Abstract
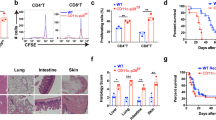
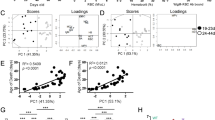
Immunological effects of IL-21 on T, B and natural killer (NK) cells have been reported, but the role of IL-21 in GVHD remains obscure. Here, we demonstrate that morbidity and mortality of GVHD was significantly reduced after BMT with splenocytes from IL-21R−/− mice compared with those from wild type mice. To further confirm our observation, we generated a decoy receptor for IL-21. GVHD was again less severe in mice receiving BM cells transduced with the IL-21 decoy receptor than control mice These results suggest that IL-21 critically regulates GVHD, and that blockade of the IL-21 signal may represent a novel strategy for the prophylaxis for GVHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozaki K, Leonard WJ . Cytokine and cytokine receptor pleiotropy redundancy. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 29355–29358.
Leonard WJ . Cytokines immunodeficiency diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 2001; 1: 200–208.
Noguchi M, Yi H, Rosenblatt HM, Filipovich AH, Adelstein S, Modi WS et al. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell 1993; 73: 147–157.
von Freeden-Jeffry U, Vieira P, Lucian LA, McNeil T, Burdach SE, Murray R . Lymphopenia in interleukin (IL)-7 gene-deleted mice identifies IL-7 as a nonredundant cytokine. J Exp Med 1995; 181: 1519–1526.
Lodolce JP, Boone DL, Chai S, Swain RE, Dassopoulos T, Trettin S et al. IL-15 receptor maintains lymphoid homeostasis by supporting lymphocyte homing and proliferation. Immunity 1998; 5: 669–676.
Ozaki K, Spolski R, Feng CG, Qi CF, Cheng J, Sher Au C et al. A critical role for IL-21 in regulating immunoglobulin production. Science 2002; 298: 1630–1634.
Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A, Hammond A, Sprecher C, Gross JA et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature 2000; 408: 57–63.
Ozaki K, Kikly K, Michalovich D, Young PR, Leonard WJ . Cloning of a type I cytokine receptor most related to the IL-2 receptor beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 11439–114344.
Brandt K, Bulfone-Paus S, Foster DC, Ruckert R . Interleukin-21 inhibits dendritic cell activation and maturation. Blood 2003; 102: 4090–4098.
Ozaki K, Hishiya A, Hatanaka K, Nakajima H, Wang G, Hwu P et al. Overexpression of IL-21 induces expansion of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Int J Hemat 2006; 84: 224–230.
Zhou L, Ivanov II, Spolski R, Min R, Shenderov K, Egawa T et al. IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 967–974.
Nurieva R, Yang XO, Martinez G, Zhang Y, Panopoulos AD, Ma L et al. Essential autocrine regulation by IL-21 in the generation of inflammatory T cells. Nature 2007; 448: 480–483.
Korn T, Bettelli E, Gao W, Awasthi A, Jäger A, Strom TB et al. IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory T(H)17 cells. Nature 2007; 448: 484–487.
Wurster AL, Rodgers VL, Satoskar AR, Whitters MJ, Young DA, Collins M et al. Interleukin 21 is a T helper (Th) cell 2 cytokine that specifically inhibits the differentiation of naive Th cells into interferon gamma-producing Th1 cells. J Exp Med 2002; 196: 969–977.
Pesce J, Kaviratne M, Ramalingam TR, Thompson RW, Urban Jr JF, Cheever AW et al. The IL-21 receptor augments Th2 effector function and alternative macrophage activation. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 2044–2055.
Fröhlich A, Marsland BJ, Sonderegger I, Kurrer M, Hodge MR, Harris NL et al. IL-21 receptor signaling is integral to the development of Th2 effector responses in vivo. Blood 2007; 109: 2023–2031.
Strengell M, Sareneva T, Foster D, Julkunen I, Matikainen S . IL-21 up-regulates the expression of genes associated with innate immunity and Th1 response. J Immunol 2002; 169: 3600–3605.
Ozaki K, Spolski R, Ettinger R, Kim HP, Wang G, Qi CF et al. Regulation of B cell differentiation and plasma cell generation by IL-21, a novel inducer of Blimp-1 and Bcl-6. J Immunol 2004; 173: 5361–5371.
Bubier JA, Sproule TJ, Foreman O, Spolski R, Shaffer DJ, Morse III HC et al. A critical role for IL-21 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus in BXSB- Yaa mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 1518–1523.
Spolski R, Kashyap M, Robinson C, Yu Z, Leonard WJ . IL-21 signaling is critical for the development of type I diabetes in the NOD mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 14028–14033.
Sutherland AP, Van Belle T, Wurster AL, Suto A, Michaud M, Zhang D et al. IL-21 is required for the development of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetes 2009; 58: 1144–1155.
Shlomchik WD . Graft-versus-host disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 340–352.
Cooke KR, Kobzik L, Martin TR, Brewer J, Delmonte Jr J, Crawford JM et al. An experimental model of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after bone marrow transplantation: I. The roles of minor H antigens and endotoxin. Blood 1996; 88: 3230–3239.
Graubert TA, DiPersio JF, Russell JH, Ley TJ . Perforin/granzyme-dependent and independent mechanisms are both important for the development of graft-versus-host disease after murine bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 904–911.
Tsukada N, Kobata T, Aizawa Y, Yagita H, Okumura K . Graft-versus-leukemia effect and graft-versus-host disease can be differentiated by cytotoxic mechanisms in a murine model of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1999; 93: 2738–2747.
Schmaltz C, Alpdogan O, Horndasch KJ, Muriglan SJ, Kappel BJ, Teshima T et al. Differential use of Fas ligand and perforin cytotoxic pathways by donor T cells in graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-leukemia effect. Blood 2001; 97: 2886–2895.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Kitamura (Institute of Medical Science, University of Tokyo, Tokyo) for donating PLAT-E, a packaging cell line. This work was supported in part by grants from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan, by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, by the Intramural Research Program of the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, USA), and by an Intramural Research Grant from Jichi Medical University, Tochigi, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meguro, A., Ozaki, K., Oh, I. et al. IL-21 is critical for GVHD in a mouse model. Bone Marrow Transplant 45, 723–729 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2009.223
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2009.223
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Role of NK Cells and Their Exosomes in Graft Versus Host Disease and Graft Versus Leukemia
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2023)
-
Interleukin-21 promotes thymopoiesis recovery following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2017)
-
Translational opportunities for targeting the Th17 axis in acute graft-vs.-host disease
Mucosal Immunology (2016)
-
IL2-IL21 gene cluster polymorphism is not associated with allograft function after kidney transplantation
International Urology and Nephrology (2014)
-
IL-21 accelerates xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease correlated with increased B-cell proliferation
Protein & Cell (2013)