Abstract
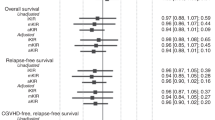
HLA class I molecules participate in natural killer cell regulation by acting as ligands for inhibitory killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIRs). One individual may express one or more inhibitory KIR lacking the corresponding HLA ligand. The role of this ‘missing KIR ligand’ constellation in hematopoietic SCT (HSCT) remains controversial and depends on incompletely defined transplant variables. We have retrospectively analyzed the effects of missing HLA-C group 1/2 and Bw4 KIR ligands in the recipients on the outcome in 382 HSCT, comparing 118 BMT to 264 PBSC transplants (PBSCT). In the multivariate Cox analysis of PBSCT, poor PFS was observed in homozygous HLA-C group 2 (C2/2) recipients (risk ratio (RR), 1.59; P=0.026). In contrast, C2 homozygosity was not unfavorable after BMT (RR, 0.68; P=0.16). C2 homozygous recipients (n=68) had better PFS after BMT than after PBSCT (RR, 0.17; P=0.001), due to fewer relapses (RR, 0.27; P=0.018). Missing Bw4 favorably influenced PFS after BMT (RR, 0.56; P=0.04), but not after PBSCT. These data suggest opposite effects of missing KIR ligands in BMT vs PBSCT. Larger studies are required to reassess whether BMT should be preferred to PBSCT as an option for C2/C2 recipients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beelen DW, Ottinger HD, Ferencik S, Elmaagacli AH, Peceny R, Trenschel R et al. Genotypic inhibitory killer immunoglobulin-like receptor ligand incompatibility enhances the long-term antileukemic effect of unmodified allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with myeloid leukemias. Blood 2005; 105: 2594–2600.
Giebel S, Locatelli F, Lamparelli T, Velardi A, Davies S, Frumento G et al. Survival advantage with KIR ligand incompatibility in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors. Blood 2003; 102: 814–819.
Hsu KC, Gooley T, Malkki M, Pinto-Agnello C, Dupont B, Bignon JD et al. KIR ligands and prediction of relapse after unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematologic malignancy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 828–836.
Kroger N, Shaw B, Iacobelli S, Zabelina T, Peggs K, Shimoni A et al. Comparison between antithymocyte globulin and alemtuzumab and the possible impact of KIR-ligand mismatch after dose-reduced conditioning and unrelated stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 2005; 129: 631–643.
Leung W, Iyengar R, Turner V, Lang P, Bader P, Conn P et al. Determinants of antileukemia effects of allogeneic NK cells. J Immunol 2004; 172: 644–650.
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Casucci M, Volpi I, Tosti A, Perruccio K et al. Role of natural killer cell alloreactivity in HLA-mismatched hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 1999; 94: 333–339.
Bornhauser M, Schwerdtfeger R, Martin H, Frank KH, Theuser C, Ehninger G . Role of KIR ligand incompatibility in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using unrelated donors. Blood 2004; 103: 2860–2861.
Davies SM, Ruggieri L, DeFor T, Wagner JE, Weisdorf DJ, Miller JS et al. Evaluation of KIR ligand incompatibility in mismatched unrelated donor hematopoietic transplants. Killer immunoglobulin-like receptor. Blood 2002; 100: 3825–3827.
De Santis D, Bishara A, Witt CS, Nagler A, Brautbar C, Slavin S et al. Natural killer cell HLA-C epitopes and killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors both influence outcome of mismatched unrelated donor bone marrow transplants. Tissue Antigens 2005; 65: 519–528.
Farag SS, Bacigalupo A, Eapen M, Hurley C, Dupont B, Caligiuri MA et al. The effect of KIR ligand incompatibility on the outcome of unrelated donor transplantation: a report from the center for international blood and marrow transplant research, the european blood and marrow transplant registry, and the dutch registry. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 876–884.
Uhrberg M, Valiante NM, Shum BP, Shilling HG, Lienert-Weidenbach K, Corliss B et al. Human diversity in killer cell inhibitory receptor genes. Immunity 1997; 7: 753–763.
Cook MA, Milligan DW, Fegan CD, Darbyshire PJ, Mahendra P, Craddock CF et al. The impact of donor KIR and patient HLA-C genotypes on outcome following HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myeloid leukemia. Blood 2004; 103: 1521–1526.
Fischer JC, Ottinger H, Ferencik S, Sribar M, Punzel M, Beelen DW et al. Relevance of C1 and C2 epitopes for hemopoietic stem cell transplantation: role for sequential acquisition of HLA-C-specific inhibitory killer Ig-like receptor. J Immunol 2007; 178: 3918–3923.
Giebel S, Locatelli F, Wojnar J, Velardi A, Mina T, Giorgiani G et al. Homozygosity for human leucocyte antigen-C ligands of KIR2DL1 is associated with increased risk of relapse after human leucocyte antigen-C-matched unrelated donor haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 2005; 131: 483–486.
Clausen J, Wolf D, Petzer AL, Gunsilius E, Schumacher P, Kircher B et al. Impact of natural killer cell dose and donor killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genotype on outcome following human leucocyte antigen-identical haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Exp Immunol 2007; 148: 520–528.
Hsu KC, Keever-Taylor CA, Wilton A, Pinto C, Heller G, Arkun K et al. Improved outcome in HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia predicted by KIR and HLA genotypes. Blood 2005; 105: 4878–4884.
Miller JS, Cooley S, Parham P, Farag SS, Verneris MR, McQueen KL et al. Missing KIR ligands are associated with less relapse and increased graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) following unrelated donor allogeneic HCT. Blood 2007; 109: 5058–5061.
Sobecks RM, Ball EJ, Maciejewski JP, Rybicki LA, Brown S, Kalaycio M et al. Survival of AML patients receiving HLA-matched sibling donor allogeneic bone marrow transplantation correlates with HLA-Cw ligand groups for killer immunoglobulin-like receptors. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 39: 417–424.
Bjorklund AT, Schaffer M, Fauriat C, Ringden O, Remberger M, Hammarstedt C et al. NK cells expressing inhibitory KIR for non-self-ligands remain tolerant in HLA-matched sibling stem cell transplantation. Blood 2010; 115: 2686–2694.
Linn YC, Phang CY, Lim TJ, Chong SF, Heng KK, Lee JJ et al. Effect of missing killer-immunoglobulin-like receptor ligand in recipients undergoing HLA full matched, non-T-depleted sibling donor transplantation: a single institution experience of 151 asian patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 1031–1037.
Clausen J, Kircher B, Auberger J, Schumacher P, Ulmer H, Hetzenauer G et al. The role of missing killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor ligands in T cell replete peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from HLA-identical siblings. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 273–280.
Gagne K, Busson M, Bignon JD, Balere-Appert ML, Loiseau P, Dormoy A et al. Donor KIR3DL1/3DS1 gene and recipient Bw4 KIR ligand as prognostic markers for outcome in unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1366–1375.
Demirer T, Weaver CH, Buckner CD, Petersen FB, Bensinger WI, Sanders J et al. High-dose cyclophosphamide, carmustine, and etoposide followed by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in patients with lymphoid malignancies who had received prior dose-limiting radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol 1995; 13: 596–602.
Nachbaur D, Eibl B, Kropshofer G, Meister B, Mitterschiffthaler A, Schennach H et al. In vivo T cell depletion with low-dose rabbit antithymocyte globulin results in low transplant-related mortality and low relapse incidence following unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Hematother Stem Cell Res 2002; 11: 731–737.
Yu J, Venstrom JM, Liu XR, Pring J, Hasan RS, O'Reilly RJ et al. Breaking tolerance to self, circulating natural killer cells expressing inhibitory KIR for non-self HLA exhibit effector function after T cell-depleted allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 2009; 113: 3875–3884.
Pan L, Delmonte Jr J, Jalonen CK, Ferrara JL . Pretreatment of donor mice with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor polarizes donor T lymphocytes toward type-2 cytokine production and reduces severity of experimental graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1995; 86: 4422–4429.
Miller JS, Prosper F, McCullar V . Natural killer (NK) cells are functionally abnormal and NK cell progenitors are diminished in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood progenitor cell collections. Blood 1997; 90: 3098–3105.
Clausen J, Enk M, Vergeiner B, Eisendle K, Petzer AL, Gastl G et al. Suppression of natural killer cells in the presence of CD34+ blood progenitor cells and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2004; 10: 691–697.
Moesta AK, Norman PJ, Yawata M, Yawata N, Gleimer M, Parham P . Synergistic polymorphism at two positions distal to the ligand-binding site makes KIR2DL2 a stronger receptor for HLA-C than KIR2DL3. J Immunol 2008; 180: 3969–3979.
Nguyen S, Dhedin N, Vernant JP, Kuentz M, Al Jijakli A, Rouas-Freiss N et al. NK cell reconstitution after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplants: immaturity of NK cells and inhibitory effect of NKG2A override GvL effect. Blood 2005; 105: 4135–4142.
Pende D, Marcenaro S, Falco M, Martini S, Bernardo ME, Montagna D et al. Anti-leukemia activity of alloreactive NK cells in KIR ligand-mismatched haploidentical HSCT for pediatric patients: evaluation of the functional role of activating KIR and redefinition of inhibitory KIR specificity. Blood 2009; 113: 3119–3129.
Weisdorf D, Spellman S, Haagenson M, Horowitz M, Lee S, Anasetti C et al. Classification of HLA-matching for retrospective analysis of unrelated donor transplantation: revised definitions to predict survival. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 748–758.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clausen, J., Kircher, B., Auberger, J. et al. Bone marrow may be the preferable graft source in recipients homozygous for HLA-C group 2 ligands for inhibitory killer Ig-like receptors. Bone Marrow Transplant 47, 791–798 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.187
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.187