Abstract
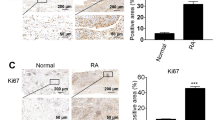
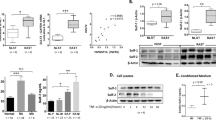
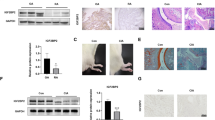
The upregulated expression of thioredoxin domain-containing protein 5 (TXNDC5) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in patients and model mice. However, the underlying mechanism by which TXNDC5 influences the pathological activation of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RASFs) remains unknown. In this study, we show that TXNDC5 expression in RASFs and their cytokine production are significantly upregulated in response to LPS, TNF-α and IL-6, but suppressed by transfection with TXNDC5-siRNA. TXNDC5 is further validated as the direct target of NF-κB signaling. Mechanistically, TXNDC5 directly interacts with heat shock cognate 70 protein (HSC70) to sequester it in the cytoplasm, and HSC70 silencing exerts the same effects as TXNDC5 on the biological activity of RASFs (for example, decreased cell viability, invasion and cytokine production). Furthermore, HSC70 activates NF-κB signaling by destabilizing IκBβ protein in the absence of LPS or facilitating its nuclear translocation in the presence of LPS. Importantly, TXNDC5 can also regulate the activity of NF-κB signaling in a HSC70-IκBβ-dependent manner. Taken together, by linking HSC70 and NF-κB signaling, TXNDC5 plays a pro-inflammatory role in RASFs, highlighting a potential approach to treat RA by blocking the TXNDC5/HSC70 interaction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lafeber FP, Van der Laan WH. Progression of joint damage despite control of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: a role for cartilage damage driven synovial fibroblast activity. Ann Rheum Dis 2012; 71: 793–795.
Chen X, Oppenheim JJ, Howard OM. Chemokines and chemokine receptors as novel therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): inhibitory effects of traditional Chinese medicinal components. Cell Mol Immunol 2004; 1: 336–342.
Brentano F, Kyburz D, Gay S. Toll-like receptors and rheumatoid arthritis. Methods Mol Biol 2009; 517: 329–343.
Horna-Terron E, Pradilla-Dieste A, Sanchez-de-Diego C, Osada J. TXNDC5, a newly discovered disulfide isomerase with a key role in cell physiology and pathology. Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 23501–23518.
Chang X, Cui Y, Zong M, Zhao Y, Yan X, Chen Y et al. Identification of proteins with increased expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues. J Rheumatol 2009; 36: 872–880.
Chang X, Zhao Y, Yan X, Pan J, Fang K, Wang L. Investigating a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2011; 13: R124.
Wang L, Zheng Y, Xu H, Yan X, Chang X. Investigate pathogenic mechanism of TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e53301.
Wang L, Song G, Zheng Y, Wang D, Dong H, Pan J et al. miR-573 is a negative regulator in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol Immunol 2016; 13: 839–849.
Sullivan DC, Huminiecki L, Moore JW, Boyle JJ, Poulsom R, Creamer D et al. EndoPDI, a novel protein-disulfide isomerase-like protein that is preferentially expressed in endothelial cells acts as a stress survival factor. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 47079–47088.
Wang L, Song G, Chang X, Tan W, Pan J, Zhu X et al. The role of TXNDC5 in castration-resistant prostate cancer-involvement of androgen receptor signaling pathway. Oncogene 2015; 34: 4735–4745.
Wang L, Song G, Zheng Y, Tan W, Pan J, Zhao Y et al. Expression of Semaphorin 4A and its potential role in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2015; 17: 227.
Siebert S, Tsoukas A, Robertson J, McInnes I. Cytokines as therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Rev 2015; 67: 280–309.
Gay NJ, Gangloff M. Structure and function of Toll receptors and their ligands. Annu Rev Biochem 2007; 76: 141–165.
Liu Y, Yin H, Zhao M, Lu Q. TLR2 and TLR4 in autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2014; 47: 136–147.
Fang H, Ang B, Xu X, Huang X, Wu Y, Sun Y et al. TLR4 is essential for dendritic cell activation and anti-tumor T-cell response enhancement by DAMPs released from chemically stressed cancer cells. Cell Mol Immunol 2014; 11: 150–159.
Hendrayani SF, Al-Harbi B, Al-Ansari MM, Silva G, Aboussekhra A. The inflammatory/cancer-related IL-6/STAT3/NF-κB positive feedback loop includes AUF1 and maintains the active state of breast myofibroblasts. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 41974–41985.
De Simone V, Franzè E, Ronchetti G, Colantoni A, Fantini MC, Di Fusco D et al. Th17-type cytokines, IL-6 and TNF-α synergistically activate STAT3 and NF-kB to promote colorectal cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2015; 34: 3493–3503.
Liu T, Daniels CK, Cao S. Comprehensive review on the HSC70 functions, interactions with related molecules and involvement in clinical diseases and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther 2012; 136: 354–374.
Schick C, Arbogast M, Lowka K, Rzepka R, Melchers I. Continuous enhanced expression of Hsc70 but not Hsp70 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: 88–93.
Fujihara SM, Cleaveland JS, Grosmaire LS, Berry KK, Kennedy KA, Blake JJ et al. A D-amino acid peptide inhibitor of NF-kappa B nuclear localization is efficacious in models of inflammatory disease. J Immunol 2000; 165: 1004–1012.
Pallangyo CK, Ziegler PK, Greten FR. IKKbeta acts as a tumor suppressor in cancer-associated fibroblasts during intestinal tumorigenesis. J Exp Med 2015; 212: 2253–2266.
Rao P, Hayden MS, Long M, Scott ML, West AP, Zhang D et al. IkappaBbeta acts to inhibit and activate gene expression during the inflammatory response. Nature 2010; 466: 1115–1119.
Suyang H, Phillips R, Douglas I, Ghosh S. Role of unphosphorylated, newly synthesized I kappa B beta in persistent activation of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 5444–5449.
Wang Y, Ren F, Wang Y, Feng Y, Wang D, Jia B et al. CHIP/Stub1 functions as a tumor suppressor and represses NF-kappaB-mediated signaling in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2014; 35: 983–991.
Dastoor Z, Dreyer J. Nuclear translocation and aggregate formation of heat shock cognate protein 70 (Hsc70) in oxidative stress and apoptosis. J Cell Sci 2000; 113: 2845–2854.
Ospelt C, Kyburz D, Pierer M, Seibl R, Kurowska M, Distler O et al. Toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis joint destruction mediated by two distinct pathways. Ann Rheum Dis 2004; 63 (Suppl 2): ii90–ii91.
Zhang Y, Wang L, Bai L, Jiang R, Guo L, Wu J et al. Effect of ebosin on modulating interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory responses in rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cell MolImmunol 2016; 13: 584–592.
Adami G, Orsolini G, Adami S, Viapiana O, Idolazzi L, Gatti D et al. Effects of TNF inhibitors on parathyroid hormone and Wnt signaling antagonists in rheumatoid arthritis. Calcif Tissue Int 2016; 99: 360–364.
Sondermann H, Becker T, Mayhew M, Wieland F, Hartl FU. Characterization of a receptor for heat shock protein 70 on macrophages and monocytes. J Biol Chem 2000; 381: 1165–1174.
Imamura Y, Fujigaki Y, Oomori Y, Usui S, Wang PL. Cooperation of salivary protein histatin 3 with heat shock cognate protein 70 relative to the G1/S transition in human gingival fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 14316–14325.
Zabel U, Baeuerle PA. Purified human I kappa B can rapidly dissociate the complex of the NF-kappa B transcription factor with its cognate DNA. Cell 1990; 61: 255–265.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81572254), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M600541), the Key Research and Development Project of Shandong (2016GSF201166), the Shandong Taishan Scholarship (No. tsqn20161076) and the Innovation Project of Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Dong, H., Song, G. et al. TXNDC5 synergizes with HSC70 to exacerbate the inflammatory phenotype of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis through NF-κB signaling. Cell Mol Immunol 15, 685–696 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.20
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.20
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Transcriptomic Analyses of Neurotoxic Astrocytes Derived from Adult Triple Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Mice
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2023)
-
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases
European Journal of Medical Research (2022)
-
The novel role of ER protein TXNDC5 in the pathogenesis of organ fibrosis: mechanistic insights and therapeutic implications
Journal of Biomedical Science (2022)
-
Inhibition of TXNDC5 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced septic shock by altering inflammatory responses
Laboratory Investigation (2022)
-
CircOAS3 Regulates Keratinocyte Proliferation and Psoriatic Inflammation by Interacting with Hsc70 via the JNK/STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Inflammation (2022)