Abstract
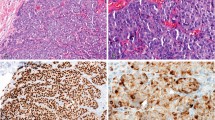
Studies using monoclonal antibody MR6, which is thought to bind to the interleukin-4 growth factor receptor (IL-4R), indicate that IL-4R molecules are upregulated in tumours of epithelial origin and that radiolabelled MR6 is effective as an in vivo tumour imaging agent. Immunohistochemical analysis of a wide range of solid tumours using monoclonal antibody MR6 has demonstrated elevated expression of the IL-4R on a variety of carcinomas. The equivalent normal tissue showed either weak or no expression of this molecule. No other tumours studied were positive. The molecular weight of the receptor on tumour cells was indistinguishable from that on normal tissue. These data raise the possibility that the IL-4R is the product of a novel oncogene such that elevated expression of this growth factor receptor could be involved in the process of carcinogenesis. Monoclonal antibodies to the IL-4R, such as MR6, may therefore be useful reagents not only for diagnosis and immunoscintigraphy, but also for in vivo antibody-guided therapy of epithelial cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al Jabaari, B., Ladyman, H., Larché, M. et al. Elevated expression of the interleukin 4 receptor in carcinoma: a target for immunotherapy?. Br J Cancer 59, 910–914 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1989.192
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1989.192
This article is cited by
-
Interleukin-4 enhances proliferation of human pancreatic cancer cells: evidence for autocrine and paracrine actions
British Journal of Cancer (2005)