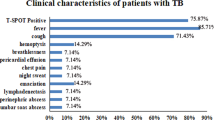
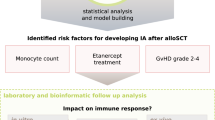
Abstract
Invasive mycoses represent a rare but severe complication following hemopoietic SCT (HSCT) in children. Their incidence is related to the type of donor, being higher after allogeneic transplant, especially from alternative donors. Moreover, the incidence of invasive mycoses varies in the different post transplant phases. Neutropenia, lymphopenia, GvHD, high-dose steroids or other immunosuppressive drugs represent well-known risk factors. The clinical features of invasive mycoses after HSCT in children are similar to those observed in adults, and the diagnostic tools, including Aspergillus galactomannan antigen detection, are feasible also in pediatrics. Mortality due to invasive mycoses after HSCT in children is high.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sepkowitz KA . Risk and epidemiology of infections after allogeneic hemopoietic stem cell transplantation. In: Bowden RA, Ljungman P, Paya CV (eds). Transplant Infections. Lippincott Willians & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2003, pp 31–38.
van Burik J, Weisdorf D . Infections in recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Doolin R (eds). Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. Churchill Livingstone: Philadelphia, 2005, pp 3486–3501.
Boeckh M, Marr KA . Infection in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In: Rubin RH, Young LS (eds). Clinical Approach to Infection in the Compromised Host. Kluwer Academic/Plenum: New York, 2002, pp 527–571.
Nucci M, Anaissie E . Revisiting the source of candidemia: skin or gut? Clin Infect Dis 2001; 33: 1959–1967.
Denning DW . Therapeutic outcome in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 1996; 23: 608–615.
Lin SJ, Schranz J, Teutsch SM . Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32: 358–366.
Anaissie EJ, Stratton SL, Dignani MC, Summerbell RC, Rex JH, Monson TP et al. Pathogenic Aspergillus species recovered from a hospital water system: a 3-year prospective study. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 780–789.
Deeg HJ, Bowden RA . Introduction to hemopoietic stem cell transplantation. In: Bowden RA, Ljungman P, Paya CV (eds). Transplant Infections. Lippincott Willians & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2003, pp 3–16.
Ochs L, Shu XO, Miller J, Enright H, Wagner J, Filipovich A et al. Late infections after allogeneic bone marrow transplantations: comparison of incidence in related and unrelated donor transplant recipients. Blood 1995; 86: 3979–3986.
Marr KA, Carter RA, Boeckh M, Martin P, Corey L . Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood 2002; 100: 4358–4366.
Ostrosky-Zeichner L, Rex JH, Bennett J, Kullberg BJ . Deeply invasive candidiasis. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2002; 16: 821–835.
Gea-Banacloche JC, Opal SM, Jorgensen J, Carcillo JA, Sepkowitz KA, Cordonnier C et al. Sepsis associated with immunosuppressive medications: an evidence-based review. Crit Care Med 2004; 32 (11 Suppl): S578–S590.
Dvorak CC, Steinbach WJ, Brown JM, Agarwal R . Risks and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in pediatric patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 621–629.
Barker JN, Hough RE, van Burik JA, DeFor TE, MacMillan ML, O’Brien MR et al. Serious infections after unrelated donor transplantation in 136 children: impact of stem cell source. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 362–370.
Benjamin DKJ, Miller WC, Bayliff S, Martel L, Alexander KA, Martin PL . Infections diagnosed in the first year after pediatric stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2002; 21: 227–234.
Hovi L, Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Vettenranta K, Saxen H . Invasive fungal infections in pediatric bone marrow transplant recipients: single center experience of 10 years. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 999–1004.
George B, Mathews V, Viswabandya A et al. Infections in children undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in India. Pediatr Transplant 2006; 10: 48–54.
Castagnola E, Cesaro S, Giacchino M, Livadiotti S, Tucci F, Zanazzo G et al. Fungal infections in children with cancer: a prospective, multicenter surveillance study. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2006; 25: 634–639.
Miller MJ . Fungal infections. In: Remington JS, Klein JO (eds). Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and the Newborn. W.B. Saunders: London, 1995, pp 703–744.
Silvestri M, Oddera S, Rossi GA, Crimi P . Sensitization to airborne allergens in children with respiratory symptoms. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1996; 76: 239–244.
van Burik JH, Leisenring W, Myerson D, Hackman RC, Shulman HM, Sale GE et al. The effect of prophylactic fluconazole on the clinical spectrum of fungal diseases in bone marrow transplant recipients with special attention to hepatic candidiasis. An autopsy study of 355 patients. Medicine 1998; 77: 246–254.
Archibald S, Park J, Geyer JR, Hawkins DS . Computed tomography in the evaluation of febrile neutropenic pediatric oncology patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2001; 20: 5–10.
Taccone A, Occhi M, Garaventa A, Manfredini L, Viscoli C . CT of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in children with cancer. Pediatr Radiol 1993; 23: 177–180.
Winer-Muram HT, Arheart KL, Jennings SG, Rubin SA, Kauffman WM, Slobod KS . Pulmonary complications in children with hematologic malignancies: accuracy of diagnosis with chest radiography and CT. Radiology 1997; 204: 643–649.
Caillot D, Casasnovas O, Bernard A, Couaillier JF, Durand C, Cuisenier B et al. Improved management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients using early thoracic computed tomographic scan and surgery. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 139–147.
Caillot D, Couaillier JF, Bernard A, Casasnovas O, Denning DW, Mannone L et al. Increasing volume and changing characteristics of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis on sequential thoracic computed tomography scans in patients with neutropenia. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 253–259.
Steinbach WJ, Marr KA . Mold infections after hemopoietic stem cell transplantation. In: Bowden RA, Ljungman P, Paya CV (eds). Transplant Infections. Lippincott Willians & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2003, pp 466–482.
Ascioglu S, Rex JH, de Pauw B, Bennett JE, Bille J, Crokaert F et al. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 7–14.
Sulahian A, Boutboul F, Ribaud P, Leblanc T, Lacroix C, Derouin F . Value of antigen detection using an enzyme immunoassay in the diagnosis and prediction of invasive aspergillosis in two adult and pediatric hematology units during a 4-year prospective study. Cancer 2001; 91: 311–318.
Herbrecht R, Letscher-Bru V, Oprea C, Lioure B, Waller J, Campos F et al. Aspergillus galactomannan detection in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 1898–1906.
Maertens J, Theunissen K, Verbeken E, Lagrou K, Verhaegen J, Boogaerts M et al. Prospective clinical evaluation of lower cut-offs for galactomannan detection in adult neutropenic cancer patients and haematological stem cell transplant recipients. Br J Haematol 2004; 126: 852–860.
Sulahian A, Touratier S, Ribaud P . False positive test for Aspergillus antigenemia related to concomitant administration of piperacillin and tazobactam. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2366–2367.
Viscoli C, Machetti M, Cappellano P, Bucci B, Bruzzi P, Van Lint MT et al. False-positive galactomannan platelia Aspergillus test results for patients receiving piperacillin-tazobactam. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 38: 913–916.
Gangneux JP, Lavarde D, Bretagne S, Guiguen C, Gandemer V . Transient Aspergillus antigenaemia: think of milk. Lancet 2002; 359: 1251.
Bart-Delabesse E, Basile M, Al Jijakli A, Souville D, Gay F, Philippe B et al. Detection of Aspergillus galactomannan antigenemia to determine biological and clinical implications of beta-lactam treatments. J Clin Microbiol 2005; 43: 5214–5220.
Hamaki T, Kami M, Kanda Y, Miyakoshi S, Ueyama J, Morinaga S et al. False-positive results of Aspergillus enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in a patient with chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 633–634.
Viscoli C, Girmenia C, Marinus A, Collette L, Martino P, Vandercam B et al. Candidemia in cancer patients: a prospective, multicenter surveillance study by the Invasive Fungal Infection Group (IFIG) of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Clin Infect Dis 1999; 28: 1071–1079.
Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Bennett JE, Greene RE, Oestmann JW et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 408–415.
Cornely OA, Maertens J, Bresnik M, Ebrahimi R, Ullmann AJ, Bouza E et al. Liposomal amphotericin B as initial therapy for invasive mold infection: a randomized trial comparing a high-loading dose regimen with standard dosing (AmBiLoad trial). Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44: 1289–1297.
Maertens J, Raad I, Petrikkos G, Boogaerts M, Selleslag D, Petersen FB et al. Efficacy and safety of caspofungin for treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients refractory to or intolerant of conventional antifungal therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 1563–1571.
Aliff TB, Maslak PG, Jurcic JG, Heaney ML, Cathcart KN, Sepkowitz KA et al. Refractory Aspergillus pneumonia in patients with acute leukemia: successful therapy with combination caspofungin and liposomal amphotericin. Cancer 2003; 97: 1025–1032.
Kontoyiannis DP, Hachem R, Lewis RE, Rivero GA, Torres HA, Thomby J et al. Efficacy and toxicity of caspofungin in combination with liposomal amphotericin B as primary or salvage treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Cancer 2003; 98: 292–299.
Marr KA, Boeckh M, Carter RA, Kim HW, Corey L . Combination antifungal therapy for invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 797–802.
Cesaro S, Visintin G . Combination antifungal therapy for invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: 1073–1075; author reply 1075–1076.
Marr KA, Boeckh M, Kim H . Combination antifungal therapy for invasive aspergillosis. Reply to Cesaro and Visintin. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: 1075–1076.
Cesaro S, Giacchino M, Locatelli F, Spiller M, Buldini B, Castellini C et al. Safety and efficacy of a caspofungin-based combination therapy for treatment of proven or probable aspergillosis in pediatric hematological patients. BMC Infect Dis 2007; 7: 28.
Viscoli C, Paesmans M, Sanz M, Castagnola E, Klastersky J, Martino P et al. Association between antifungal prophylaxis and rate of documented bacteremia in febrile neutropenic cancer patients. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32: 1532–1537.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
None of the authors declared any financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castagnola, E., Faraci, M., Moroni, C. et al. Invasive mycoses in children receiving hemopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 41 (Suppl 2), S107–S111 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.67
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.67
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cerebral Fungal Infection in Pediatric Cancer Patients
Current Fungal Infection Reports (2015)
-
Predictors of invasive fungal infection in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic SCT recipients
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Safety, tolerability, and feasibility of antifungal prophylaxis with micafungin at 2 mg/kg daily in pediatric patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Infection (2014)