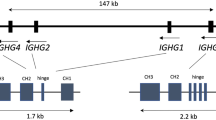
Abstract
The immunoglobulin (IG) loci consist of repeated and highly homologous sets of genes of different types, variable (V), diversity (D) and junction (J), that rearrange in developing B cells to produce an individual’s highly variable repertoire of expressed antibodies, designed to bind to a vast array of pathogens. This repeated structure makes these loci susceptible to a high frequency of insertion and deletion events through evolutionary time, and also makes them difficult to characterize at the genomic level or assay with high-throughput techniques. Given the central role of antibodies in the adaptive immune system, it is not surprising that early candidate gene approaches showed that germline polymorphisms in these regions correlated with susceptibility to both infectious and autoimmune diseases. However, more recent studies, particularly those using high-throughput genome-wide arrays, have failed to implicate these loci in disease. In this review of the IG heavy chain variable gene cluster (IGHV), we examine how poorly we understand the distribution of haplotype variation in this genomic region, and we argue that this lack of information may mask candidate loci in the IGHV gene cluster as causative factors for infectious and autoimmune diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy KM, Travers P, Walport M . Janeway’s Immunobiology 7th edn. Garland Science London, 2007.
Lefranc M-P, Lefranc G . The Immunoglobulin FactsBook. Academic Press London, 2001.
Lefranc M-P, Lefranc G . The T Cell Receptor FactsBook. Academic Press London, 2001.
Tonegawa S . Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 1983; 302: 575–581.
Liu L, Lucas AH . IGH V3-23*01 and its allele V3-23*03 differ in their capacity to form the canonical human antibody combining site specific for the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type B. Immunogenetics 2003; 55: 336–338.
Boyd SD, Gaeta BA, Jackson KJ, Fire AZ, Marshall EL, Merker JD et al. Individual variation in the germline Ig gene repertoire inferred from variable region gene rearrangements. J Immunol 2010; 184: 6986–6992.
Glanville J, Kuo TC, von Budingen HC, Guey L, Berka J, Sundar PD et al. Naive antibody gene-segment frequencies are heritable and unaltered by chronic lymphocyte ablation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 20066–20071.
1000 Genomes Project Consortium A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 2010; 467: 1061–1073.
Matsuda F, Ishii K, Bourvagnet P, Kuma K, Hayashida H, Miyata T et al. The complete nucleotide sequence of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region locus. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 2151–2162.
IMGT. The International ImMunoGeneTics information system: http://www.imgt.org.
Pallarès N, Lefebvre S, Contet V, Matsuda F, Lefranc MP . The human immunoglobulin heavy variable genes. Exp Clin Immunogenet 1999; 16: 36–60.
Ruiz M, Pallarès N, Contet V, Barbi V, Lefranc MP . The human immunoglobulin heavy diversity (IGHD) and joining (IGHJ) segments. Exp Clin Immunogenet 1999; 16: 173–184.
Lefranc MP . Nomenclature of the human immunoglobulin heavy (IGH) genes. Exp Clin Immunogenet 2001; 18: 100–116.
Lefranc MP . Nomenclature of the human immunoglobulin heavy (IGH) genes. In: Current Protocols in Immunology. John Wiley and Sons Hoboken, 2001.
Giudicelli V, Chaume D, Lefranc MP . IMGT/GENE-DB: a comprehensive database for human and mouse immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: D256–D261.
The Immunoglobulin Polymorphism Database: cgi.cse.unsw.edu.au/∼ihmmune/IgPdb/.
Wang Y, Jackson KJ, Gaeta B, Pomat W, Siba P, Sewell WA et al. Genomic screening by 454 pyrosequencing identifies a new human IGHV gene and sixteen other new IGHV allelic variants. Immunogenetics 2011; 63: 259–265.
Romo-Gonzalez T, Morales-Montor J, Rodriguez-Dorantes M, Vargas-Madrazo E . Novel substitution polymorphisms of human immunoglobulin VH genes in Mexicans. Hum Immunol 2005; 66: 732–740.
Lefranc MP, Lefranc G, Rabbitts TH . Inherited deletion of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes in normal human individuals. Nature 1982; 300: 760–762.
Lefranc G, Chaabani H, Van Loghem E, Lefranc MP, De Lange G, Helal AN . Simultaneous absence of the human IgG1, IgG2, IgG4 and IgA1 subclasses: immunological and immunogenetical considerations. Eur J Immunol 1983; 13: 240–244.
Lefranc MP, Lefranc G, de Lange G, Out TA, van den Broek PJ, van Nieuwkoop J et al. Instability of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region locus indicated by different inherited chromosomal deletions. Mol Biol Med 1983; 1: 207–217.
Keyeux G, Lefranc G, Lefranc MP . A multigene deletion in the human IGH constant region locus involves highly homologous hot spots of recombination. Genomics 1989; 5: 431–441.
Lefranc MP, Hammarström L, Smith CI, Lefranc G . Gene deletions in the human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region locus: molecular and immunological analysis. Immunodefic Rev 1991; 2: 265–281.
Wiebe V, Helal A, Lefranc MP, Lefranc G . Molecular analysis of the T17 immunoglobulin CH multigene deletion (del A1-GP-G2-G4-E). Hum Genet 1994; 93: 520–528.
Hammarström L, Ghanem N, Smith CI, Lefranc G, Lefranc MP . RFLP of human immunoglobulin genes. Exp Clin Immunogenet 1990; 7: 7–19.
Chen PP, Yang PM . A segment of human Vh gene locus is duplicated. Scand J Immunol 1990; 31: 593–599.
Sasso EH, Willems van Dijk K, Bull AP, Milner EC . A fetally expressed immunoglobulin VH1 gene belongs to a complex set of alleles. J Clin Invest 1993; 91: 2358–2367.
Shin EK, Matsuda F, Ozaki S, Kumagai S, Olerup O, Ström H et al. Polymorphism of the human immunoglobulin variable region segment V1-4.1. Immunogenetics 1993; 38: 304–306.
Sasso EH, Buckner JH, Suzuki LA . Ethnic differences in VH gene polymorphism. Ann NY Acad Sci 1995; 764: 72–73.
Milner EC, Hufnagle WO, Glas AM, Suzuki I, Alexander C . Polymorphism and utilization of human VH Genes. Ann NY Acad Sci 1995; 764: 50–61.
Walter MA, Surti U, Hofker MH, Cox DW . The physical organization of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain gene complex. EMBO J 1990; 9: 3303–3313.
Shin EK, Matsuda F, Nagaoka H, Fukita Y, Imai T, Yokoyama K et al. Physical map of the 3′ region of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain locus: clustering of autoantibody-related variable segments in one haplotype. EMBO J 1991; 10: 3641–3645.
Walter G, Tomlinson IM, Cook GP, Winter G, Rabbitts TH, Dear PH . HAPPY mapping of a YAC reveals alternative haplotypes in the human immunoglobulin VH locus. Nucleic Acids Res 1993; 21: 4524–4529.
Cook GP, Tomlinson IM, Walter G, Riethman H, Carter NP, Buluwela L et al. A map of the human immunoglobulin VH locus completed by analysis of the telomeric region of chromosome 14q. Nat Genet 1994; 7: 162–168.
Cook GP, Tomlinson IM . The human immunoglobulin VH repertoire. Immunol Today 1995; 16: 237–242.
Cui X, Li H . Determination of gene organization in individual haplotypes by analyzing single DNA fragments from single spermatozoa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 10791–10796.
Pramanik S, Li H . Direct detection of insertion/deletion polymorphisms in an autosomal region by analyzing high-density markers in individual spermatozoa. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1342–1352.
Chimge NO, Pramanik S, Hu G, Lin Y, Gao R, Shen L et al. Determination of gene organization in the human IGHV region on single chromosomes. Genes Immun 2005; 6: 186–193.
Pramanik S, Cui X, Wang HY, Chimge NO, Hu G, Shen L et al. Segmental duplication as one of the driving forces underlying the diversity of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene region. BMC Genomics 2011; 12: 78.
Kidd MJ, Chen Z, Wang Y, Jackson KJ, Zhang LN, Boyd SD et al. The inference of phased haplotypes for the immunoglobulin H chain V region gene loci by analysis of VDJ gene rearrangements. J Immunol 2012; 188: 1333–1340.
Cho CS, Wang X, Zhao Y, Carson DA, Chen PP . Genotyping by PCR-ELISA of a complex polymorphic region that contains one to four copies of six highly homologous human VH3 genes. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 1997; 109: 558–564.
Romo-Gonzalez T, Vargas-Madrazo E . Structural analysis of substitution patterns in alleles of human immunoglobulin VH genes. Mol Immunol 2005; 42: 1085–1097.
Lefranc MP . IMGT unique numbering for the variable (V), constant (C), and groove (G) domains of IG, TR, MH, IgSF, and MhSF. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2011; 2011: 633–642.
Lefranc MP . IMGT Collier de Perles for the variable (V), constant (C), and groove (G) domains of IG, TR, MH, IgSF, and MhSF. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2011; 2011: 643–651.
Ehrenmann F, Lefranc MP . IMGT/3D structure-DB: querying the IMGT database for 3D structures in immunology and immunoinformatics (IG or antibodies, TR, MH, RPI, and FPIA). Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2011; 2011: 750–761.
Scott MG, Crimmins DL, McCourt DW, Zocher I, Thiebe R, Zachau HG et al. Clonal characterization of the human IgG antibody repertoire to Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide. III. A single VKII gene and one of several JK genes are joined by an invariant arginine to form the most common L chain V region. J Immunol 1989; 143: 4110–4116.
Feeney AJ, Atkinson MJ, Cowan MJ, Escuro G, Lugo G . A defective Vkappa A2 allele in Navajos which may play a role in increased susceptibility to Haemophilus influenzae type b disease. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 2277–2282.
Nadel B, Tang A, Lugo G, Love V, Escuro G, Feeney AJ . Decreased frequency of rearrangement due to the synergistic effect of nucleotide changes in the heptamer and nonamer of the recombination signal sequence of the V kappa gene A2b, which is associated with increased susceptibility of Navajos to Haemophilus influenzae type b disease. J Immunol 1998; 161: 6068–6073.
Sasso EH, Johnson T, Kipps TJ . Expression of the immunoglobulin VH gene 51p1 is proportional to its germline gene copy number. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 2074–2080.
Sasso EH, Ghillani P, Musset L, Piette JC, Cacoub P . Effect of 51p1-related gene copy number (V1-69 locus) on production of hepatitis C-associated cryoglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol 2001; 123: 88–93.
Watson CT, Ramagopalan SV, Morrison KM, Ebers GC, Breden F . IGHV4-39 deletion polymorphism does not associate with risk or outcome of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 2010; 225: 164–166.
van Zelm MC, Geertsema C, Nieuwenhuis N, de Ridder D, Conley ME, Schiff CC et al. Gross deletions involving IGHM, BTK, or Artemis: a model for genomic lesions mediated by transposable elements. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 320–332.
Prabakaran P, Chen W, Singarayan MG, Stewart CC, Streaker E, Feng Y et al. Expressed antibody repertoires in human cord blood cells: 454 sequencing and IMGT/HighV-QUEST analysis of germline gene usage, junctional diversity, and somatic mutations. Immunogenetics 2011; 5: 337–350.
Foreman AL, Van de Water J, Gougeon ML, Gershwin ME . B cells in autoimmune diseases: insights from analyses of immunoglobulin variable (Ig V) gene usage. Autoimmun Rev 2007; 6: 387–401.
Scheid JF, Mouquet H, Feldhahn N, Seaman MS, Velinzon K, Pietzsch J et al. Broad diversity of neutralizing antibodies isolated from memory B cells in HIV-infected individuals. Nature 2009; 458: 636–640.
Gorny MK, Wang XH, Williams C, Volsky B, Revesz K, Witover B et al. Preferential use of the VH5-51 gene segment by the human immune response to code for antibodies against the V3 domain of HIV-1. Mol Immunol 2009; 46: 917–926.
Breden F, Lepik C, Longo NS, Montero M, Lipsky PE, Scott JK . Comparison of antibody repertoires produced by HIV-1 infection, other chronic and acute infections, and systemic autoimmune disease. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16857.
Huang CC, Venturi M, Majeed S, Moore MJ, Phogat S, Zhang MY et al. Structural basis of tyrosine sulfation and VH-gene usage in antibodies that recognize the HIV type 1 coreceptor-binding site on gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 2706–2711.
Kashyap AK, Steel J, Oner AF, Dillon MA, Swale RE, Wall KM et al. Combinatorial antibody libraries from survivors of the Turkish H5N1 avian influenza outbreak reveal virus neutralization strategies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 5986–5991.
Throsby M, van den Brink E, Jongeneelen M, Poon LL, Alard P, Cornelissen L et al. Heterosubtypic neutralizing monoclonal antibodies cross-protective against H5N1 and H1N1 recovered from human IgM+ memory B cells. PLoS One 2008; 3: e3942.
Sui J, Hwang WC, Perez S, Wei G, Aird D, Chen LM et al. Structural and functional bases for broad-spectrum neutralization of avian and human influenza A viruses. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2009; 16: 265–273.
Lerner RA . Rare antibodies from combinatorial libraries suggests an S.O.S. component of the human immunological repertoire. Mol Biosyst 2011; 7: 1004–1012.
Sui J, Sheehan J, Hwang WC, Bankston LA, Burchett SK, Huang CY et al. Wide prevalence of heterosubtypic broadly neutralizing human anti-influenza A antibodies. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 52: 1003–1009.
Wrammert J, Koutsonanos D, Li GM, Edupuganti S, Sui J, Morrissey M et al. Broadly cross-reactive antibodies dominate the human B cell response against 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus infection. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 181–193.
Cho ML, Chen PP, Seo YI, Hwang SY, Kim WU, Min DJ et al. Association of homozygous deletion of the Humhv3005 and the VH3-30.3 genes with renal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2003; 12: 400–405.
Olee T, Yang PM, Siminovitch KA, Olsen NJ, Hillson J, Wu J et al. Molecular basis of an autoantibody-associated restriction fragment length polymorphism that confers susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. J Clin Invest 1991; 88: 193–203.
Mo L, Leu SJ, Berry C, Liu F, Olee T, Yang YY et al. The frequency of homozygous deletion of a developmentally regulated Vh gene (Humhv3005) is increased in patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Autoimmunity 1996; 24: 257–263.
Gregersen PK, Olsson LM . Recent advances in the genetics of autoimmune disease. Annu Rev Immunol 2009; 27: 363–391.
Vencovsky J, Zd'arsky E, Moyes SP, Hajeer A, Ruzickova S, Cimburek Z et al. Polymorphism in the immunoglobulin VH gene V1-69 affects susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in subjects lacking the HLA-DRB1 shared epitope. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002; 41: 401–410.
Tsai FJ, Lee YC, Chang JS, Huang LM, Huang FY, Chiu NC et al. Identification of novel susceptibility Loci for kawasaki disease in a Han chinese population by a genome-wide association study. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16853.
Walter MA, Gibson WT, Ebers GC, Cox DW . Susceptibility to multiple sclerosis is associated with the proximal immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region. J Clin Invest 1991; 87: 1266–1273.
Hashimoto LL, Walter MA, Cox DW, Ebers GC . Immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region polymorphisms and multiple sclerosis susceptibility. J Neuroimmunol 1993; 44: 77–83.
Sawcer S, Jones HB, Feakes R, Gray J, Smaldon N, Chataway J et al. A genome screen in multiple sclerosis reveals susceptibility loci on chromosome 6p21 and 17q22. Nat Genet 1996; 13: 464–468.
Feakes R, Chataway J, Sawcer S, Jones HB, Clayton D, Goodfellow PN et al. Susceptibility to multiple sclerosis and the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene cluster. Ann Neurol 1998; 44: 984.
Feakes R, Sawcer S, Smillie B, Chataway J, Broadley S, Compston A . No evidence for the involvement of interleukin 2 or the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene cluster in determining genetic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2000; 68: 679.
Walter MA, Cox DW . Nonuniform linkage disequilibrium within a 1500-kb region of the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain complex. Am J Hum Genet 1991; 49: 917–931.
Terwilliger JD, Hiekkalinna T . An utter refutation of the ‘fundamental theorem of the HapMap’. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 426–437.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
de Bakker PI, Yelensky R, Pe'er I, Gabriel SB, Daly MJ, Altshuler D . Efficiency and power in genetic association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 37: 1217–1223.
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ, Goldstein DB, Hindorff LA, Hunter DJ et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009; 461: 747–753.
Eichler EE, Flint J, Gibson G, Kong A, Leal SM, Moore JH et al. Missing heritability and strategies for finding the underlying causes of complex disease. Nat Rev Genet 2010; 11: 446–450.
Conrad DF, Pinto D, Redon R, Feuk L, Gokcumen O, Zhang Y et al. Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the human genome. Nature 2010; 464: 704–712.
Craddock N, Hurles ME, Cardin N, Pearson RD, Plagnol V, Robson S et al. Genome-wide association study of CNV in 16 000 cases of eight common diseases and 3 000 shared controls. Nature 2010; 464: 713–720.
Kato M, Kawaguchi T, Ishikawa S, Umeda T, Nakamichi R, Shapero MH et al. Population-genetic nature of copy number variations in the human genome. Hum Mol Genet 2010; 19: 761–773.
Campbell CD, Sampas N, Tsalenko A, Sudmant PH, Kidd JM, Malig M et al. Population-genetic properties of differentiated human copy-number polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 317–332.
Levy S, Sutton G, Ng PC, Feuk L, Halpern AL, Walenz BP et al. The diploid genome sequence of an individual human. PLoS Biol 2007; 5: e254.
Axelrod N, Lin Y, Ng PC, Stockwell TB, Crabtree J, Huang J et al. The HuRef Browser: a web resource for individual human genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37 (Database issue) D1018–D1024.
Alkan C, Sajjadian S, Eichler EE . Limitations of next-generation genome sequence assembly. Nat Methods 2011; 8: 61–65.
Tuzun E, Sharp AJ, Bailey JA, Kaul R, Morrison VA, Pertz LM et al. Fine-scale structural variation of the human genome. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 727–732.
Kidd JM, Cooper GM, Donahue WF, Hayden HS, Sampas N, Graves T et al. Mapping and sequencing of structural variation from eight human genomes. Nature 2008; 453: 56–64.
Kidd JM, Sampas N, Antonacci F, Graves T, Fulton R, Hayden HS et al. Characterization of missing human genome sequences and copy-number polymorphic insertions. Nat Methods 2010; 7: 365–371.
Mills RE, Walter K, Stewart C, Handsaker RE, Chen K, Alkan C et al. Mapping copy number variation by population-scale genome sequencing. Nature 2011; 470: 59–65.
Huang DF, Siminovitch KA, Liu XY, Olee T, Olsen NJ, Berry C et al. Population and family studies of three disease-related polymorphic genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 1766–1772.
Veijola R, Knip M, Puukka R, Reijonen H, Cox DW, Ilonen J . The immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: affected-sib-pair analysis and association studies. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 59: 462–470.
Field LL, Larsen Z, Pociot F, Nerup J, Tobias R, Bonnevie-Nielsen V . Evidence for a locus (IDDM16) in the immunoglobulin heavy chain region on chromosome 14q32.3 producing susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. Genes Immun 2002; 3: 338–344.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Bernard Crespi for helpful comments on early drafts of this manuscript, as well as three anonymous reviewers for their many useful suggestions for improvement of our original submission. We would also like to thank Dr Marie-Paule Lefranc, founder and director of IMGT, for ongoing encouragement and support of our continued research efforts in the immunoglobulin regions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watson, C., Breden, F. The immunoglobulin heavy chain locus: genetic variation, missing data, and implications for human disease. Genes Immun 13, 363–373 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2012.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2012.12
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
UniAligner: a parameter-free framework for fast sequence alignment
Nature Methods (2023)
-
Genetic variation in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus shapes the human antibody repertoire
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Enhancer-instructed epigenetic landscape and chromatin compartmentalization dictate a primary antibody repertoire protective against specific bacterial pathogens
Nature Immunology (2023)
-
An efficient urine peptidomics workflow identifies chemically defined dietary gluten peptides from patients with celiac disease
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Enhanced neutralization potency of an identical HIV neutralizing antibody expressed as different isotypes is achieved through genetically distinct mechanisms
Scientific Reports (2022)