Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
We tested the hypothesis that, the red blood cell (RBC) mass, estimated by hematocrit (HCT) or hemoglobin (Hb) level, influences the carbon monoxide (CO) production rate.
STUDY DESIGN:
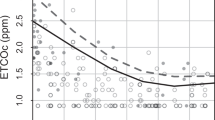
The relationship between end tidal CO corrected for ambient carbon monoxide level (ETCOc) and the RBC mass have been studied in 58 full-term infants at the mean age 4.9 hours.
RESULTS:
Mean ETCOc was 1.88 ppm (1.3 to 3.4 ppm). ETCOc correlated significantly with HCT (R2=10.1%, p=0.015) and with Hb (R2=11%, p=0.011). Infants with a capillary HCT >65% had significantly higher ETCOc (mean 1.99±0.49 ppm) than infants with a capillary HCT <65% (1.74±0.39 ppm), p=0.035. When CO production was corrected for HCT (ETCOc/HCT), this difference did not longer exist.
CONCLUSIONS:
In newborn infants ETCOc significantly correlates with RBC mass. Comparing different infant's CO generation rate one should take into consideration their initial RBC level. In order to adjust for the existing differences in RBC, we suggest the use of the ETCOc/HCT index.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartoletti AL, Stevenson DK, Ostrander CR, Johnson JD . Pulmonary excretion of carbon monoxide in the human infants as an index of bilirubin production. J Pediatr 1979;94:952–955.
Stevenson DK, Vreman HJ, Oh W, et al. Bilirubin production in healthy term infants as measured by carbon monoxide in breath. Clin Chem 1994;40 (10):1934–1939.
American Academy of Pediatrics. Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatr 2004;114:297–316.
Wrane L . Studies on erytho-kinetics in infancy. VII. Quantitative estimation of the haemoglobin catabolism by carbon monoxide technique in young infants. Acta Paediatr Scand 1967;56:381.
Mathot Y, Zaizov R, Varsano I . Postnatal changes in some red cell parameters. Acta Paediatr Scand 1971;60:317–323.
Horecker BL, Smyrniotis A . Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. In: Colowick N, Kaplan NO, editors. Methods in Enzymology. New York: Academic Press. Inc.; 1955: p. 323.
Seidman DS, Shiloh M, Stevenson DK, Vreman HJ, Paz I, Gale R . Role of hemolysis in neonatal jaundice associated with G6PD deficiency. J Pediatr 1995;127:804–806.
Kaplan M, Hershel M, Hammerman C, Hoyer JD, Stevenson DK . Hyperbilirubinemia among African American, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient neonates. Pediatrics 2004;114:e213.
Okuyama H, Yonetani M, Uetani Y, Nakamura H . End-tidal carbon monoxide is predictive for neonatal non-hemolytic hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatr Int 2001;43:329–333.
Stevenson DK, Fanaroff AA, Maisels MJ, et al. Prediction of hyperbilirubinemia in near-term and term infants. Pediatrics 2001;109:31–39.
Kaplan M, Muraca M, Hammerman C, et al. Imbalance between production and conjugation of bilirubin: a fundamental concept in the mechanism of neonatal jaundice. Pediatrics 2002;110:e47.
Javier MC, Krauss A, Nesin M . Corrected end-tidal carbon monoxide closely correlates with the corrected reticulocyte count in Coombs’ test-positive term neonates. Pediatrics 2003;112:1333–1337.
Balaraman V, Pelke S, DiMauro S, Cheung S, Stevenson DK, Easa D . End-tidal carbon monoxide in newborn infants: observations during the 1st week of life. Biol Neonate 1995;67:182–185.
Yamashita H, Kukita J, Ohga S, Nakayama H, Akazawa K, Ueda K . Serum erythropoietin levels in term and preterm infants during the first year of life. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1994;16:123–128.
Green DW, Mimouni F . Nucleated erythrocytes in healthy infants and in infants of diabetic mothers. J Pediatr 1990;116:129–131.
Mimouni F, Miodovnik M, Siddiqi T, Butler JB, Holroyde J, Tsang RC . Neonatal polycythemia in infants of insulin-dependent diabetic mothers. Obstet Gynecol 1986;68:370–372.
Hintz SR, Gaylord TD, Oh W, et al. Serum bilirubin levels at 72 hours by selected characteristics in breastfed and formula-fed term infants delivered by cesarean section. Acta Paediatr 2001;90:776–781.
Shohat M, Reisner SH, Mimouni F, Merlob P . Neonatal polycythemia: II. Definition related to time of sampling. Pediatrics 1984;73:11–13.
Hayde M, Widness JA, Pollak A, Kohlhauser-Vollmuth C, Vreman HJ, Stevenson DK . Rhesus isoimmunization: increased hemolysis during early infancy. Pediatr Res 1997;41:716–721.
Vreman HJ, Mahoney JJ, Stevenson DK . Carbon monoxide and carboxyhemoglobin. Advances in Pediatrics 1995;42:303–334.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barak, M., Oron, T., Mimouni, F. et al. Effect of Hematocrit on Exhaled Carbon Monoxide in Healthy Newborn Infants. J Perinatol 25, 784–787 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211388
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211388
This article is cited by
-
End-tidal carbon monoxide and hemolysis
Journal of Perinatology (2014)