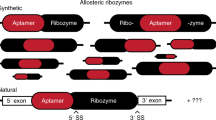
Abstract
In the last two decades, remarkable advances have been made in the development of technologies used to engineer new aptamers and ribozymes. This has encouraged interest among researchers who seek to create new types of gene-control systems that can be made to respond specifically to small-molecule signals. Validation of the fact that RNA molecules can exhibit the characteristics needed to serve as precision genetic switches has come from the discovery of numerous classes of natural ligand-sensing RNAs called riboswitches. Although a great deal of progress has been made toward engineering useful designer riboswitches, considerable advances are needed before the performance characteristics of these RNAs match those of protein systems that have been co-opted to regulate gene expression. In this review, we will evaluate the potential for engineered RNAs to regulate gene expression and lay out possible paths to designer riboswitches based on currently available technologies. Furthermore, we will discuss some technical advances that would empower RNA engineers who seek to make routine the production of designer riboswitches that can function in eukaryotes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gold L, Polisky B, Uhlenbeck O, Yarus M . Diversity of oligonucleotide functions. Annu Rev Biochem 1995; 64: 763–797.
Osborne SE, Ellington AD . Nucleic acid selection and the challenge of combinatorial chemistry. Chem Rev 1997; 97: 349–370.
Wilson DS, Szostak JW . In vitro selection of functional nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biochem 1999; 68: 611–647.
Breaker RR . Engineered allosteric ribozymes as biosensor components. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2002; 13: 31–39.
Silverman SK . Rube Goldberg goes (ribo)nuclear? Molecular switches and sensors made from RNA. RNA 2003; 9: 377–383.
Breaker RR . Natural and engineered nucleic acids as tools to explore biology. Nature 2004; 432: 838–845.
Davidson EA, Ellington AD . Engineering regulatory RNAs. Trends Biotechnol 2005; 23: 109–112.
Isaacs FJ, Dwyer DJ, Collins JJ . RNA synthetic biology. Nat Biotechnol 2006; 24: 545–554.
Bauer G, Suess B . Engineered riboswitches as novel tools in molecular biology. J Biotechnol 2006; 124: 4–11.
Gallivan JP . Toward reprogramming bacteria with small molecules and RNA. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2007; 11: 612–619.
Win MN, Smolke CD . RNA as a versatile and powerful platform for engineering genetic regulatory tools. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 2007; 24: 311–346.
Ellington A . What's so great about RNA? ACS Chem Biol 2007; 2: 445–448.
Doudna JA, Lorsch JR . Ribozyme catalysis: not different, just worse. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2005; 12: 395–402.
Ptashne M, Gann A . Genes & Signals. CSHL Press: Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 2002.
Terpe K . Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2006; 72: 211–222.
Toniatti C, Bujard H, Cortese R, Ciliberto G . Gene therapy progress and prospects: transcription regulatory systems. Gene Therapy 2004; 11: 649–657.
Goverdhana S, Puntel M, Xiong W, Zirger JM, Barcia C, Curtin JF et al. Regulatable gene therapy expression systems for gene therapy applications: progress and future challenges. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 189–211.
Moore I, Samalova M, Kurup S . Transactivated and chemically inducible gene expression in plants. Plant J 2006; 45: 651–683.
Phan TT, Schumann W . Development of a glycine-inducible expression system for Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 2007; 128: 486–499.
Dugas DV, Bartel B . MicroRNA regulation of gene expression in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2004; 7: 512–520.
He L, Hannon GJ . MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 522–531.
Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP . The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008; 455: 64–71.
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N . Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 2008; 455: 58–63.
Rana TM . Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 23–36.
Tang J, Breaker RR . Rational design of allosteric ribozymes. Chem Biol 1997; 4: 453–459.
Soukup GA, Breaker RR . Engineering precision RNA molecular switches. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 3584–3589.
Jaeger L, Chworos A . The architectonics of programmable RNA and DNA nanostructures. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2006; 16: 531–543.
Koizumi M, Soukup GA, Kerr JNQ, Breaker RR . Allosteric selection of ribozymes that respond to the second messengers cGMP and cAMP. Nat Struct Biol 1999; 6: 1062–1071.
Soukup GA, DeRose EC, Koizumi M, Breaker RR . Generating new ligand-binding RNAs by affinity maturation and disintegration of allosteric ribozymes. RNA 2001; 7: 524–536.
Seetharaman S, Zivarts M, Sudarsan N, Breaker RR . Immobilized RNA switches for the analysis of complex chemical and biological mixtures. Nat Biotechnol 2001; 19: 336–341.
Hesselberth JR, Robertson MP, Knudsen SM, Ellington AD . Simultaneous detection of diverse analytes with an aptazyme ligase array. Anal Biochem 2003; 312: 106–112.
Thompson KM, Syrett HA, Knudsen SM, Ellington AD . Group I aptazymes as genetic regulatory switches. BMC Biotechnol 2002; 2: 21–33.
Werstuck G, Green MR . Controlling gene expression in living cells through small molecule-RNA interactions. Science 1998; 282: 296–298.
Grate D, Wilson C . Inducible regulation of the S. cerevisiae cell cycle mediated by an RNA aptamer-ligand complex. Bioorg Med Chem 2001; 9: 2565–2570.
Mandal M, Breaker RR . Gene regulation by riboswitches. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 451–463.
Winkler WC, Breaker RR . Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches. Annu Rev Microbiol 2005; 59: 487–517.
Coppins RL, Hall KB, Groisman EA . The intricate world of riboswitches. Curr Opin Microbiol 2007; 10: 176–181.
Barrick JE, Breaker RR . The distributions, mechanisms, and structures of metabolite-binding riboswitches. Genome Biol 2007; 8: R239.
Nahvi A, Sudarsan N, Ebert MS, Zoy X, Brown KL, Breaker RR . Genetic control by a metabolite binding mRNA. Chem Biol 2002; 9: 1043–1049.
Stoddard CD, Batey RT . Mix-and-match riboswitches. ACS Chem Biol 2006; 1: 751–754.
Breaker RR . Complex riboswitches. Science 2008; 319: 1795–1797.
Sudarsan N, Hammond MC, Block KF, Welz R, Barrick JE, Roth A et al. Tandem riboswitch architectures exhibit complex gene control functions. Science 2006; 314: 300–304.
Welz R, Breaker RR . Ligand binding and gene control characteristics of tandem riboswitches in Bacillus anthracis. RNA 2007; 13: 573–582.
Mandal M, Lee M, Barrick JE, Weinberg Z, Emilsson GM, Ruzzo WL et al. A glycine-dependent riboswitch that uses cooperative binding to control gene expression. Science 2004; 306: 275–279.
Jose AM, Soukup GA, Breaker RR . Cooperative binding of effectors by an allosteric ribozyme. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: 1631–1637.
Yarnell WS, Roberts JW . Mechanism of intrinsic transcription termination and antitermination. Science 1999; 284: 611–615.
Gusarov I, Nudler E . The mechanism of intrinsic transcription termination. Mol Cell 1999; 3: 495–504.
Wickiser JK, Winkler WC, Breaker RR, Crothers DM . The speed of RNA transcription and metabolite binding kinetics operate an FMN riboswitch. Mol Cell 2005; 18: 49–60.
Wickiser JK, Cheah MT, Breaker RR, Crothers DM . The kinetics of ligand binding by an adenine-sensing riboswitch. Biochemistry 2005; 44: 13404–13414.
Nou XW, Kadner RJ . Adenosylcobalamin inhibits ribosome binding to btuB RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 7190–7195.
Winkler W, Nahvi A, Breaker RR . Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. Nature 2002; 419: 952–956.
Fuchs RT, Grundy FJ, Henkin TM . S-adnosylmethionine directly inhibits binding of 30S ribosomal subunits to the SMK box translational riboswitch RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 4876–4880.
Rodionov DA, Vitreschak AG, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS . Comparative genomics of the methionine metabolism in Gram-positive bacteria: a variety of regulatory systems. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: 3340–3353.
Winkler WC, Nahvi A, Roth A, Collins JA, Breaker RR . Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme. Nature 2004; 428: 281–286.
Klein DJ, Ferré-D'Amaré AR . Structural basis of glmS ribozyme activation by glucosamine-6-phosphate. Science 2006; 313: 1752–1756.
Cochrane JC, Lipchock SV, Strobel SA . Structural investigation of the glmS ribozyme bound to its catalytic cofactor. Chem Biol 2007; 14: 97–105.
Collins JA, Irnov I, Baker S, Winkler WC . Mechanism of mRNA destabilization by the glmS ribozyme. Genes Dev 200; 21: 3356–3368.
Mironov AS, Gusarov I, Rafikov R, Lopez LE, Shatalin K, Kreneva RA et al. Sensing small molecules by nascent RNA: a mechanism to control transcription in bacteria. Cell 2002; 111: 747–756.
Sudarsan N, Barrick JE, Breaker RR . Metabolite-binding RNA domains are present in the genes of eukaryotes. RNA 2003; 9: 644–647.
Kubodera T, Watanabe M, Yoshiuchi K, Yamashita N, Nishimura A, Nakai S et al. Thiamine-regulated gene expression of Aspergillus oryzae thiA requires splicing of the intron containing a riboswitch-like domain in the 5′-UTR. FEBS Lett 2003; 555: 516–520.
Cheah MT, Wachter A, Sudarsan N, Breaker RR . Control of alternative RNA splicing and gene expression by eukaryotic riboswitches. Nature 2007; 447: 497–500.
Wachter A, Tunc-Ozdemir M, Grove BC, Green PJ, Shintani DK, Breaker RR . Riboswitch control of gene expression in plants by splicing and alternative 3′ end processing of mRNAs. Plant Cell 2007; 19: 3437–3450.
Bocobza S, Adato A, Mandel T, Shapira M, Nudler E, Aharoni A . Riboswitch-dependent gene regulation and its evolution in the plant kingdom. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 2874–2879.
Croft MT, Moulin M, Webb ME, Smith AG . Thiamine biosynthesis in algae is regulated by riboswitches. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 20770–20775.
Woodson SA . Structure and assembly of group I introns. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2005; 15: 324–330.
Harvey I, Garneau P, Pelletier J . Inhibition of translation by RNA-small molecule interactions. RNA 2002; 8: 452–463.
Buskirk AR, Landrigan A, Liu DR . Engineering a ligand-dependent RNA transcriptional activator. Chem Biol 2004; 11: 1157–1163.
Weigand JE, Sanchez M, Gunnesch EB, Zeiher S, Schroeder R, Suess B . Screening for engineered neomycin riboswitches that control translation initiation. RNA 2008; 14: 89–97.
Weigand JE, Suess B . Tetracycline aptamer-controlled regulation of pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: 4179–4185.
Desai SK, Gallivan JP . Genetic screens and selections for small molecules based on a synthetic riboswitch that activates protein translation. J Am Chem Soc 2004; 126: 13247–13254.
Koizumi M, Soukup GA, Kerr JN, Breaker RR . Allosteric selection of ribozymes that respond to the second messengers cGMP and cAMP. Nat Struct Biol 1999; 6: 1062–1071.
Soukup GA, Emilsson GA, Breaker RR . Altering molecular recognition of RNA aptamers by allosteric selection. J Mol Biol 2000; 298: 623–632.
Zivarts M, Liu Y, Breaker RR . Engineered allosteric ribozymes that respond to specific divalent metal ions. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: 622–631.
Link KH, Guo L, Ames TD, Yen L, Mulligan RC, Breaker RR . Engineering high-speed allosteric hammerhead ribozymes. Biol Chem 2007; 388: 776–786.
Roth A, Breaker RR . Selection in vitro of allosteric ribozymes. Methods Mol Biol 2004; 252: 145–164.
Nutiu R, Li YF . In vitro selection of structure-switching signaling aptamers. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2005; 44: 1061–1065.
Morse DP . Direct selection of RNA beacon aptamers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 359: 94–101.
Suess B, Weigand JE . Engineered riboswitches. RNA Biol 2008; 5: 24–29.
Wieland M, Hartig J . Artificial riboswitches: synthetic mRNA-based regulators of gene expression. Chembiochemistry 2008; 9: 1873–1878.
Sachs AB, Sarnow P, Hentze MW . Starting at the beginning, middle, and end: translation initiation in eukaryotes. Cell 1997; 98: 831–838.
Hanson S, Berthelot K, Fink B, McCarthy JEG, Suess B . Tetracycline-aptamer-mediated translational regulation in yeast. Mol Microbiol 2003; 49: 1627–1637.
Hanson S, Bauer G, Fink B, Suess B . Molecular analysis of a synthetic tetracycline-binding riboswitch. RNA 2005; 11: 503–511.
Kaberdin VR, Bläsi U . Translation initiation and the fate of bacterial mRNAs. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2006; 30: 967–979.
Kim D-S, Gusti V, Pillai SG, Gaur RK . An artificial riboswitch for controlling pre-mRNA splicing. RNA 2005; 11: 1667–1677.
Gusti V, Kim DS, Gaur RK . Sequestering of the 3′ splice site in a theophylline-responsive riboswitch allows ligand-dependent control of alternative splicing. Oligonucleotides 2008; 18: 93–99.
Soukup GA, Breaker RR . Relationship between internucleotide linkage geometry and the stability of RNA. RNA 1999; 5: 1308–1325.
Rieder R, Lang K, Graber D, Micura R . Ligand-induced folding of the adenosine deaminase A-riboswitch and implications on riboswitch translational control. Chembiochemistry 2007; 8: 896–902.
Wang JX, Breaker RR . Riboswitches that sense S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine. Biochem Cell Biol 2008; 86: 157–168.
Tomšič J, McDaniel BA, Grundy FJ, Henkin TM . Natural variability in S-adenoslymethionine (SAM)-dependent riboswitches: S-box elements in Bacillus subtilis exhibit differential sensitivity to SAM in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol 2008; 190: 823–833.
Lynch SA, Desai SK, Sajja HK, Gallivan JP . A high-throughput screen for synthetic riboswitches reveals mechanistic insight into their function. Chem Biol 2007; 14: 173–184.
Topp S, Gallivan JP . Guiding bacteria with small molecules and RNA. J Am Chem Soc 2007; 129: 6807–6811.
Topp S, Gallivan JP . Random walks to synthetic riboswitches—a high-throughput selection based on cell motility. Chembiochemistry 2008; 9: 210–213.
Cochrane JC, Strobel SA . Catalytic strategies of self-cleaving ribozymes. Acc Chem Res 2008; 41: 1027–1035.
Khvorova A, Lescoute A, Westhof E, Jayasena SD . Sequence elements outside the hammerhead ribozyme catalytic core enable intracellular activity. Nat Struct Biol 2003; 10: 708–712.
De la Pena M, Gago S, Flores R . Peripheral regions of natural hammerhead ribozymes greatly increase their self-cleavage activity. EMBO J 2003; 22: 5561–5570.
Shepotinovskaya IV, Uhlenbeck OC . Catalytic diversity of extended hammerhead ribozymes. Biochemistry 2008; 47: 7034–7042.
Yen L, Svendsen J, Lee JS, Gray JT, Magnier M, Baba T et al. Exogenous control of mammalian gene expression through modulation of RNA self-cleavage. Nature 2004; 431: 471–476.
Yen L, Magnier M, Weissleder R, Stockwell BR, Mulligan RC . Identification of inhibitors of ribozyme self-cleavage in mammalian cells via high-throughput screening of chemical libraries. RNA 2006; 12: 797–806.
Martick M, Horan LH, Noller HF, Scott WG . A discontinuous hammerhead ribozyme embedded in a mammalian messenger RNA. Nature 2008; 454: 899–903.
Kertsburg A, Soukup GA . A versatile communication module for controlling RNA folding and catalysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30: 4599–4606.
Hall B, Hesselberth JR, Ellington AD . Computational selection of nucleic acid biosensors via a slip structure model. Biosens Bioelectron 2007; 22: 1939–1947.
Win MN, Smolke CD . A modular and extensible RNA-based gene-regulatory platform for engineering cellular function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 14283–14288.
Win MN, Smolke CD . Higher-order cellular information processing with synthetic RNA devices. Science 2008; 322: 456–460.
Wieland M, Hartig J . Improved aptazyme design and in vivo screening enable riboswitching in bacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2008; 47: 2604–2607.
Topp A, Gallivan JP . Riboswitches in unexpected places—a synthetic riboswitch in a protein coding region. RNA 14: 2498–2503.
Ogawa A, Maeda M . An artificial aptazyme-based riboswitch and its cascading system in E. coli. Chembiochemistry 2008; 9: 206–209.
Ogawa A, Maeda M . Aptazyme-based riboswitches as label-free and detector-free sensors for cofactors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2007; 17: 3156–3160.
Agop-Nersesian C, Pfahler J, Lanzer M, Meissnerr M . Functional expression of ribozymes in Apicomplexa: towards exogenous control of gene expression by inducible RNA-cleavage. Int J Parasitol 2008; 38: 673–681.
An C, Trinh VB, Yokobayashi Y . Artificial control of gene expression in mammalian cells by modulating RNA interference through aptamer-small molecule interaction. RNA 2006; 12: 710–716.
Tuleuova N, An C, Ramanculov E, Revzin A, Yokobayashi Y . Modulating endogenous gene expression of mammalian cells via RNA-small molecule interaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 376: 169–173.
Barrick JE, Sudarsan N, Weinberg Z, Ruzzo WL, Breaker RR . 6S RNA is a widespread regulator of eubacterial RNA polymerase that resembles an open promoter. RNA 2005; 11: 774–784.
Trotochaud AE, Wassarman KM . A highly conserved 6S RNA structure is required for regulation of transcription. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2005; 12: 313–319.
Allen TA, Von Kaenel S, Goodrich JA, Jugel JF . The SINE-encoded mouse B2 RNA represses mRNA transcription in response to heat shock. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2004; 11: 816–821.
Espinosa CA, Allen TA, Hieb AR, Kugel JF, Goodrich JA . B2 RNA binds directly to RNA polymerase II to repress transcript synthesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2004; 11: 822–829.
Barrandon C, Spiluttini B, Bensaude O . Non-coding RNAs regulating the transcriptional machinery. Biol Cell 2008; 100: 83–95.
Gottesman S . Micros for microbes: non-coding regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Trends Genet 2005; 21: 399–404.
Amaral PP, Dinger ME, Mercer TR, Mattick JS . The eukaryotic genome as an RNA machine. Science 2008; 319: 1787–1789.
Buskirk AR, Kehayova PD, Landrigan A, Liu DR . In vivo evolution of an RNA-based transcriptional activator. Chem Biol 2003; 10: 533–540.
Grate D, Wilson C . Laser-mediated, site-specific inactivation of RNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 6131–6136.
Nomura Y, Yokobayashi Y . Reengineering a natural riboswitch by dual genetic selection. J Am Chem Soc 2007; 129: 13814–13815.
Mandal M, Boese B, Barrick JE, Winkler WC, Breaker RR . Riboswitches control fundamental biochemical pathways in Bacillus subtilis and other bacteria. Cell 2003; 113: 577–586.
Mandal M, Breaker RR . Adenine riboswitches and gene activation by disruption of a transcription terminator. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2004; 11: 29–35.
Rentmeister A, Mayer G, Kuhn K, Famulok M . Conformational changes in the expression domain of the Escherichia coli thiM riboswitch. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: 3713–3722.
Canny MD, Jucker FM, Kellogg E, Khvorova A, Jayasena SD, Pardi A . Fast cleavage kinetics of a natural hammerhead ribozyme. J Am Chem Soc 2004; 126: 10848–10849.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Breaker laboratory for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and by grants from the NSF and the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Link, K., Breaker, R. Engineering ligand-responsive gene-control elements: lessons learned from natural riboswitches. Gene Ther 16, 1189–1201 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2009.81
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2009.81
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The case of the missing allosteric ribozymes
Nature Chemical Biology (2021)
-
Aptazyme-embedded guide RNAs enable ligand-responsive genome editing and transcriptional activation
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Twister ribozymes as highly versatile expression platforms for artificial riboswitches
Nature Communications (2016)
-
Riboswitch-mediated Attenuation of Transgene Cytotoxicity Increases Adeno-associated Virus Vector Yields in HEK-293 Cells
Molecular Therapy (2015)
-
Emerging biomedical applications of synthetic biology
Nature Reviews Genetics (2012)