Abstract
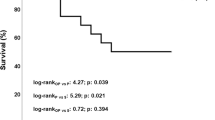
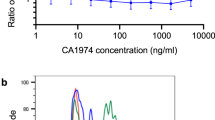
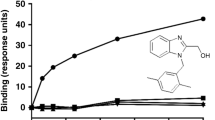
Sera from rabbits injected with BCG and then with endotoxin contain a factor (tumour-necrosis factor TNF) which, even at high dilutions, is cytotoxic in vitro for mouse L cells and some other cell lines. Using a 51Cr-release assay, cytotoxicity was detected as early as 7-8 h after addition of TNF serum to L cells and cell death was evident microscopically by 24 h. TNF was cytotoxic at 37 degrees C but not at 21 degrees C or 4 degrees C, and acted on both dividing and non-dividing cells. The antimetabolites sodium azide and dinitrophenol partially protected L cells from TNF, suggesting that actively metabolizing cells are the most sensitive. Treatment of L cells with trypsin did not delay cytotoxicity nor was cytotoxicity inhibited in the presence of various saccharide derivatives of cell-surface glycoproteins. Rabbit TNF was remarkably stable with a mol. wt. of 40-50,000. It was eluted with the more acidic serum proteins on ion-exchange chromatography, but precipitated in 50%-saturated ammonium sulphate. Sensitivity to TNF could not be correlated with tumourigenicity of several animal and human lines tested nor with the production of C-type viruses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matthews, N., Watkins, J. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. I. Mode of action, specificity and physicochemical properties. Br J Cancer 38, 302–309 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1978.202
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1978.202
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of apoptotic and inflammatory signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma via Caesalpinia gilliesii galactomannan
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2019)
-
A Practical Approach to the Use of Conventional Synthetic, Biologic and Targeted Synthetic Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs for the Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis in Patients with a History of Malignancy
Current Rheumatology Reports (2018)
-
Correlation of cytotoxic effect of transmembrane and secretory TNF-α to cell cycle
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences] (2012)
-
Selective inhibition of TNF-α-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and metastatic activities by gefitinib
British Journal of Cancer (2005)
-
Cycloheximide-induced modulation of TNF-mediated cytotoxicity in sensitive and resistant ovarian tumor cells
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (1990)