Abstract
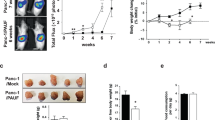
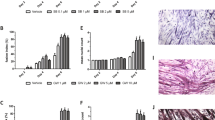
An antigen of apparent molecular weight of 24,000, reactive with a murine monoclonal antibody, has been isolated from a cachexia-inducing tumour (MAC 16) and has been shown to initiate muscle protein degradation in vitro using isolated soleus muscle. Administration of this material to female NMRI mice (20 g) produced a pronounced depression in body weight (2.72 +/- 0.14 g; P<0.005 from control) over a 24 h period. This weight loss was attenuated in mice pretreated with the monoclonal antibody (0.06 +/- 0.26 g over 24 h) and occurred without a reduction in food and water intake. There was no change in body water composition, and the major contribution to the decrease in body weight was a decrease in the non-fat carcass dry weight (mainly lean body mass). The plasma levels of glucose and most amino acids were also significantly depressed. The decrease in lean body mass was accounted for by an increase (by 50%) in protein degradation and a decrease (by 50%) in protein synthesis in gastrocnemius muscle. Protein degradation was significantly decreased and protein synthesis increased to control values in mice pretreated with the monoclonal antibody. Protein degradation initiated in vitro with the proteolysis-inducing factor was abolished in mice pretreated with eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which had been shown to prevent muscle wastage in mice bearing the MAC16 tumour. Protein degradation was associated with a significant elevation of prostaglandin E2 production by isolated soleus muscle, which was inhibited by both the monoclonal antibody and EPA. These results suggest that this material may be the humoral factor mediating changes in skeletal muscle protein homeostasis during the process of cancer cachexia in animals bearing the MAC16 tumour, and could potentially be involved in other cases of cachexia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorite, M., Cariuk, P. & Tisdale, M. Induction of muscle protein degradation by a tumour factor. Br J Cancer 76, 1035–1040 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1997.504
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1997.504
This article is cited by
-
Functional identity of receptors for proteolysis-inducing factor on human and murine skeletal muscle
British Journal of Cancer (2014)
-
C-Reactive Protein Levels and Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphisms as Markers in Predicting Cachectic Syndrome in Cancer Patients
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2012)
-
Attenuation of muscle atrophy by an N-terminal peptide of the receptor for proteolysis-inducing factor (PIF)
British Journal of Cancer (2011)
-
Metabolic and morphological alterations induced by proteolysis-inducing factor from Walker tumour-bearing rats in C2C12myotubes
BMC Cancer (2008)
-
Variation in dermcidin expression in a range of primary human tumours and in hypoxic/oxidatively stressed human cell lines
British Journal of Cancer (2008)