Abstract
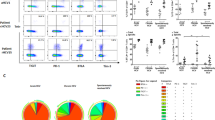
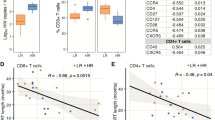
It was previously reported that several kinds of intercellular adhesion molecules are closely related to chronic HBV infection. The complex of CD2 and CD58 plays an important role in enhancing the adhesion of T lymphocytes to target cells, and promoting hyperplasia and activation of T lymphocytes. In this study, we detected the level of CD2 expressed on the surface of PBMC, the expression level of CD2 mRNA in PBMC and the percentage of CD2 positive cells in PBMC of patients with chronic HBV infection and compared them with the expression level of normal controls. We also determined the level of serum HBV DNA from patients with chronic HBV infection and from normal controls. The clinical characteristics of hepatic function were tested as well. The results showed that the expression of CD2 significantly increased with the severity of chronic HBV infection, which suggested that CD2 might contribute to the hepatocyte damage in chronic HBV infection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Qi, B., Chen, P. et al. The Expression of CD2 in Chronic HBV Infection. Cell Mol Immunol 5, 69–73 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2008.9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2008.9