Abstract
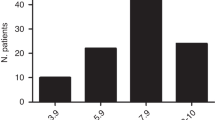
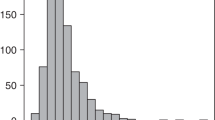
CD34+ cell dose calculations are usually based on actual body weight (ABW). We have shown that ideal body weight (IBW) may provide a better basis for this in a small population of patients with hematologic malignancies. This was studied further in 514 myeloma autografts. The CD34+ cell doses (106/kg) by IBW and ABW were 1.37–39.36 (median 6.03) and 1.15–29.67 (median 4.84), respectively. IBW-based cell doses correlated slightly better with engraftment than ABW-based doses (higher r2): 0.5 × 109/l neutrophils 0.83 versus 0.82, 1.0 × 109/l neutrophils 0.78 versus 0.77, 20 × 109/l platelets 0.54 versus 0.53 and 50 × 109/l platelets 0.57 versus 0.55. When outliers (hematologic recovery in <8 or >16 days) were excluded, the findings were similar: 0.5 × 109/l neutrophils 0.85 versus 0.84, 1.0 × 109/l neutrophils 0.85 versus 0.84, 20 × 109/l platelets 0.86 versus 0.85 and 50 × 109/l platelets 0.85 versus 0.84. CD34+ cell doses based on IBW as well as ABW significantly affected engraftment when analyzed separately as continuous variables. However, when analyzed together, only the dose based on IBW retained significance. We conclude that calculation of CD34+ cell numbers for autotransplantation should be based on IBW.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waples JM, Moreb JS, Sugrue M, Belanger G, Kubilis P, Lynch JW et al. Comparison of autologous peripheral blood stem cell dosing by ideal vs actual body weight. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 23: 867–873.
Singhal S, Powles R, Sirohi B, Kulkarni S, Treleaven J, Mehta J . CD34+ cell dose based upon ideal body weight (IBW) is a better predictor of transplant-related mortality (TRM) and disease-free survival (DFS) than that based upon actual body weight (ABW). Blood 2002; 100: 1667.
Ali MY, Oyama Y, Monreal J, Winter JN, Tallman MS, Williams SF et al. Ideal or actual body weight to calculate CD34+ cell doses for autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation? Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 861–864.
Cilley J, Rihn C, Monreal J, Gordon LI, Singhal S, Tallman MS et al. Ideal or actual body weight to calculate CD34+ cell doses for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation? Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 161–164.
Singhal S, Gordon LI, Tallman MS, Winter JN, Evens AO, Frankfurt O et al. Ideal rather than actual body weight should be used to calculate cell dose in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 553–557 erratum in: Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 1067).
Maclean PS, Parker AN, McQuaker IG, Clark AD, Farrell E, Douglas KW . Body weight correlates better with engraftment after PBSC autograft than actual body weight, but is under-estimated in myeloma patients possibly due to disease-related height loss. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 665–669.
Topcuoglu P, Akcaglayan Soydan E, Ekiz F, Ayyildiz E, Dalva K, Ozcan M et al. To calculate the quantity of CD34+ cells infused? A single center cohort study based on actual, ideal or adjusted ideal body weight. Transfus Apher Sci 2007; 36: 275–280.
Mehta J, Singhal S . High-dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in myeloma patients under the age of 65 years. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 1101–1114.
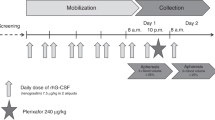
Gidron A, Verma A, Doyle M, Boggio L, Evens A, Gordon L et al. Can the stem cell mobilization technique influence CD34+ cell collection efficiency of leukapheresis procedures in patients with hematologic malignancies? Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 243–246.
Egan K, Singh V, Gidron A, Mehta J . Correlation between serum lactate dehydrogenase and stem cell mobilization. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 931–934.
Devine DJ . Gentamicin therapy. Drug Intell Clin Pharm 1974; 8: 650–655.
Sutherland DR, Anderson L, Keeney M, Nayar R, Chin-Yee I . The ISHAGE guidelines for CD34+ cell determination by flow cytometry. International Society of Hematotherapy and Graft Engineering. J Hematother 1996; 5: 213–226.
Verma A, Pedicano J, Trifilio S, Singhal S, Tallman M, Winter J et al. How long after neutrophil recovery should myeloid growth factors be continued in autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients? Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 715–719.
Ali MY, Oyama Y, Monreal J, Winter J, Tallman M, Gordon LI et al. Reassessing the definition of myeloid engraftment after autotransplantation: it is not necessary to see 0.5 × 109/l neutrophils on 3 consecutive days to define myeloid recovery. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 749–752.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, V., Krishnamurthy, J., Duffey, S. et al. Actual or ideal body weight to calculate CD34+ cell dose in patients undergoing autologous hematopoietic SCT for myeloma?. Bone Marrow Transplant 43, 301–305 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.322
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.322
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Is it time to revisit our current hematopoietic progenitor cell quantification methods in the clinic?
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2012)
-
The use of adjusted ideal body weight for overweight patients undergoing HPC mobilisation for autologous transplantation
Annals of Hematology (2012)
-
Optimal mobilization method and CD34+ dose calculation for autologous PBSC transplant in myeloma patients: two important unresolved questions
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2009)