Abstract
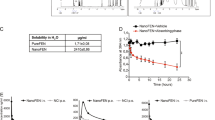
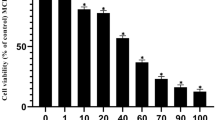
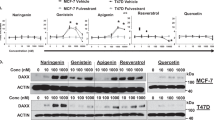
The clinical use of all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) in the treatment of cancer is significantly hampered by the prompt emergence of resistance, believed to be caused by increased ATRA catabolism. Inhibitors of ATRA catabolism may therefore prove valuable for cancer therapy. Liarozole-fumarate is an anti-tumour drug that inhibits the cytochrome P450-dependent catabolism of ATRA. ATRA, but also its naturally occurring catabolites, 4-oxo-ATRA and 5,6-epoxy-ATRA, as well as its stereoisomers, 9-cis-RA and 13-cis-RA, show significant antiproliferative activity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. To further elucidate its mechanism of action, we investigated whether liarozole-fumarate was able to enhance the antiproliferative activity of ATRA catabolites and isomers. Liarozole-fumarate alone up to a concentration of 10(-6) M had no effect on MCF-7 cell proliferation. However, in combination with ATRA or the ATRA catabolites, liarozole-fumarate (10(-6) M) significantly enhanced their antiproliferative activity. On the contrary, liarozole-fumarate (10(-6) M) was not able to potentiate the antiproliferative activity of the ATRA stereoisomers, most probably because of the absence of cytochrome P450-dependent catabolism. Together, these findings show that liarozole-fumarate acts as a versatile inhibitor of retinoid catabolism in that it not only blocks the breakdown of ATRA, but also inhibits the catabolic pathway of 4-oxo-ATRA and 5,6-epoxy-ATRA, thereby enhancing their antiproliferative activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van heusden, J., Wouters, W., Ramaekers, F. et al. The antiproliferative activity of all-trans-retinoic acid catabolites and isomers is differentially modulated by liarozole-fumarate in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 77, 1229–1235 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1998.207
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1998.207
This article is cited by
-
Retinoic acid metabolism in cancer: potential feasibility of retinoic acid metabolism blocking therapy
Medical Molecular Morphology (2023)
-
Oncogenic and cell survival properties of the retinoic acid metabolizing enzyme, CYP26A1
Oncogene (2010)
-
Inhibition of all-TRANS-retinoic acid metabolism by R116010 induces antitumour activity
British Journal of Cancer (2002)