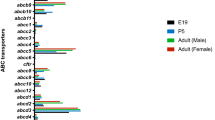Abstract
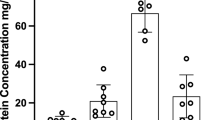
P-glycoprotein (Pgp), an ATP-dependent plasma membrane efflux pump, is expressed in abundance on the luminal aspect of brain capillary endothelial cells and astrocytes of the blood–brain barrier where it limits the passage of a variety of lipophilic substrates into the central nervous system. This review summarizes current evidence characterizing (1) unconjugated bilirubin as a potential substrate for Pgp and (2) the ontogeny of Pgp expression at the blood–brain barrier and apical brush border epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract, findings that may provide insights regarding the disposition of bilirubin in immature subjects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maisels MJ Neonatal jaundice In: Avery G, editor. Neonatology: Pathophysiology and Management of the Newborn Philadelphia: JB Lippincott 1987 p. 534–629
Watchko JF, Daood MJ, Hansen TWR Brain bilirubin content is increased in P-glycoprotein–deficient transgenic null mutant mice Pediatr Res 1998 44 763–6
Jette L, Murphy GF, Leclerc JM, et al Interaction of drugs with P-glycoprotein in brain capillaries Biochem Pharmacol 1995 50 1701–9
Gosland MP, Brophy NA, Duran AM, et al Bilirubin: a physiologic substrate for the multidrug transporter Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 1991 32 426
Bellamy WT P-glycoproteins and multidrug resistance Annu Rev Toxicol 1996 36 161–83
Schinkel AH, Smit JJM, van Tellingen O, et al Disruption of the mouse mdrla P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood–brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs Cell 1994 77 491–502
Tsai C, Lane R, Daood MJ, et al The ontogeny of P-glycoprotein expression in mouse brain microvessels Biol Neonate 2001 [In press]
Tsai C, Ahdab-Barmada M, Daood MJ, et al P-glycoprotein expression in the developing human central nervous system: cellular and tissue localization Pediatr Res 2000 47 436A
Golden PL, Pardridge WM Brain microvascular P-glycoprotein and a revised model of multidrug resistance in brain Cell Mol Neurobiol 2000 20 165–81
Gottesman MM, Patan I Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter Annu Rev Biochem 1993 62 385–427
Daood MJ, Tsai C, Hansen TWR, et al Regional expression of P-glycoprotein in adult mouse brain Pediatr Res 2000 47 395A
Hunter J, Jepson MA, Tsuruo T, et al Functional expression of P-glycoprotein in apical membranes of human intestinal Caco-2 cells J Biol Chem 1993 268 14991–7
Mahmood B, Daood MJ, Wasserloos KJ, et al Bilirubin efflux by P-glycoprotein in human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cell monolayers in vitro Pediatr Res 2000 47 414A
Mahmood B, Daood MJ, Hart C, et al Ontogeny of P-glycoprotein in mouse intestine, liver, and kidney J Invest Med 2001 49 250–7
Seelig A A general pattern for substrate recognition by P-glycoprotein Eur J Biochem 1998 251 252–61
Demeule M, Jodoin J, Beaulieu E, et al Dexamethasone modulation of multidrug transporters in normal tissues FEBS Lett 1999 442 208–14
Vats KR, Hart CD, Daood MJ, et al The effect of prenatal dexamethasone on P-glycoprotein (Pgp) expression in brain capillary endothelial cells of mouse pups Pediatr Res 2000 47 437A
Takanaga H, Onishi A, Matsuo H, et al Inhibition of vinblastine efflux mediated by P-glycoprotein by grapefruit juice components in Caco-2 cells Biol Pharm Bull 1998 21 1062–6
Hansen TWR, Tommarello S, Watchko JF Inhibition of blood–brain barrier P-glycoprotein function by various drugs enhances acute bilirubin entry into brain Pediatr Res 1998 43 176A
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, et al Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 97 3473–8
Mectizan® Program Notes, Issue 12 1994 Mectizan® Donation Program, One Copenhill, Atlanta, GA
Tanabe M, Ieri I, Nagata N, et al Expression of P-glycoprotein in human placenta: Relation to genetic polymorphism of the multidrug resistance (MDR)-1 gene J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001 297 1137–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants HD-35847 and NS-38993 from the National Institutes of Health, the Irene McClenahan Young Investigator Research Fund of the Magee-Womens Health Research Foundation, the Mario Lemieux Centers for Patient Care and Research, and the 25 Club of Magee-Womens Hospital.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watchko, J., Daood, M., Mahmood, B. et al. P-Glycoprotein and Bilirubin Disposition. J Perinatol 21 (Suppl 1), S43–S47 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7210633
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7210633
This article is cited by
-
Bilirubin accumulation and Cyp mRNA expression in selected brain regions of jaundiced Gunn rat pups
Pediatric Research (2012)
-
Commentary on the bilirubin supplement
Journal of Perinatology (2009)