 2 vector genome into multiple AAV serotypes enables transduction with broad specificity. J Virol 2002; 76: 791–801.
Foust KD, Flotte TR, Reier PJ, Mandel RJ . Recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated global anterograde delivery of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor to the spinal cord: comparison of rubrospinal and corticospinal tracts in the rat. Human Gene Ther 2008; 19: 71–82.
Ciesielska A, Mittermeyer G, Hadaczek P, Kells AP, Forsayeth J, Bankiewicz KS . Anterograde axonal transport of AAV2-GDNF in rat basal ganglia. Mol Ther 2011; 19: 922–927.
Hutson TH, Verhaagen J, Yanez-Munoz RJ, Moon LD . Corticospinal tract transduction: a comparison of seven adeno-associated viral vector serotypes and a non-integrating lentiviral vector. Gene Therapy 2012; 19: 49–60.
Hutson TH, Kathe C, Menezes SC, Rooney MC, Bueler H, Moon LD . The use of an adeno-associated viral vector for efficient bicistronic expression of two genes in the central nervous system. Methods Mol Biol 2014; 1162: 189–207.
Lemon RN . Descending pathways in motor control. Annu Rev Neurosci 2008; 31: 195–218.
Brosamle C, Schwab ME . Cells of origin, course, and termination patterns of the ventral, uncrossed component of the mature rat corticospinal tract. J Comp Neurol 1997; 386: 293–303.
Raineteau O, Fouad K, Bareyre FM, Schwab ME . Reorganization of descending motor tracts in the rat spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci 2002; 16: 1761–1771.
Liang FY, Moret V, Wiesendanger M, Rouiller EM . Corticomotoneuronal connections in the rat: evidence from double-labeling of motoneurons and corticospinal axon arborizations. J Comp Neurol 1991; 311: 356–366.
Smith JB, Alloway KD . Functional specificity of claustrum connections in the rat: interhemispheric communication between specific parts of motor cortex. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 16832–16844.
Briggs F, Usrey WM . Emerging views of corticothalamic function. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2008; 18: 403–407.
Naito A, Kita H . The cortico-nigral projection in the rat: an anterograde tracing study with biotinylated dextran amine. Brain Res 1994; 637: 317–322.
Bareyre FM, Kerschensteiner M, Misgeld T, Sanes JR . Transgenic labeling of the corticospinal tract for monitoring axonal responses to spinal cord injury. Nat Med 2005; 11: 1355–1360.
Kathe C, Hutson TH, Chen Q, Shine HD, McMahon SB, Moon LDF . Unilateral pyramidotomy of the corticospinal tract in rats for assessment of neuroplasticity-inducing therapies. J Vis Exp 2014; (94: 51843.
Wu Z, Miller E, Agbandje-McKenna M, Samulski RJ . Alpha2,3 and alpha2,6 N-linked sialic acids facilitate efficient binding and transduction by adeno-associated virus types 1 and 6. J Virol 2006; 80: 9093–9103.
Neafsey EJ, Bold EL, Haas G, Hurley-Gius KM, Quirk G, Sievert CF et al. The organization of the rat motor cortex: a microstimulation mapping study. Brain Res 1986; 396: 77–96.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the European Research Council under the EU's Seventh Framework Programme (FP/2007–2013) Grant Agreement no. 309731, by the Henry Smith Charity and by a Nathalie Rose Barr PhD studentship from The International Spinal Research Trust which included funding from the Rosetrees Trust. Thanks to Hansruedi Bueler (University of Kentucky, KY, USA) for the psubCMV-2A-WPRE plasmid. We thank the Penn Vector Core at the Gene Therapy Program of the University of Pennsylvania for production of AAVs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutson, T., Kathe, C. & Moon, L. Trans-neuronal transduction of spinal neurons following cortical injection and anterograde axonal transport of a bicistronic AAV1 vector. Gene Ther 23, 231–236 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2015.103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2015.103
This article is cited by
-
Reward and aversion processing by input-defined parallel nucleus accumbens circuits in mice
Nature Communications (2022)
-
NAc-VTA circuit underlies emotional stress-induced anxiety-like behavior in the three-chamber vicarious social defeat stress mouse model
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Transneuronal delivery of hyper-interleukin-6 enables functional recovery after severe spinal cord injury in mice
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Direct evidence for transport of RNA from the mouse brain to the germline and offspring
BMC Biology (2020)