Abstract
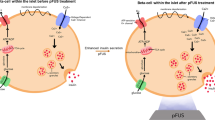
This study uses a novel approach to gene therapy in which plasmid DNA is targeted to the pancreas in vivo using ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD) to achieve islet regeneration. Intravenous microbubbles carrying plasmids are destroyed within the pancreatic microcirculation by ultrasound, achieving local gene expression that is further targeted to β-cells by a modified rat insulin promoter (RIP3.1). A series of genes implicated in endocrine development were delivered to rats 2 days after streptozotocin-induced diabetes. The genes, PAX4, Nkx2.2, Nkx6.1, Ngn3 and Mafa, produced α-cell hyperplasia, but no significant improvement in β-cell mass or blood glucose level 30 days after UTMD. In contrast, RIP3.1-NeuroD1 promoted islet regeneration from surviving β-cells, with normalization of glucose, insulin and C-peptide levels at 30 days. In a longer-term experiment, four of six rats had a return of diabetes at 90 days, accompanied by β-cell apoptosis on Tunel staining. Pretreatment with the JNK inhibitor SP600125 successfully blocked β-cell apoptosis and resulted in restoration of β-cell mass and normalization of blood glucose level for up to 90 days. This technique allows in vivo islet regeneration, restoration of β-cell mass and normalization of blood sugar, insulin and C-peptide in rats without viruses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonner-Weir S, Wier GC . New sources of pancreatic β-cells. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 857–861.
Butler PC, Meier JJ, Butler AE, Bhushan A . The replication of β cells in normal physiology, in disease, and for therapy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2007; 3: 758–768.
Shapiro AMJ, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP et al. International trial of the edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. New Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1318–1330.
Ferber S, Halkin A, Cohen H, Ber I, Einav Y, Goldberg I et al. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 induces expression of insulin genes in liver and ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Nat Med 2000; 6: 568–572.
Kojima H, Fujimiya M, Matsumura K, Younan P, Imaeda H, Maeda M et al. NeuroD-betacellulin gene therapy induces islet neogenesis in the liver and reverses diabetes in mice. Nat Med 2003; 9: 596–603.
Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Miyatsuka T, Matsuoka TA, Matsuhisa M, Hori M et al. PDX-1/VP16 fusion protein, together with NeuroD or Ngn3, markedly induces insulin gene transcription and ameliorates glucose tolerance. Diabetes 2005; 54: 1009–1102.
Wang AY, Ehrhardt A, Xu H, Kay MA . Adenovirus transduction is required for the correction of diabetes using Pdx-1 or Neurogenin-3 in the liver. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 255–263.
Chen S, Ding JH, Bekeredjian R, Yang BZ, Shohet RV, Johnston SA et al. Efficient gene delivery to pancreatic islets with ultrasonic microbubble destruction technology. Proc Natl Acad Sc USA 2006; 103: 8469–8474.
Chai R, Chen S-Y, Ding J-H, Grayburn PA . Efficient, glucose responsive, and islet-specific transgene expression by a modified rat insulin promoter. Gene Ther 2009; 16: 1202–1209.
Chen S, Ding J, Yu C, Yang B, Wood DR, Grayburn PA . Reversal of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats by gene therapy with betacellulin and pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1. Gene Ther 2007; 14: 1102–1110.
Zhou Q, Brown J, Kanarek A, Rajagopal J, Melton DA . In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine cells to β−cells. Nature 2008; 455: 627–632.
Scharfman R . Control of early development of the pancreas in rodents and humans: implications of signals from the mesenchyme. Diabetologia 2000; 43: 1083–1092.
Bouwens L, Rooman I . Regulation of pancreatic beta-cell mass. Physiol Rev 2005; 85: 1255–1270.
Noguchi H, Nakai Y, Ueda M, Masui Y, Futaki S, Kobayashi N et al. Activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway during islet transplantation and prevention of islet graft loss by intraportal injection of JNK inhibitor. Diabetologia 2007; 50: 612–619.
Naya FJ, Stellrecht CM, Tsai MJ . Tissue-specific regulation of the insulin gene by a novel basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. Genes Dev 1995; 9: 1009–1019.
Naya FJ, Huang HP, Qiu Y, Mutoh H, DeMayo FJ, Leiter AB et al. Diabetes, defective pancreatic morphogenesis, and abnormal enteroendocrine differentiation in BETA2/neuroD-deficient mice. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 2323–2334.
Dhawan S, Georgia S, Bhushan A . Formation and regeneration of the endocrine pancreas. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2007; 19: 634–645.
Chao CS, Loomis ZL, Lee JE, Sussel L . Genetic identification of a novel NeuroD1 function in the early differentiation of islet alpha, PP and epsilon cells. Dev Biol 2007; 312: 523–532.
Apelqvist A, Li H, Sommer L, Beatus P, Anderson DJ, Honjo T et al. Notch signalling controls pancreatic cell differentiation. Nature 1999; 400: 877–881.
Grapin-Botton A, Majithia AR, Melton DA . Key events of pancreas formation are triggered in gut endoderm by ectopic expression of pancreatic regulatory genes. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 444–454.
Zhan Y, Brady JL, Johnston AM, Lew AM . Predominate transgene expression in exocrine pancreas directed by the CMV promoter. DNA Cell Biol 2000; 19: 639–645.
Wang AY, Peng PD, Ehrhardt A, Storm TA, Kay MA . Comparison of adenoviral and adeno-associated viral vectors for pancreatic gene delivery in vivo. Hum Gene Ther 2004; 15: 405–413.
Dor Y, Brown J, Martinez OI, Melton DA . Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather than stem cell differentiation. Nature 2004; 429: 41–46.
Teta M, Rankin MM, Long SY, Stein GM, Kushner JA . Growth and regeneration of adult β cells does not involve specialized progenitors. Dev Cell 2007; 12: 817–826.
Meier JJ, Bhushan A, Butler AE, Rizza RA, Butler PC . Sustained beta cell apoptosis in patients with long-standing type I diabetes: indirect evidence for islet regeneration? Diabetologia 2005; 48: 2221–2228.
Dror V, Nguyen V, Walia P, Kalynyak TB, Hill JA, Johnson JD . Notch signaling suppresses apoptosis in adult human and mouse pancreatic islet cells. Diabetologia 2007; 50: 2504–2515.
Drucker DJ . Glucagon-like peptide-1 and the islet beta-cell: augmentation of cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. Endocrinology 2003; 144: 5145–5148.
Lin CY, Gurlo T, Haataja L, Hsueh WA, Butler PC . Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma by rosiglitazone protects human islet cells against human islet amyloid polypeptide toxicity by a phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase-dependent pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 6678–6686.
Nir T, Melton DA, Dor Y . Recovery from diabetes in mice by β cell regeneration. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2553–2561.
Terauchi Y, Takamoto I, Kubota N, Matsui J, Suzuki R, Komeda K et al. Glucokinase and IRS-2 are required for compensatory β cell hyperplasia in response to high-fat diet–induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 246–257.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Mark and Mary Alice Shepherd endowment of the Baylor Foundation, and by NIDDK grant P02 DK58398 (Newgard, PI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Shimoda, M., Wang, MY. et al. Regeneration of pancreatic islets in vivo by ultrasound-targeted gene therapy. Gene Ther 17, 1411–1420 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.85
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.85
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The promising shadow of microbubble over medical sciences: from fighting wide scope of prevalence disease to cancer eradication
Journal of Biomedical Science (2021)
-
In vivo targeted delivery of ANGPTL8 gene for beta cell regeneration in rats
Diabetologia (2015)