Abstract
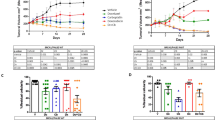
Five lines of human breast-carcinoma xenografts have been tested for sensitivity to cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil, adriamycin, vincristine and melphalan, alone and in combination, using tumour growth delay as an end-point. The xenograft lines were established and passaged in mice immune-suppressed by thymectomy and whole-body irradiation. There was a considerable range of sensitivity of the different lines to the agents studied, and within this variation there was evidence that the most effective single agent or combination differed for each tumour. Combination chemotherapy was more effective than single agents in 3 of the lines, but melphalan was more effective than either combination in the other 2. It is suggested that a panel of human breast tumours grown in immune-suppressed mice may prove useful in testing new cytotoxic agents for activity against breast cancer before their use in clinical trials, and that more effective combinations of existing drugs might be designed with the aid of this system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bailey, M., Gazet, J., Smith, I. et al. Chemotherapy of human breast-carcinoma xenografts. Br J Cancer 42, 530–536 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1980.276
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1980.276
This article is cited by
-
17β-Oestradiol treatment modulates nitric oxide synthase activity in MDA231 tumour with implications on growth and radiation response
British Journal of Cancer (2002)
-
Human tumor xenografts as model for drug testing
CANCER AND METASTASIS REVIEW (1988)
-
Development of new anti-cancer drugs
Medical Oncology and Tumor Pharmacotherapy (1986)