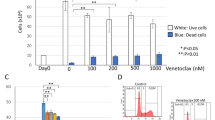
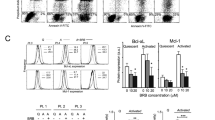
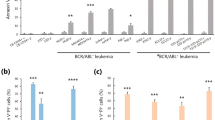
Abstract
A derivative of butyric acid, pivalyloxymethyl butyrate (AN-9), inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis of mouse monocytic leukaemia Mm-A cells, although sodium butyrate, but not AN-9, induced differentiation of the cells. AN-9 and DNA-specific antineoplastic agents synergistically inhibited the growth of Mm-A cells, and the simultaneous treatment was required to evoke the maximum growth-inhibitory effect. On the other hand, there was no synergy between butyrate and the drugs, or AN-9 and anti-metabolic agents in inhibiting the growth of the cells, suggesting that the synergistic effect is specific to AN-9 and DNA-reacting agents. AN-9 as a single agent prolonged the survival of mice inoculated with Mm-A cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, administration of AN-9 plus daunorubicin (DNR) markedly prolonged their survival. These results suggest that combination with AN-9 and DNR entails an obvious therapeutic potential.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasukabe, T., Rephaeli, A. & Honma, Y. An anti-cancer derivative of butyric acid (pivalyloxmethyl buterate) and daunorubicin cooperatively prolong survival of mice inoculated with monocytic leukaemia cells. Br J Cancer 75, 850–854 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1997.151
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1997.151
This article is cited by
-
Pygidial glands of the blue ground beetle Carabus intricatus: chemical composition of the secretion and its antimicrobial activity
The Science of Nature (2022)
-
Formaldehyde-releasing prodrugs specifically affect cancer cells by depletion of intracellular glutathione and augmentation of reactive oxygen species
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2008)
-
Mode of interaction between butyroyloxymethyl-diethyl phosphate (AN-7) and doxorubicin in MCF-7 and resistant MCF-7/Dx cell lines
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2006)
-
The selectivty and anti-metastatic activity of oral bioavailable butyric acid prodrugs
Investigational New Drugs (2006)