Abstract
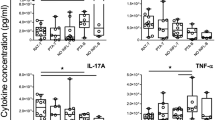
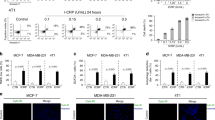
The i.v. administration of Corynebacterium parvum (CP) to patients who had recently undergone resection of colorectal tumours was found to have the following effects: 1. Polymorphonuclear leucocyte counts were raised 24 h after CP administration, while both lymphocyte and monocyte counts fell during this period. Polymorph and lymphocyte counts had returned to pre-infusion levels at one week, but monocyte counts were significantly increased at this time. 2. The lymphocyte mitotic response to PHA was reduced during the 24 h after CP infusion. 3 The spontaneous, antibody-induced, and PHA-induced lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against a nucleated target cell fell significantly 3 h after CP infusion, but these functions recovered by 7 days. 4. A rise in serum lysozyme was found 3 and 24 h after CP administration. However, these increased levels were not maintained beyond 24 h.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, P., Waller, C., MacClennan, I. et al. Effect of intravenous corynebacterium parvum on peripheral-blood effector cells of cancer patients. Br J Cancer 41, 782–789 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1980.142
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1980.142