Abstract
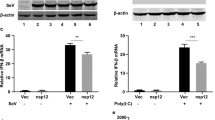
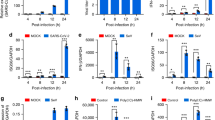
Non-structural protein 1 (NS1) is an important virulence factor of the highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus. A five-amino-acid (5 aa) deletion at position 80–84 and an aspartic acid to glutamic acid substitution at position 92 (D92E) are two major NS1 mutations that are highly correlated with enhanced virulence. To investigate the effect of these mutations in H5N1 virulence, three H5N1-NS1 variants were constructed: NS51 (lacking 5 aa at position 80–84), NS51(I) (carrying a 5-aa insertion at position 80–84) and NS51(IM) (carrying both the 5-aa insertion and the D92E mutation). We examined the effects of these mutations on interferon (IFN) induction, tumor-necrosis factor (TNF)α response, p53 activity and apoptosis. We found that the D92E mutation eliminated NS1's repressive effect on IFN induction, while the 5-aa deletion resulted in enhanced resistance to TNFα responses. We also observed that all three variants exhibited a similar suppressive effect on p53 transcriptional activity, although none of them significantly influenced apoptosis of host cells. Our findings shed new light on the role of NS1 in the pathogenicity of H5N1 virus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hale BG, Randall RE, Ortin J, Jackson D . The multifunctional NS1 protein of influenza A viruses. J Gen Virol 2008; 89: 2359–2376.
Li KS, Guan Y, Wang J, Smith GJ, Xu KM, Duan L et al. Genesis of a highly pathogenic and potentially pandemic H5N1 influenza virus in eastern Asia. Nature 2004; 430: 209–213.
Guan Y, Poon LL, Cheung CY, Ellis TM, Lim W, Lipatov AS et al. H5N1 influenza: a protean pandemic threat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 8156–8161.
Lipatov AS, Andreansky S, Webby RJ, Hulse DJ, Rehg JE, Krauss S et al. Pathogenesis of Hong Kong H5N1 influenza virus NS gene reassortants in mice: the role of cytokines and B- and T-cell responses. J Gen Virol 2005; 86: 1121–1130.
Zhou H, Jin M, Chen H, Huag Q, Yu Z . Genome-sequence analysis of the pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza A virus isolated in China in 2004. Virus Genes 2006; 32: 85–95.
Zhu Q, Yang H, Chen W, Cao W, Zhong G, Jiao P et al. A naturally occurring deletion in its NS gene contributes to the attenuation of an H5N1 swine influenza virus in chickens. J Virol 2008; 82: 220–228.
Bornholdt ZA, Prasad BV . X-ray structure of NS1 from a highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus. Nature 2008; 456: 985–988.
Garten RJ, Davis CT, Russell CA, Shu B, Lindstrom S, Balish A et al. Antigenic and genetic characteristics of swine-origin 2009 A(H1N1) influenza viruses circulating in humans. Science 2009; 325: 197–201.
Long JX, Peng DX, Liu YL, Wu YT, Liu XF . Virulence of H5N1 avian influenza virus enhanced by a 15-nucleotide deletion in the viral nonstructural gene. Virus Genes 2008; 36: 471–478.
Jiao P, Tian G, Li Y, Deng G, Jiang Y, Liu C et al. A single-amino-acid substitution in the NS1 protein changes the pathogenicity of H5N1 avian influenza viruses in mice. J Virol 2008; 82: 1146–1154.
Li Z, Jiang Y, Jiao P, Wang A, Zhao F, Tian G et al. The NS1 gene contributes to the virulence of H5N1 avian influenza viruses. J Virol 2006; 80: 11115–11123.
Donelan NR, Basler CF, Garcia-Sastre A . A recombinant influenza A virus expressing an RNA-binding-defective NS1 protein induces high levels of beta interferon and is attenuated in mice. J Virol 2003; 77: 13257–13266.
Seo SH, Hoffmann E, Webster RG . Lethal H5N1 influenza viruses escape host anti-viral cytokine responses. Nat Med 2002; 8: 950–954.
Twu KY, Kuo RL, Marklund J, Krug RM . The H5N1 influenza virus NS genes selected after 1998 enhance virus replication in mammalian cells. J Virol 2007; 81: 8112–8121.
Seo SH, Hoffmann E, Webster RG . The NS1 gene of H5N1 influenza viruses circumvents the host anti-viral cytokine responses. Virus Res 2004; 103: 107–113.
Heikkinen LS, Kazlauskas A, Melén K, Wagner R, Ziegler T, Julkunen I et al. Avian and 1918 Spanish influenza a virus NS1 proteins bind to Crk/CrkL Src homology 3 domains to activate host cell signaling. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 5719–5727.
Li W, Wang G, Zhang H, Zhang D, Zeng J, Chen X et al. Differential suppressive effect of promyelocytic leukemia protein on the replication of different subtypes/strains of influenza A virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 389: 84–89.
Turpin E, Luke K, Jones J, Tumpey T, Konan K, Schultz-Cherry S . Influenza virus infection increases p53 activity: role of p53 in cell death and viral replication. J Virol 2005; 79: 8802–8811.
Takaoka A, Hayakawa S, Yanai H, Stoiber D, Negishi H, Kikuchi H et al. Integration of interferon-alpha/beta signalling to p53 responses in tumour suppression and antiviral defence. Nature 2003; 424: 516–523.
Yeung MC, Lau AS . Tumor suppressor p53 as a component of the tumor necrosis factor-induced, protein kinase PKR-mediated apoptotic pathway in human promonocytic U937 cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 25198–25202.
Cheng Y, Qiu F, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T . ERK and JNK mediate TNFalpha-induced p53 activation in apoptotic and autophagic L929 cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 376: 483–488.
Schultz-Cherry S, Dybdahl-Sissoko N, Neumann G, Kawaoka Y, Hinshaw VS . Influenza virus ns1 protein induces apoptosis in cultured cells. J Virol 2001; 75: 7875–7881.
Lam WY, Tang JW, Yeung AC, Chiu LC, Sung JJ, Chan PK . Avian influenza virus A/HK/483/97(H5N1) NS1 protein induces apoptosis in human airway epithelial cells. J Virol 2008; 82: 2741–2751.
Ehrhardt C, Wolff T, Pleschka S, Planz O, Beermann W, Bode JG et al. Influenza A virus NS1 protein activates the PI3K/Akt pathway to mediate antiapoptotic signaling responses. J Virol 2007; 81: 3058–3067.
Hayman A, Comely S, Lackenby A, Hartgroves LC, Goodbourn S, McCauley JW et al. NS1 proteins of avian influenza A viruses can act as antagonists of the human alpha/beta interferon response. J Virol 2007; 81: 2318–2327.
Kim MO, Suh HS, Brosnan CF, Lee SC . Regulation of RANTES/CCL5 expression in human astrocytes by interleukin-1 and interferon-beta. J Neurochem 2004; 90: 297–308.
Rani MR, Shrock J, Appachi S, Rudick RA, Williams BR, Ransohoff RM . Novel interferon-beta-induced gene expression in peripheral blood cells. J Leukoc Biol 2007; 82: 1353–1360.
Rudick RA, Ransohoff RM, Peppler R, VanderBrug Medendorp S, Lehmann P, Alam J . Interferon beta induces interleukin-10 expression: relevance to multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 1996; 40: 618–627.
Cheung CY, Poon LL, Lau AS, Luk W, Lau YL, Shortridge KF et al. Induction of proinflammatory cytokines in human macrophages by influenza A (H5N1) viruses: a mechanism for the unusual severity of human disease? Lancet 2002; 360: 1831–1837.
Wang G, Zhang J, Li W, Xin G, Su Y, Gao Y et al. Apoptosis and proinflammatory cytokine responses of primary mouse microglia and astrocytes induced by human H1N1 and avian H5N1 influenza viruses. Cell Mol Immunol 2008; 5: 113–120.
Seo SH, Webster RG . Tumor necrosis factor alpha exerts powerful anti-influenza virus effects in lung epithelial cells. J Virol 2002; 76: 1071–1076.
Shen Y, Wang X, Guo L, Qiu Y, Li X, Yu H et al. Influenza A virus induces p53 accumulation in a biphasic pattern. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 382: 331–335.
Zhirnov OP, Klenk HD . Control of apoptosis in influenza virus-infected cells by up-regulation of Akt and p53 signaling. Apoptosis 2007; 12: 1419–1432.
Vijaya Lakshmi AN, Ramana MV, Vijayashree B, Ahuja YR, Sharma G . Detection of influenza virus induced DNA damage by comet assay. Mutat Res 1999; 442: 53–58.
Appella E, Anderson CW . Post-translational modifications and activation of p53 by genotoxic stresses. Eur J Biochem 2001; 268: 2764–2772.
Talon J, Salvatore M, O'Neill RE, Nakaya Y, Zheng H, Muster T et al. Influenza A and B viruses expressing altered NS1 proteins: a vaccine approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 4309–4314.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr William Ba-Thein for helpful discussion and editing of the manuscript. We thank Dr Xu Liyan for the use of a TD20/20 luminometer. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30771988and No. 30972766), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20094402110004), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (No. 8151503102000022 and 9451503102003499), Outstanding Young Scientists Foundation of Guangdong Province Education Department (No. LYM08056), State Key Lab of Agriculture Microbiology Open Foundation (No. AML200910) and Shantou University Medical College Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Wang, G., Zhang, H. et al. Effects of NS1 variants of H5N1 influenza virus on interferon induction, TNFα response and p53 activity. Cell Mol Immunol 7, 235–242 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.6
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of NS1 domains of avian H5N1 influenza virus which influence the interaction with the NOLC1 protein
Virus Genes (2015)
-
An overview of the highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus
Virologica Sinica (2013)
-
Inability of NS1 protein from an H5N1 influenza virus to activate PI3K/Akt signaling pathway correlates to the enhanced virus replication upon PI3K inhibition
Veterinary Research (2012)
-
Variability among the neuraminidase, non-structural 1 and PB1-F2 proteins in the influenza A virus genome
Virus Genes (2012)
-
Cellular transcriptional profiling in human lung epithelial cells infected by different subtypes of influenza A viruses reveals an overall down-regulation of the host p53 pathway
Virology Journal (2011)