Abstract
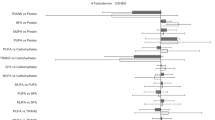
Mean serum insulin-like growth factor-I was 9% lower in 233 vegan men than in 226 meat-eaters and 237 vegetarians (P = 0.002). Vegans had higher testosterone levels than vegetarians and meat-eaters, but this was offset by higher sex hormone binding globulin, and there were no differences between diet groups in free testosterone, androstanediol glucuronide or luteinizing hormone. © 2000 Cancer Research Campaign
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
16 November 2011
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Bélanger A, Locong A, Noel C, Cusan L, Dupont A, Prévost J, Caron S and Sévigny J (1989) Influence of diet on plasma steroid and sex plasma binding globulin levels in adult men. J Steroid Biochem 32: 829–833
Bingham SA, Gill C, Welch A, Cassidy A, Runswick SA, Oakes S, Lubin R, Thurnham DI, Key TJ, Roe L, Khaw KT and Day NE (1997) Validation of dietary assessment methods in the UK arm of EPIC using weighed records, and 24-hour urinary nitrogen and potassium and serum vitamin C and carotenoids as biomarkers. Int J Epidemiol 26: S137–S151
Bosland MC, Oakley-Girvan L and Whittemore AS (1999) Dietary fat, calories and prostate cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 91: 489–491
Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Gann PH, Wilkinson P, Hennekens CH and Pollak M (1998) Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science 279: 563–566
Cohen P, Peehl DM and Rosenfeld RG (1994) IGF axis in the prostate. Horm Metab Res 26: 81–84
Deslypere JP and Vermeulen A (1984) Leydig cell function in normal men: effect of age, lifestyle, residence, diet and activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 59: 955–962
Eaton NE, Reeves GK, Appleby PN and Key TJ (1999) Endogenous sex hormones and prostate cancer: a quantitative review of prospective studies. Br J Cancer 80: 930–934
Gann PH, Hennekens CH, Ma J, Longcope C and Stampfer MJ (1996) Prospective study of sex hormone levels and risk of prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 88: 1118–1126
Giles G and Ireland P (1997) Diet, nutrition and prostate cancer. Int J Cancer (Suppl 10): S13–S17
Howie BJ and Shultz TD (1985) Dietary and hormonal interrelationships among vegetarian Seventh Day Adventists and nonvegetarian men. Am J Clin Nutr 42: 127–134
Key TJ, Roe L, Thorogood M, Moore JW, Clark GM and Wang DY (1990) Testosterone, sex hormone binding globulin, calculated free testosterone and oestradiol in male vegans and omnivores. Br J Nutr 64: 111–119
Key TJ, Fraser GE, Thorogood M, Appleby PN, Beral V, Reeves G, Burr ML, Chang-Claude J, Frentzel-Beyme R, Kuzma JW, Mann J and McPherson K (1999) Mortality in vegetarians and non-vegetarians: detailed findings from a collaborative analysis of 5 prospective studies. Am J Clin Nutr 70: 516S–524S
Montie JE and Pienta KJ (1994) A review of the role of androgenic hormones in the pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Urology 43: 892–899
Pusateri DJ, Roth WT, Ross JK and Shultz TD (1990) Dietary and hormonal evaluation of men at different risks for prostate cancer: plasma and fecal hormone–nutrient interrelationships. Am J Clin Nutr 51: 371–377
Södergaard RR, Backstrom T, Shanbhag V and Carstensen H (1982) Calculation of free and unbound fractions of testosterone and estradiol-17β to human plasma proteins at body temperature. J Steroid Biochem 6: 801–810
Thorogood M, Carter R, Benfield L, McPherson K and Mann JI (1987) Plasma lipids and lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations in people with different diets in Britain. BMJ 295: 351–353
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, N., Appleby, P., Davey, G. et al. Hormones and diet: low insulin-like growth factor-I but normal bioavailable androgens in vegan men. Br J Cancer 83, 95–97 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1152
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2000.1152
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Risk of cancer in regular and low meat-eaters, fish-eaters, and vegetarians: a prospective analysis of UK Biobank participants
BMC Medicine (2022)
-
Adolescent animal product intake in relation to later prostate cancer risk and mortality in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study
British Journal of Cancer (2021)
-
The association between plant-based content in diet and testosterone levels in US adults
World Journal of Urology (2021)
-
Animal foods, protein, calcium and prostate cancer risk: the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition
British Journal of Cancer (2008)
-
Comparative fracture risk in vegetarians and nonvegetarians in EPIC-Oxford
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2007)