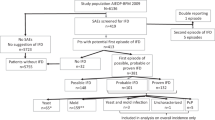
Abstract
This study was aimed at finding predictors of invasive fungal infection (IFI) after pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic SCT (HSCT). All children who received allogeneic HSCT in the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital Utrecht between 2004 and 2012 were included. HSCT data were prospectively collected. Patients were retrospectively classified into high- or low-risk groups for developing IFI using criteria based on available literature. Predictors for the occurrence of IFI were analyzed using Cox regression models. We used logistic regression models to analyze the association between other HSCT-related complications and IFI. Secondary outcomes were overall survival and treatment-related mortality (TRM). Two-hundred nine patients were included in the analysis; median age was 6.6 years. The cumulative incidence of IFI was 12%. In patients classified as ‘low risk’ (n=75), only 5.3% developed IFI (odds ratio (OR): 0.325; P=0.047). In multivariate analysis, a predictor for the occurrence of IFI was an a priori determined HSCT TRM risk >20% (based on EBMT-risk score). Post-HSCT, the administration of high-dose steroids was associated with IFI (OR: 4.458; P=0.010). Patients who developed IFI showed an increased risk of TRM (OR: 3.773; P=0.004). These results confirm that risk group stratification should guide intensity of monitoring for IFI and use of antifungal prophylaxis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dvorak CC, Steinbach WJ, Brown JMY, Agarwal R . Risks and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in pediatric patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 621–629.
Kobayashi R, Kaneda M, Sato T, Suzuki D, Ichikawa M, Ariga T . Evaluation of risk factors for invasive fungal infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2007; 29: 786–791.
Kobayashi R, Kaneda M, Sato T, Ichikawa M, Suzuki D, Ariga T . The clinical feature of invasive fungal infection in pediatric patients with hematologic and malignant diseases: a 10-year analysis at a single institution at Japan. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2008; 30: 886–890.
Hovi L, Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Vettenranta K, Saxen H . Invasive fungal infections in pediatric bone marrow transplant recipients: single center experience of 10 years. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 999–1004.
Benjamin DK Jr, Miller WC, Bayliff S, Martel L, Alexander KA, Martin PL . Infections diagnosed in the first year after pediatric stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2002; 21: 227–234.
Crassard N, Hadden H, Pondarre C, Hadden R, Galambrun C, Piens MA et al. Invasive aspergillosis and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children: a 15-year experience. Transpl Infect Dis 2008; 10: 177–183.
Mikulska M, Raiola AM, Bruno B, Furfaro E, Van Lint MT, Bregante S et al. Risk factors for invasive aspergillosis and related mortality in recipients of allogeneic SCT from alternative donors: an analysis of 306 patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 44: 361–370.
Srinivasan A, Wang C, Srivastava DK, Burnette K, Shenep JL, Leung W et al. Timeline, epidemiology, and risk factors for bacterial, fungal, and viral infections in children and adolescents after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012 pii S1083-8791: 00334–00335.
Marr KA, Carter RA, Crippa F, Wald A, Corey L . Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 909–917.
Barnes PD, Risks Marr KA . Diagnosis and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Br J Haematol 2007; 139: 519–531.
Castagnola E, Faraci M, Moroni C, Bandettini R, Granata C, Caruso S et al. Invasive mycoses in children receiving hemopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: S107–S111.
Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, Park BJ, Alexander BD, Anaissie EJ, Walsh TJ et al. Prospective surveillance for invasive fungal infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, 2001-2006: overview of the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network (TRANSNET) Database. Clin Infect Dis 2010 15 50: 1091–1100.
Kontoyiannis DP . Antifungal prophylaxis in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: the unfinished tale of imperfect success. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 165–173.
Rogers TR, Slavin MA, Donnelly JP . Antifungal prophylaxis during treatment for haematological malignancies: are we there yet? Br J Haematol 2011; 153: 681–697.
Pauw de BE . What are fungal infections? Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis 2011; 3: e2011001.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Gratwohl A . The EBMT risk score. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 749–756.
Pauw DeB, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from European organisation for research and treatment of cancer/invasive fungal infections cooperative Group and the national institute of allergy and infectious diseases mycoses study Group (EORTC/MSG) concensus Group. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: 1813–1821.
Blyth CC, Hale K, Palasanthiran P, O'Brien T, Bennett MH . Antifungal therapy in infants and children with proven, probable or suspected invasive fungal infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010; 17 CD006343.
Snelders E, van der Lee HA, Kuijpers J, Rijs AJ, Varga J, Samson RA et al. Emergence of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus and spread of a single resistance mechanism. PLoS Med 2008; 5: e219.
Bartelink IH, Wolfs T, Martine J, de Waal M, Egberts TC, Ververs TT et al. Immune reconstitution kinetics as an early predictor for mortality using various hematopoietic stem cell sources in children. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012 22. pii S1083-8791: 00426–0.
Ram R, Gafter-Gvili A, Yeshurun M, Paul M, Raanani P, Shpilberg O . Prophylaxis regimens for GVHD: systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 43: 643–653.
Ferrara JL, Levine JE, Reddy P, Holler E . Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet 2009; 373: 1550–1561.
Rocha V, Locatelli F . Searching for alternative hematopoietic stem cell donors for pediatric patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 207–214.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hol, J., Wolfs, T., Bierings, M. et al. Predictors of invasive fungal infection in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic SCT recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 49, 95–101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.136
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.136
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant in a Pediatric Patient with Invasive Fungal Infections: Challenges and Indications
Current Fungal Infection Reports (2021)
-
Risk factors associated with development and mortality by invasive fungal diseases in pediatric allogeneic stem cell transplantation. A pediatric subgroup analysis of data from a prospective study of the Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo (GITMO)
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2018)
-
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Caspofungin Versus Micafungin in Pediatric Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: A Retrospective Analysis
Advances in Therapy (2017)
-
Incidence and risk factors of post-engraftment invasive fungal disease in adult allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients receiving oral azoles prophylaxis
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)