Abstract
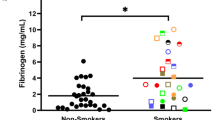
Chemotaxis of blood monocytes was measured in 31 patients with bronchial carcinoma and 19 cigarette smokers. Thirteen patients with metastatic bronchial carcinoma had significantly less (P less than 0.005) chemotactic response than matched controls. Those with disease confined to the chest, or with recurrent or operable bronchial carcinoma, had no significant depression of monocyte chemotaxis. There was also no significant difference in monocyte chemotaxis between cigarette smokers and matched controls. These results support the concept that in human cancer there is a defect in monocyte chemotaxis, but in bronchial carcinoma significant depression was only apparent in those with advanced disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kay, A., McVie, J. Monocyte chemotaxis in bronchial carcinoma and cigarette smokers. Br J Cancer 36, 461–466 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1977.215
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1977.215
This article is cited by
-
?Activated? monocytes in gastric cancer patients
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (1982)