Abstract
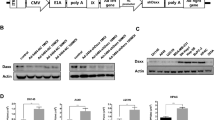
Apollon, a membrane-associated inhibitor of apoptosis protein, protects cells against apoptosis and is upregulated in certain tumor cells. In this study, the effects of Apollon protein knockdown by RNA interference on the growth of human HeLa, HT-1080 and MCF-7 cells in vitro and in vivo were investigated. An oncolytic adenovirus (ZD55) containing the RNA polymerase III-dependent U6 promoter to express short hairpin RNA (shRNA) directed against Apollon (ZD55-siApollon) was constructed. Our data show that ZD55-siApollon successfully exerts a gene knockdown effect and causes the inhibition of tumor cell growth both in culture and in athymic mice in vivo. Cell cycle analysis, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining and western blot analysis reveal that ZD55-siApollon-mediated suppression of Apollon induces apoptosis. Intratumoral injection of ZD55-siApollon significantly inhibits tumor growth in HT-1080 xenograft mice. Furthermore, ZD55-siApollon enhances the antitumor effect of 5-fluorouracil, a chemotherapeutic agent. In conclusion, these results suggest that the depletion of Apollon by oncolytic adenovirus–shRNA delivery system provides a promising method for cancer therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liston P, Roy N, Tamai K, Lefebvre C, Baird S, Cherton-Horvat G et al. Suppression of apoptosis in mammalian cells by NAIP and a related family of IAP genes. Nature 1996; 379: 349–353.
Uren AG, Pakusch M, Hawkins CJ, Puls KL, Vaux DL . Cloning and expression of apoptosis inhibitory protein homologs that function to inhibit apoptosis and/or bind tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 4974–4978.
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC . A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 1997; 3: 917–921.
Duckett CS, Nava VE, Gedrich RW, Clem RJ, Van Dongen JL, Gilfillan MC et al. A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus iap gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors. EMBO J 1996; 15: 2685–2694.
Hay BA, Wassarman DA, Rubin GM . Drosophila homologs of baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis proteins function to block cell death. Cell 1995; 83: 1253–1262.
Hinds MG, Norton RS, Vaux DL, Day CL . Solution structure of a baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) repeat. Nat Struct Biol 1999; 6: 648–651.
Goyal L . Cell death inhibition: keeping caspases in check. Cell 2001; 104: 805–808.
Shi Y . Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell 2002; 9: 459–470.
Vaux DL, Silke J . IAPs, RINGs and ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 287–297.
Verhagen AM, Coulson EJ, Vaux DL . Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins and their relatives: IAPs and other BIRPs. Genome Biol 2001; 2: reviews3009.1–reviews3009.10.
Reed JC, Bischoff JR . BIRinging chromosomes through cell division-and survivin' the experience. Cell 2000; 102: 545–548.
Hauser HP, Bardroff M, Pyrowolakis G, Jentsch S . A giant ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme related to IAP apoptosis inhibitors. J Cell Biol 1998; 141: 1415–1422.
Chen Z, Naito M, Hori S, Mashima T, Yamori T, Tsuruo T . A human IAP-family gene, apollon, expressed in human brain cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 264: 847–854.
Vernooy SY, Chow V, Su J, Verbrugghe K, Yang J, Cole S et al. Drosophila Bruce can potently suppress Rpr- and Grim-dependent but not Hid-dependent cell death. Curr Biol 2002; 12: 1164–1168.
Lotz K, Pyrowolakis G, Jentsch S . BRUCE, a giant E2/E3 ubiquitin ligase and inhibitor of apoptosis protein of the trans-Golgi network, is required for normal placenta development and mouse survival. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 9339–9350.
Bartke T, Pohl C, Pyrowolakis G, Jentsch S . Dual role of BRUCE as an antiapoptotic IAP and a chimeric E2/E3 ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell 2004; 14: 801–811.
Hao Y, Sekine K, Kawabata A, Nakamura H, Ishioka T, Ohata H et al. Apollon ubiquitinates SMAC and caspase-9, and has an essential cytoprotection function. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 849–860.
Qiu XB, Goldberg AL . The membrane-associated inhibitor of apoptosis protein, BRUCE/Apollon, antagonizes both the precursor and mature forms of Smac and caspase-9. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 174–182.
Hannon GJ . RNA interference. Nature 2002; 418: 244–251.
Czauderna F, Santel A, Hinz M, Fechtner M, Durieux B, Fisch G et al. Inducible shRNA expression for application in a prostate cancer mouse model. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: e127.
Paddison PJ, Caudy AA, Bernstein E, Hannon GJ, Conklin DS . Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) induce sequence-specific silencing in mammalian cells. Genes Dev 2002; 16: 948–958.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell 2002; 2: 243–247.
Xia H, Mao Q, Paulson HL, Davidson BL . siRNA-mediated gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 2002; 20: 1006–1010.
Carette JE, Overmeer RM, Schagen FH, Alemany R, Barski OA, Gerritsen WR et al. Conditionally replicating adenoviruses expressing short hairpin RNAs silence the expression of a target gene in cancer cells. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 2663–2667.
Qiu XB, Markant SL, Yuan J, Goldberg AL . Nrdp1-mediated degradation of the gigantic IAP, BRUCE, is a novel pathway for triggering apoptosis. EMBO J 2004; 23: 800–810.
Ren J, Shi M, Liu R, Yang QH, Johnson T, Skarnes WC et al. The Birc6 (Bruce) gene regulates p53 and the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis and is essential for mouse embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 565–570.
O'Shea CC, Johnson L, Bagus B, Choi S, Nicholas C, Shen A et al. Late viral RNA export, rather than p53 inactivation, determines ONYX-015 tumor selectivity. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 611–623.
Liu XY, Qiu SB, Zou WG, Pei ZF, Gu JF, Luo CX et al. Effective gene-virotherapy for complete eradication of tumor mediated by the combination of hTRAIL (TNFSF10) and plasminogen k5. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 531–541.
Zhao L, Gu J, Dong A, Zhang Y, Zhong L, He L et al. Potent antitumor activity of oncolytic adenovirus expressing mda-7/IL-24 for colorectal cancer. Hum Gene Ther 2005; 16: 845–858.
Kretschmer-Kazemi Far R, Sczakiel G . The activity of siRNA in mammalian cells is related to structural target accessibility: a comparison with antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 4417–4424.
Grünweller A, Wyszko E, Bieber B, Jahnel R, Erdmann VA, Kurreck J . Comparison of different antisense strategies in mammalian cells using locked nucleic acids, 2′-O-methyl RNA, phosphorothioates and small interfering RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 3185–3193.
Verma UN, Surabhi RM, Schmaltieg A, Becerra C, Gaynor RB . Small interfering RNAs directed against β-Catenin inhibit the in vitro and in vivo growth of colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 1291–1300.
Li H, Fu X, Chen Y, Hong Y, Tan Y, Cao H et al. Use of adenovirus-delivered siRNA to target oncoprotein p28GANK in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 2029–2041.
Saydam O, Glauser DL, Heid I, Turkeri G, Hilbe M, Jacobs AH et al. Herpes simplex virus 1 amplicon vector-mediated siRNA targeting epidermal growth factor receptor inhibits growth of human glioma cells in vivo. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 803–812.
Sui G, Soohoo C, Affar el B, Gay F, Shi Y, Forrester WC et al. A DNA vector-based RNAi technology to suppress gene expression in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 5515–5520.
Zhang ZL, Zou WG, Luo CX, Li BH, Wang JH, Sun LY et al. An armed oncolytic adenovirus system, ZD55-gene, demonstrating potent antitumoral efficacy. Cell Res 2003; 13: 481–489.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001; 25: 402–408.
Chu L, Gu J, He Z, Xiao T, Liu X . Adenoviral vector expressing CYLD augments antitumor activity of TRAIL by suppression of NF-kappaB survival signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 2006; 5: 615–622.
Pei ZF, Chu L, Zou WG, Zhang ZL, Qiu SB, Qi R et al. An oncolytic adenoviral vector of Smac increases antitumor activity of TRAIL against HCC in human cells and in mice. Hepatology 2004; 39: 1371–1381.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Hi-Tech Research Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2007AA021006); the Key Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KSCX2-YW-R-09); the 973 Project (No. 2004CB518804); Grant 30623003 from National Nature Science Foundation of China and Grant 06DZ22032 from Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality. We thank Yi Shi (Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for his professional technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, L., Gu, J., Sun, L. et al. Oncolytic adenovirus-mediated shRNA against Apollon inhibits tumor cell growth and enhances antitumor effect of 5-fluorouracil. Gene Ther 15, 484–494 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.6
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ki67 targeted strategies for cancer therapy
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2018)
-
BRUCE Protein, New Marker for Targeted Therapy of Gastric Carcinoma
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer (2017)
-
Expression and clinical significance of BIRC6 in human epithelial ovarian cancer
Tumor Biology (2014)
-
BIRC6 (APOLLON) is down-regulated in acute myeloid leukemia and its knockdown attenuates neutrophil differentiation
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2012)
-
Screening siRNAs targeting a novel gene (HA117) and the development of a derivative recombinant adenovirus delivery system
Cancer Gene Therapy (2011)