Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To determine the relative risk of severe intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) between two very early indomethacin treatment strategies.
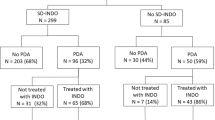
STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective chart review of infants <29 weeks gestation and <1350 g who received either indomethacin prophylaxis or very early echocardiography with indomethacin treatment only if the ductus arteriosus was patent.
RESULTS: A total of one hundred and two infants received prophylactic indomethacin (pINDO). Echochardiography was performed on 158 infants, of whom 117 received indomethacin. Infants receiving pINDO had lower gestational age, but similar birth weight, gender, race, antenatal steroid exposure, delivery mode, Apgar scores, and need for resuscitation as infants evaluated by echocardiography. Grades III to IV IVH was observed less frequently in infants who received pINDO (OR 0.27, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.77, p=0.014). Frequency of side effects and recurrent patent ductus arteriosus did not differ between treatment groups.
CONCLUSION: pINDO reduces severe IVH when compared to an early echocardiography strategy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandstra ES, Montalvo BM, Goldberg RN, et al. Prophylactic indomethacin for prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants. Pediatrics 1988;82(4):533–542.
Ment LR, Oh W, Ehrenkranz RA, Philip AG, et al. Low-dose indomethacin and prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage: a multicenter randomized trial. Pediatrics 1994;93(4):543–550.
Fowlie PW, Davis PG . Prophylactic intravenous indomethacin for preventing mortality and morbidity in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002; Issue 4.
Schmidt B, Davis P, Moddemann D, et al. Long-term effects of indomethacin prophylaxis in extremely-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med 2001;344(26):1966–1972.
Evans N, Kluckow M . Early ductal shunting and intraventricular haemorrhage in ventilated preterm infants. Arch Dis Childhood Fetal Neonatal Ed 1996;75(3):F183-6.
Perlman JM, Hill A, Volpe JJ . The effect of patent ductus arteriosus on flow velocity in the anterior cerebral arteries: ductal steal in the premature newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1981;99(5):767–771.
Ment LR, Vohr B, Allan W, et al. Outcome of children in the indomethacin intraventricular hemorrhage prevention trial. Pediatrics 2000;105(3 Pt 1):485–491.
Leffler CW, Busija DW, Fletcher AM, Beasley DG, Hessler JR, Green RS . Effects of indomethacin upon cerebral hemodynamics of newborn pigs. Pediatr Res 1985;19(11):1160–1164.
Ment LR, Stewart WB, Ardito TA, Huang E, Madri JA . Indomethacin promotes germinal matrix microvessel maturation in the newborn beagle pup. Stroke 1992;23(8):1132–1137.
Papile L-A, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H . Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemmorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr 1978 9(2;4):529–534.
Walsh MC, Kliegman RM, Fanaroff AA . Necrotizing enterocolitis: A practitioner's perspective. Pediatr Rev 1988;9(7):219–226.
Volpe JJ . Neurology of the Newborn. 4 ed. Philadelphia; W.B. Saunders Company, 2001; p. 435–447.
Van Bel F, Bartelds B, Teitel DF, Rudolph AM . Effect of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow and oxygenation in the normal and ventilated fetal lamb. Pediatr Res 1995;38(2):243–250.
Hayden JE, Leffler CW . The effects of treatment with indomethacin on the cerebral vasculature of newborn piglets before and during hemorrhagic hypotension. Pediatr Res 1997;41(1):78–82.
Zuckerman SL, Mirro R, Armstead WM, Shibata M, Leffler CW . Indomethacin reduces ischemia-induced alteration of blood-brain barrier transport in piglets. Am J Physiol 1994;266(6 Pt 2):H2198-203.
Pourcyrous M, Leffler CW, Bada HS, Korones SB, Busija DW . Brain superoxide anion generation in asphyxiated piglets and the effect of indomethacin at therapeutic dose. Pediat Res 1993;34(3):366–369.
Yaffe SJ . The disposition of indomethacin in preterm babies. J Pediatr 1980;97(6):1001–1006.
Coombs RC, Morgan ME, Durbin GM, Booth IW, McNeish AS . Gut blood flow velocities in the newborn: effects of patent ductus arteriosus and parenteral indomethacin. Arch Dis Child 1990;65(10 Spec No):1067–1071.
Ohlsson A, Bottu J, Govan J, Ryan ML, Fong K, Myhr T . Effect of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow velocities in very low birth weight neonates with a patent ductus arteriosus. Dev Pharmacol Therap 1993;20(1–2):100–106.
Van Bel F, Van Zoeren D, Schipper J, Guit GL, Baan J . Effect of indomethacin on superior mesenteric artery blood flow velocity in preterm infants. J Pediatr 1990;116(6):965–970.
Cowan F . Indomethacin, patent ductus arteriosus, and cerebral blood flow. J Pediatr 1986;109(2):341–344.
Yanowitz TD, Yao AC, Werner JC, Pettigrew KD, Oh W, Stonestreet BS . Effects of prophylactic low-dose indomethacin on hemodynamics in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 1998;132(1):28–34.
Ment LR, Vohr B, Oh W, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 36 months’ corrected age of preterm infants in the Multicenter Indomethacin Intraventricular Hemorrhage Prevention Trial. Pediatrics 1996;98(4 Pt 1):714–718.
Moya MP, Goldberg RN . Cost-effectiveness of prophylactic indomethacin in very-low-birth-weight infants. Ann Pharmacother 2002;36(2):218–224.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NIH K23 HD01317
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanowitz, T., Baker, R. & Sobchak Brozanski, B. Prophylactic Indomethacin Reduces Grades III and IV Intraventricular Hemorrhages when Compared to Early Indomethacin Treatment of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus. J Perinatol 23, 317–322 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7210893
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7210893
This article is cited by
-
Outcomes in infants < 29 weeks of gestation following single-dose prophylactic indomethacin
Journal of Perinatology (2021)
-
A risk prediction model for severe intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight infants and the effect of prophylactic indomethacin
Journal of Perinatology (2014)
-
Patent ductus arteriosus treatment in preterm infants—time to consider shunt volume?
Journal of Perinatology (2013)
-
A Predictive Model for SIVH risk in Preterm Infants and Targeted Indomethacin Therapy for Prevention
Scientific Reports (2013)
-
Serum ibuprofen levels of extremely preterm infants treated prophylactically with oral ibuprofen to prevent patent ductus arteriosus
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2013)