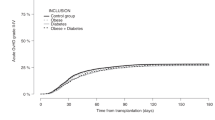
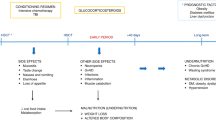
Abstract
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) recipients frequently develop glucose intolerance and post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM). The clinical importance of PTDM and its detrimental impact on HSCT outcomes are under-recognized. After allo-HSCT, various mechanisms can contribute to the development of PTDM. Here we review information about hyperglycemia and PTDM after allo-HSCT as well as PTDM after solid organ transplantation and describe ways to manage hyperglycemia/PTDM after allogeneic HSCT. Taking into consideration a lack of well-established evidence in the field of allo-HSCT, more studies should be conducted in the future, which will require closer multidisciplinary collaboration between hematologists, endocrinologists and nutritionists.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Majhail NS, Rizzo JD, Lee SJ, Aljurf M, Atsuta Y, Bonfim C et al. Recommended screening and preventive practices for long-term survivors after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 348–371.
Fuji S, Einsele H, Savani BN, Kapp M . Systematic nutritional support in allogeneic HSCT recipients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015; 21: 1707–1713.
Geiss LS, Wang J, Cheng YJ, Thompson TJ, Barker L, Li Y et al. Prevalence and incidence trends for diagnosed diabetes among adults aged 20 to 79 years, United States, 1980-2012. JAMA 2014; 312: 1218–1226.
Dabelea D, Mayer-Davis EJ, Saydah S, Imperatore G, Linder B, Divers J et al. Prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents from 2001 to 2009. JAMA 2014; 311: 1778–1786.
Jenssen T, Hartmann A . Emerging treatments for post-transplantation diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Nephrol 2015; 11: 465–477.
Sharif A . Treatment options for post-transplantation diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev 2015; 11: 155–162.
Vincenti F, Friman S, Scheuermann E, Rostaing L, Jenssen T, Campistol JM et al. Results of an international, randomized trial comparing glucose metabolism disorders and outcome with cyclosporine versus tacrolimus. Am J Transplant 2007; 7: 1506–1514.
Webster AC, Woodroffe RC, Taylor RS, Chapman JR, Craig JC . Tacrolimus versus ciclosporin as primary immunosuppression for kidney transplant recipients: meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomised trial data. BMJ 2005; 331: 810.
Angelopoulos TP, Tentolouris NK, Bertsias GK, Boumpas DT . Steroid-induced diabetes in rheumatologic patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2014; 32: 126–130.
Magee MH, Blum RA, Lates CD, Jusko WJ . Prednisolone pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in relation to sex and race. J Clin Pharmacol 2001; 41: 1180–1194.
Toth GG, Kloosterman C, Uges DR, Jonkman MF . Pharmacokinetics of high-dose oral and intravenous dexamethasone. Ther Drug Monit 1999; 21: 532–535.
Majhail NS, Challa TR, Mulrooney DA, Baker KS, Burns LJ . Hypertension and diabetes mellitus in adult and pediatric survivors of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1100–1107.
Paris C, Yates L, Lama P, Zepeda AJ, Gutierrez D, Palma J . Evaluation of metabolic syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children and adolescents. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2012; 59: 306–310.
Majhail NS, Flowers ME, Ness KK, Jagasia M, Carpenter PA, Arora M et al. High prevalence of metabolic syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 43: 49–54.
Taskinen M, Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Hovi L, Lipsanen-Nyman M . Impaired glucose tolerance and dyslipidaemia as late effects after bone-marrow transplantation in childhood. Lancet 2000; 356: 993–997.
Bizzarri C, Pinto RM, Ciccone S, Brescia LP, Locatelli F, Cappa M . Early and progressive insulin resistance in young, non-obese cancer survivors treated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2015; 62: 1650–1655.
Hirabayashi K, Nakazawa Y, Matsuura H, Hara Y, Kurata T, Hirabayashi K et al. Risk factors for diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients with hematological malignancies. Int J Hematol 2014; 99: 477–486.
Baker KS, Chow E, Goodman P, Koves I, Leisenring W, Hoffmeister P et al. Adverse impact of hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) on body composition and insulin resistance (IR) is associated with increased cardiovascular risk. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: S174–S175.
Baker KS, Chow E, Steinberger J . Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk in survivors after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 619–625.
Neville KA, Cohn RJ, Steinbeck KS, Johnston K, Walker JL . Hyperinsulinemia, impaired glucose tolerance, and diabetes mellitus in survivors of childhood cancer: prevalence and risk factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 4401–4407.
Pham TM, Ekwaru JP, Setayeshgar S, Veugelers PJ . The effect of changing serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations on metabolic syndrome: a longitudinal analysis of participants of a preventive health program. Nutrients 2015; 7: 7271–7284.
Joseph RW, Alousi A, Konda B, Komanduri K, Neumann J, Trevino C et al. High incidence of vitamin D deficiency in patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol 2011; 86: 954–956.
Robien K, Strayer LG, Majhail N, Lazovich D, Baker KS, Smith AR et al. Vitamin D status among long-term survivors of hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 1472–1479.
Benrashid M, Moyers K, Mohty M, Savani BN . Vitamin D deficiency, autoimmunity, and graft-versus-host-disease risk: Implication for preventive therapy. Exp Hematol 2012; 40: 263–267.
Henden AS, Hill GR . Cytokines in graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol 2015; 194: 4604–4612.
DiCarlo J, Agarwal-Hashmi R, Shah A, Kim P, Craveiro L, Killen R et al. Cytokine and chemokine patterns across 100 days after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 361–369.
Airaghi L, Usardi P, Forti S, Orsatti A, Baldini M, Annaloro C et al. A comparison between metabolic syndrome post-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and spontaneously occurring metabolic syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest 2011; 34: e6–11.
Chow EJ, Simmons JH, Roth CL, Baker KS, Hoffmeister PA, Sanders JE et al. Increased cardiometabolic traits in pediatric survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with total body irradiation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 1674–1681.
Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998; 352: 837–853.
Sharif A, Hecking M, de Vries AP, Porrini E, Hornum M, Rasoul-Rockenschaub S et al. Proceedings from an international consensus meeting on posttransplantation diabetes mellitus: recommendations and future directions. Am J Transplant 2014; 14: 1992–2000.
Ghisdal L, Van Laecke S, Abramowicz MJ, Vanholder R, Abramowicz D . New-onset diabetes after renal transplantation: risk assessment and management. Diabetes Care 2012; 35: 181–188.
Sharif A, Moore RH, Baboolal K . The use of oral glucose tolerance tests to risk stratify for new-onset diabetes after transplantation: An underdiagnosed phenomenon. Transplantation 2006; 82: 1667–1672.
Dagogo-Jack S . Pitfalls in the use of HbA(1)(c) as a diagnostic test: the ethnic conundrum. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2010; 6: 589–593.
Healy SJ, Dungan KM . Hyperglycemia in patients with hematologic malignancies. Curr Diab Rep 2015; 15: 8.
Koh GC, Peacock SJ, van der Poll T, Wiersinga WJ . The impact of diabetes on the pathogenesis of sepsis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2012; 31: 379–388.
Seshasai SR, Kaptoge S, Thompson A, Di Angelantonio E, Gao P, Sarwar N et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 829–841.
Kornum JB, Thomsen RW, Riis A, Lervang HH, Schonheyder HC, Sorensen HT . Diabetes, glycemic control, and risk of hospitalization with pneumonia: a population-based case-control study. Diabetes Care 2008; 31: 1541–1545.
Bertoni AG, Saydah S, Brancati FL . Diabetes and the risk of infection-related mortality in the U.S. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 1044–1049.
Wolfe F, Caplan L, Michaud K . Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of hospitalization for pneumonia: associations with prednisone, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 628–634.
Greenberg JD, Reed G, Kremer JM, Tindall E, Kavanaugh A, Zheng C et al. Association of methotrexate and tumour necrosis factor antagonists with risk of infectious outcomes including opportunistic infections in the CORRONA registry. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69: 380–386.
Ananthakrishnan AN, Cagan A, Cai T, Gainer VS, Shaw SY, Churchill S et al. Diabetes and the risk of infections with immunomodulator therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2015; 41: 1141–1148.
Caira M, Candoni A, Verga L, Busca A, Delia M, Nosari A et al. Pre-chemotherapy risk factors for invasive fungal diseases: prospective analysis of 1,192 patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (SEIFEM 2010-a multicenter study). Haematologica 2015; 100: 284–292.
Penfornis A, Kury-Paulin S . Immunosuppressive drug-induced diabetes. Diabetes Metab 2006; 32: 539–546.
Sharif A, Baboolal K . Complications associated with new-onset diabetes after kidney transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol 2012; 8: 34–42.
Hayer MK, Farrugia D, Begaj I, Ray D, Sharif A . Infection-related mortality is higher for kidney allograft recipients with pretransplant diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2014; 57: 554–561.
Wyzgal J, Paczek L, Ziolkowski J, Pawlowska M, Rowinski W, Durlik M . Early hyperglycemia after allogenic kidney transplantation. Ann Transplant 2007; 12: 40–45.
Kasiske BL, Snyder JJ, Gilbertson D, Matas AJ . Diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation in the United States. Am J Transplant 2003; 3: 178–185.
Cole EH, Johnston O, Rose CL, Gill JS . Impact of acute rejection and new-onset diabetes on long-term transplant graft and patient survival. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2008; 3: 814–821.
Valderhaug TG, Hjelmesaeth J, Jenssen T, Roislien J, Leivestad T, Hartmann A . Early posttransplantation hyperglycemia in kidney transplant recipients is associated with overall long-term graft losses. Transplantation 2012; 94: 714–720.
Hosseini MS, Nemati E, Pourfarziani V, Taheri S, Nourbala MH, Einollahi B . Early hyperglycemia after allogenic kidney transplantation: does it induce infections. Ann Transplant 2007; 12: 23–26.
Griffith ML, Jagasia MH, Misfeldt AA, Chen H, Engelhardt BG, Kassim A et al. Pretransplantation C-Peptide level predicts early posttransplantation diabetes mellitus and has an impact on survival after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 86–92.
Engelhardt BG, Jagasia SM, Crowe JE Jr., Griffith ML, Savani BN, Kassim AA et al. Predicting posttransplantation diabetes mellitus by regulatory T-cell phenotype: implications for metabolic intervention to modulate alloreactivity. Blood 2012; 119: 2417–2421.
Rassias AJ, Marrin CA, Arruda J, Whalen PK, Beach M, Yeager MP . Insulin infusion improves neutrophil function in diabetic cardiac surgery patients. Anesth Analg 1999; 88: 1011–1016.
Hecking M, Haidinger M, Doller D, Werzowa J, Tura A, Zhang J et al. Early basal insulin therapy decreases new-onset diabetes after renal transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 23: 739–749.
Keddis MT, El Ters M, Rodrigo E, Dean P, Wohlfahrtova M, Kudva YC et al. Enhanced posttransplant management of patients with diabetes improves patient outcomes. Kidney Int 2014; 86: 610–618.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005; 106: 2912–2919.
Takano K, Fuji S, Uchida N, Ogawa H, Ohashi K, Eto T et al. Pre-transplant diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for non-relapse mortality, especially infection-related mortality, after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2015; 50: 553–558.
Radfar M, Faghihi T, Hadjibabaie M, Ebrahimi F, Qorbani M, Iravani M et al. Impact of preexisting diabetes mellitus on transplantation outcomes in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Endocr Res 2015; 40: 20–24.
Goldberg RB . Cytokine and cytokine-like inflammation markers, endothelial dysfunction, and imbalanced coagulation in development of diabetes and its complications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94: 3171–3182.
Fuji S, Yakushijin K, Kim SW, Yoshimura K, Kurosawa S, Fukuda T . Dynamic change of glycemic status during the early phase after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2015; 50: 1473–1475.
Hammer MJ, Casper C, Gooley TA, O'Donnell PV, Boeckh M, Hirsch IB . The contribution of malglycemia to mortality among allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 344–351.
Fuji S, Kim SW, Mori S, Fukuda T, Kamiya S, Yamasaki S et al. Hyperglycemia during the neutropenic period is associated with a poor outcome in patients undergoing myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transplantation 2007; 84: 814–820.
Derr RL, Hsiao VC, Saudek CD . Antecedent hyperglycemia is associated with an increased risk of neutropenic infections during bone marrow transplantation. Diabetes Care 2008; 31: 1972–1977.
Gebremedhin E, Behrendt CE, Nakamura R, Parker P, Salehian B . Severe hyperglycemia immediately after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation is predictive of acute graft-versus-host disease. Inflammation 2013; 36: 177–185.
Sheean PM, Freels SA, Helton WS, Braunschweig CA . Adverse clinical consequences of hyperglycemia from total parenteral nutrition exposure during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 656–664.
Pidala J, Kim J, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Nishihori T, Field T, Perkins J et al. Dysglycemia following glucocorticoid therapy for acute graft-versus-host disease adversely affects transplantation outcomes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 239–248.
Tichelli A, Bucher C, Rovo A, Stussi G, Stern M, Paulussen M et al. Premature cardiovascular disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Blood 2007; 110: 3463–3471.
Tichelli A, Passweg J, Wojcik D, Rovo A, Harousseau JL, Masszi T et al. Late cardiovascular events after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective multicenter study of the Late Effects Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2008; 93: 1203–1210.
Chow EJ, Mueller BA, Baker KS, Cushing-Haugen KL, Flowers ME, Martin PJ et al. Cardiovascular hospitalizations and mortality among recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Intern Med 2011; 155: 21–32.
van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Weekers F, Verwaest C, Bruyninckx F, Schetz M et al. Intensive insulin therapy in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 1359–1367.
Langouche L, Vanhorebeek I, Van den Berghe G . Therapy insight: the effect of tight glycemic control in acute illness. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2007; 3: 270–278.
Krinsley JS . Glycemic control in the critically ill: what have we learned since NICE-SUGAR? Hosp Pract (1995) 2015; 43: 191–197.
Van den Berghe G, Schetz M, Vlasselaers D, Hermans G, Wilmer A, Bouillon R et al. Clinical review: Intensive insulin therapy in critically ill patients: NICE-SUGAR or Leuven blood glucose target? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94: 3163–3170.
Dandona P, Chaudhuri A, Ghanim H, Mohanty P . Anti-inflammatory effects of insulin and the pro-inflammatory effects of glucose. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006; 18: 293–301.
Marik PE, Preiser JC . Toward understanding tight glycemic control in the ICU: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Chest 2010; 137: 544–551.
Fuji S, Kim SW, Mori S, Kamiya S, Yoshimura K, Yokoyama H et al. Intensive glucose control after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective matched-cohort study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 44: 105–111.
Queale WS, Seidler AJ, Brancati FL . Glycemic control and sliding scale insulin use in medical inpatients with diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 1997; 157: 545–552.
Krinsley JS . Glycemic variability: a strong independent predictor of mortality in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 2008; 36: 3008–3013.
Asudani D, Calles-Escandon J . Inpatient hyperglycemia: slide through the scale but cover the bases first. J Hosp Med 2007; 2 (Suppl 1): 23–32.
Hirsch IB . Sliding scale insulin—time to stop sliding. JAMA 2009; 301: 213–214.
Michota F . What are the disadvantages of sliding-scale insulin? J Hosp Med 2007; 2 (Suppl 1): 20–22.
Umpierrez GE, Smiley D, Jacobs S, Peng L, Temponi A, Mulligan P et al. Randomized study of basal-bolus insulin therapy in the inpatient management of patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing general surgery (RABBIT 2 surgery). Diabetes Care 2011; 34: 256–261.
Umpierrez G, Cardona S, Pasquel F, Jacobs S, Peng L, Unigwe M et al. Randomized controlled trial of intensive versus conservative glucose control in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery: GLUCO-CABG trial. Diabetes Care 2015; 38: 1665–1672.
Olveira G, Tapia MJ, Ocon J, Cabrejas-Gomez C, Ballesteros-Pomar MD, Vidal-Casariego A et al. Parenteral nutrition-associated hyperglycemia in non-critically ill inpatients increases the risk of in-hospital mortality (multicenter study). Diabetes Care 2013; 36: 1061–1066.
Sheean P, Braunschweig C . The incidence and impact of dextrose dose on hyperglycemia from parenteral nutrition (PN) exposure in hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2006; 30: 345–350.
Sheean PM, Braunschweig C, Rich E . The incidence of hyperglycemia in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients receiving total parenteral nutrition: a pilot study. J Am Diet Assoc 2004; 104: 1352–1360.
Mirtallo J, Canada T, Johnson D, Kumpf V, Petersen C, Sacks G et al. Safe practices for parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2004; 28: S39–S70.
Lenssen P, Aker S. Nutrition support of the hematopoietic cell transplant recipient. In: Appelbaum FR, Forman SJ, Negrin RS, Blume KG (eds). Thomas' Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009, pp 1551–1569.
Muscaritoli M, Conversano L, Torelli GF, Arcese W, Capria S, Cangiano C et al. Clinical and metabolic effects of different parenteral nutrition regimens in patients undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1998; 66: 610–616.
Lenssen P, Bruemmer BA, Bowden RA, Gooley T, Aker SN, Mattson D . Intravenous lipid dose and incidence of bacteremia and fungemia in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 67: 927–933.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2014. Diabetes Care 2014; 37 (Suppl 1): S14–S80.
Handelsman Y, Bloomgarden ZT, Grunberger G, Umpierrez G, Zimmerman RS, Bailey TS et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology - clinical practice guidelines for developing a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan - 2015. Endocr Pract 2015; 21: 1–87.
Evert AB, Boucher JL, Cypress M, Dunbar SA, Franz MJ, Mayer-Davis EJ et al. Nutrition therapy recommendations for the management of adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013; 36: 3821–3842.
Chow EJ, Baker KS, Lee SJ, Flowers ME, Cushing-Haugen KL, Inamoto Y et al. Influence of conventional cardiovascular risk factors and lifestyle characteristics on cardiovascular disease after hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 191–198.
Berkowitz SA, Krumme AA, Avorn J, Brennan T, Matlin OS, Spettell CM et al. Initial choice of oral glucose-lowering medication for diabetes mellitus: a patient-centered comparative effectiveness study. JAMA Intern Med 2014; 174: 1955–1962.
American Diabetes Association. (7) Approaches to glycemic treatment. Diabetes Care 2015; 38: S41–S48.
Meah F, Juneja R . Insulin tactics in type 2 diabetes. Med Clin North Am 2015; 99: 157–186.
Wesorick D, O'Malley C, Rushakoff R, Larsen K, Magee M . Management of diabetes and hyperglycemia in the hospital: a practical guide to subcutaneous insulin use in the non-critically ill, adult patient. J Hosp Med 2008; 3 (5 Suppl): 17–28.
Lovre D, Fonseca V . Benefits of timely basal insulin control in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications 2015; 29: 295–301.
Jenssen T, Hartmann A . Prevention and management of transplant-associated diabetes. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2011; 12: 2641–2655.
Gilbert RE, Krum H . Heart failure in diabetes: effects of anti-hyperglycaemic drug therapy. Lancet 2015; 385: 2107–2117.
Billington EO, Grey A, Bolland MJ . The effect of thiazolidinediones on bone mineral density and bone turnover: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2015; 58: 2238–2246.
Kahn SE, Haffner SM, Heise MA, Herman WH, Holman RR, Jones NP et al. Glycemic durability of rosiglitazone, metformin, or glyburide monotherapy. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2427–2443.
Mikhail N . Safety of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Curr Drug Saf 2011; 6: 304–309.
Ahren B . Insulin plus incretin: a glucose-lowering strategy for type 2-diabetes. World J Diabetes 2014; 5: 40–51.
O'Leary H, Ou X, Broxmeyer HE . The role of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 in hematopoiesis and transplantation. Curr Opin Hematol 2013; 20: 314–319.
El Ghandour S, Azar S . Incretin based therapy in the management of steroid induced diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev 2014; 10: 360–363.
van Raalte DH, van Genugten RE, Linssen MM, Ouwens DM, Diamant M . Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment prevents glucocorticoid-induced glucose intolerance and islet-cell dysfunction in humans. Diabetes Care 2011; 34: 412–417.
Halimi S, Verges B . Adverse effects and safety of SGLT-2 inhibitors. Diabetes Metab 2014; 40 (Suppl 1): S28–S34.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research in Japan. This work was also supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Grant 1K23HL122143-01A (to BGE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuji, S., Rovó, A., Ohashi, K. et al. How do I manage hyperglycemia/post-transplant diabetes mellitus after allogeneic HSCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 51, 1041–1049 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.81
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.81
This article is cited by
-
The European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) roadmap and perspectives to improve nutritional care in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on behalf of the Cellular Therapy and Immunobiology Working Party (CTIWP) and the Nurses Group (NG) of the EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Antiemetic Strategies in Patients Who Undergo Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Clinical Hematology International (2022)
-
How we can mitigate the side effects associated with systemic glucocorticoid after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Optimization of nutrition support practices early after hematopoietic cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Hyperglycemia as a possible risk factor for mold infections—the potential preventative role of intensified glucose control in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)