Abstract
OBJECTIVES:To establish reference ranges for the more sensitive assays of thyrotropin and the best available assays of free thyroxine in premature infants after the first week of life.
STUDY DESIGN:Free thyroxine measurements by direct equilibrium dialysis and thyrotropin measurements by third generation immunometric assay were measured in 120 healthy premature infants 25 to 36 weeks' gestation at birth and every 3 weeks until hospital discharge. Infants were stratified by postconceptional age. Differences in free thyroxine and thyrotropin levels among groups were determined by ANOVA. Correlations between hormone measurements and gestational and postnatal ages were sought by linear regression analysis. Reference ranges were determined as arithmetic (free thyroxine) and geometric (thyrotropin) mean±2 SD ranges.
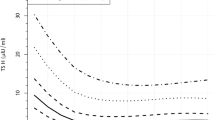
RESULTS:From 120 infants, 164 samples were obtained and grouped by postconceptional age at sampling. Free thyroxine was not different among postconceptional age groups and did not correlate with gestational or postnatal age. The free thyroxine reference range based on these data was 10 to 33 pmol/l (0.8 to 2.6 ng/dl). Thyrotropin did not correlate with gestational age. There was a clinically trivial but statistically significant (r2=0.03, p<0.05) correlation of thyrotropin with postnatal age. The thyrotropin reference based on these data was 0.8 to 12 mU/l.
CONCLUSIONS:Free thyroxine was closely regulated in these premature infants and levels were similar to those in older children and adults, once the natal surge in thyrotropin has subsided. After the first week of life a single range for each hormone appeared appropriate for all premature infants until 40 weeks postconceptional age.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobsen BB, Peitersen B, Anderson HJ, Hummer L Serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin, prealbumin and albumin in healthy fullterm, small-for-gestational age and preterm newborn infants Acta Paediatr Scand 1979 68 49–55
Hirano T, Singh J, Srinivasan G, Pildes R Post-natal thyroid function in low birth weight infants; a longitudinal assessment of free thyroxine and thyroid hormone binding globulin Acta Endocrinol 1985 110 56–60
Fisher DA Euthyroid low thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) states in prematures and sick infants Pediatr Clin North Am 1990 37 1297–312
Redding RA, Pereira C Thyroid function in respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) of the newborn Pediatrics 1974 54 423–8
Klein AH, Stinson D, Foley B, Larsen PR, Foley TP Thyroid function studies in preterm infants recovering from the respiratory distress syndrome J Pediatr 1977 91 261–3
Cuestas RA, Engel RR Thyroid function in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome J Pediatr 1979 94 643–6
Wilson DM, Hopper AO, McDougal IR, et al Serum free thyroxine values in term, premature, and sick infants J Pediatr 1982 101 113–7
Franklin RC, Purdie GL, O'Grady CM Neonatal thyroid function: prematurity, prenatal steroids, and respiratory distress syndrome Arch Dis Child 1986 61 589–92
Stahnke N, Stenzel E, Hellwege H Thyroid function in prematures with respiratory distress syndrome Acta Endocrinol Suppl 1986 279 354–60
Nelson JC, Tomei RT Direct determination of free thyroxin in undiluted serum by equilibrium dialysis/radioimmunoassay Clin Chem 1988 34 1737–44
Kaptein EM Clinical application of free thyroxine determinations In: Klee GE, editor. Clinics in Laboratory Medicine vol. 13 1993 p. 653–72
Spencer CA Clinical utility and cost-effectiveness of sensitive thyrotropin assays in ambulatory and hospitalized patients Mayo Clin Proc 1988 63 1214–22
Nicoloff JT, Spencer CA Clinical review 12: the use and misuse of the sensitive thyrotropin assays J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1990 71 553–8
Nelson JC, Wilcox RB Further studies on thyroxin-binding globulin-dependence in equilibrium dialysis assays of free thyroxin Clin Chem 1991 37 128–9
Nelson JC, Wilcox RB, Pandian MR Dependence of free thyroxine estimates obtained with equilibrium tracer dialysis on the concentration of thyroxine-binding globulin Clin Chem 1992 38 1294–300
Nelson JC, Weiss RM, Wilcox RB Underestimates of serum free T4 concentrations by free T4 immunoassays J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994 79 76–9
Wang R, Nelson JC, Weiss RM, Wilcox RB Accuracy of free thyroxine measurements across natural ranges of thyroxine binding to serum proteins Thyroid 2000 10 31–9
Nelson JC, Clark SJ, Borut dl, Tomei RT, Carlton EI Age-related change in serum free thyroxine during childhood and adolescence J Pediatr 1993 123 899–905
Adams LM, Emery JR, Clark SJ, Carlton EI, Nelson JC Reference ranges for newer thyroid function tests in premature infants J Pediatr 1995 126 122–7
Babson SG Growth of low-birth-weight infants J Pediatr 1970 77 11–8
Babson SG, Benda GI Growth graphs for the clinical assessment of infants of varying gestational age J Pediatr 1976 89 814–20
Ballard JL, Khoury JC, Wedig K, Wang L, Eilers-Walsman BL, Lipp R New Ballard score, expanded to include extremely premature infants J Pediatr 1991 119 417–23
Odell WD, Griffin J, Zahradnik R Two-monoclonal-antibody sandwich-type assay for thyrotropin, with use of avidin–biotin separation technique Clin Chem 1986 32 1873–8
Conover WJ Practical Nonparametric Statistics. 2nd ed Wiley 1980
Grubbs FE, Green B Extension of sample sizes and percentage points for significance tests of outlying observations Technometrics 1972 14 847–54
Klein RZ, Carlton EL, Faix JD, et al Thyroid function in very low birth weight infants Clin Endocrinol 1997 47 411–7
van Wassenaer AG, Kok JH, Dekker FW, de Vulder JJM Thyroid function in very preterm infants: influences of gestational age and disease Pediatr Res 1997 42 604–9
Rooman RP, Du Caju MVL, Op De Beeck L, Van Reempts P, Van Acker KJ Low thyroxinaemia occurs in the majority of very preterm newborns Eur J Pediatr 1996 155 211–5
Kodama S, Mori Y, Miyoshi M, et al Thyroid function in premature infants Kobe J Med Sci 1992 38 109–16
Hirano T, Singh J, Srinivasan G, Pildes R Postnatal thyroid function in low birth weight infants: a cross-sectional assessment of free thyroxine and thyroid hormone binding globulin Eur J Pediatr 1982 139 244–6
Fuse Y, Shimizu M, Uga N, Fujii T, Irie M Maturation of feedback control of thyrotropin in premature infants J Dev Physiol 1990 14 17–22
Mantagos S, Koulouris A, Makri M, Vagenakis AG Development of thyrotopin circadian rhythm in infancy J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1992 74 71–4
Fisher DA, Nelson JC, Carlton EI, Wilcox RB Maturation of human hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid function and control Thyroid 2000 10 229–34
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Grenith Zimmerman for helpful review and criticism of the manuscript. We also thank the medical students, David Huang and Suzanne Clark, who assisted us in computer data entry and chart review for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
There was no extramural funding for this study.
3626 NE 46th St., Suite 30C, Seattle, WA, 98105, USA
Utah Valley Regional Medical Center, 1034 North 500 West, Provo, UT, 84604, USA
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, S., Deming, D., Emery, J. et al. Reference Ranges for Thyroid Function Tests in Premature Infants Beyond the First Week of Life. J Perinatol 21, 531–536 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7210572
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7210572
This article is cited by
-
Nomogram-based evaluation of thyroid function in appropriate-for-gestational-age neonates in intensive care unit
Journal of Perinatology (2015)
-
Incidence of Low Free T4 Values in Premature Infants as Determined by Direct Equilibrium Dialysis
Journal of Perinatology (2004)