Abstract
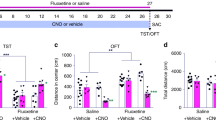
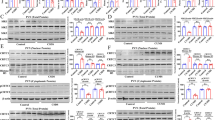
Although a putative role has been attributed to inflammation in the pathogenesis of depressive disorders, the relationship of prostaglandins, known mediators of inflammation, and depression has not been elucidated. Clomipramine is an antidepressive drug with a pro-depressive paradoxical effect in adult rats when administrated neonatally. Using this effect as a model of depression, we investigated the differential expression of the cyclooxygenase (COX-2) gene in rat brains. Rats injected neonatally with clomipramine showed depressive-like symptoms in adulthood, as well as decreased levels of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and a quantitative differential expression of the COX-2 gene (Real Time PCR) and protein (immunohistochemistry) in the hippocampus. As evidenced, the relationship between a key enzyme in the prostaglandin synthesis and biological and behavioral depression-like changes opens an interesting line of investigation regarding the molecular bases of depression and its potential treatment through immunomodulatory drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murray CJ, Lopez AD . Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 1997; 349: 1498–1504.
Kessler RC, McGonagle KA, Zhao S, Nelson CB, Hughes M, Eshleman S et al. Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R psychiatric disorders in the United States. Results from the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1994; 51: 8–19.
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt T, Taylor A, Craig I, Harrington H et al. Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HT gene. Science 2003; 301: 386–389.
Maes M, Meltzer HY . Psycopharmacology. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds). The Fourth Generation of Progress. Raven Press: New York, 1995 pp 933–944.
Connor TJ, Leonor BE . Depression, stress and immunological activation: the role of cytokines in depressive desorders. Life Sci 1998; 26: 583–606.
Leonard BE . The immune system, depression and the action of antidepressants. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2001; 25: 767–780.
Hopkins SJ, Rothwell NJ . Cytokines and the nervous system I: expression and recognition. Trends Neurosci 1995; 18: 83–88.
Komaki G, Arimura A, Koves K . Effect of intravenous injection of IL-1 beta on PGE2 levels in several brain areas as determined by microdialysis. Am J Physiol 1992; 262: 246–251.
Nogawa S, Zhang F, Ross ME, Iadecola C . Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in neurons contributes to ischemic brain damage. J Neurosci 1997; 17: 2746–2755.
Kim EJ, Lee JE, Kwon KJ, Lee SH, Moon CH, Baik EJ . Differential roles of cyclooxygenase isoforms after kainic acid-induced prostaglandin E2 production and neurodegenertation in cortical and hippocampal cell cultures. Brain Res 2001; 908: 1–9.
Pepicelli O, Fedele E, Bonanno G, Raiteri M, Amone-Cat M, Grecco A et al. In vivo activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the rat hippocampus increases prostaglandin E2 extracellular levels and trigges lipid peroxidation through cyclooxygenase-mediated mechanisms. J Neurochem 2002; 81: 1028–1034.
Chen C, Jeffery M, Bazan N . Cyclooxygenase-2 regulates prostaglandin E2 signaling in Hippocampal Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity. J Neurophysiol 2002; 87: 2851–2857.
Shaw KN, Commins S, O'Mara SM . Deficits in spatial learning and synaptic plasticity induced by the rapid and competitive broad-spectrum cyclooxygenase inhibitor ibuprofen are reversed by increasing endogenous brain-derived neurtrophic factor. Eur J Neurosci 2003; 17: 2438–2446.
Vogel G, Neill D, Hagler M, Kors D . A new animal model of endogenous depression: a summary of present findings. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1990; 14: 85–91.
Vogel G, Hartley P, Neill D, Hagler M, Kors D . Animal depression model by neonatal clomipramine: reduction of shock induced aggression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1988; 31: 103–106.
Feenstra MG, van Galen H, Te Riele PJ, Botterblom MH, Mirmiran M . Decreased hypothalamic serotonin levels in adult rats treated neonatally with clomipramine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1996; 55: 647–652.
Mavanji V, Meti B, Datta S . Sleep-wake effects of meta-chlorophenyl piperazine and mianserin in the behaviorally depressed rat. Eur J Pharmacol 2002; 455: 35–41.
Neill D, Vogel G, Hagler M, Kors D, Hennessey A . Diminished sexual activity in a new animal model of endogenous depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1190; 14: 73–76.
Andersen SL, Dumont NL, Teicher MH . Differences in behavior and monoamine laterality following neonatal clomipramine treatment. Dev Psychobiol 2002; 41: 50–57.
Prathiba J, Kumar KB, Karanth KS . Hyperactivity of hypothalamic pituitary axis in neonatal clomipramine model of depression. J Neural Trans 1998; 105: 1335–1339.
Bonilla-Jaime H, Retana-Marquez S, Vazquez-Palacios G, Velazquez-Moctezuma J . Plasma levels of corticosterone and testosterone after sexual activity in male rats treated neonatally with clomipramine. Behav Pharmacol 2003; 14: 357–362.
Bonilla-Jaime H, Retana-Marquez S, Velazquez-Moctezuma J . Pharmacological features of masculine sexual behavior in an animal model of depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1998; 60: 39–45.
Mavanji V, Datta S . Clomipramine treatment in neonatal rats alters the brain acetylcholinesterase activity in adulthood. Neurosci Lett 2002; 330: 119–121.
Angelucci F, Aloe L, Iannitelli A, Gruber SH, Mathe AA . Effect of chronic olanzapine treatment on nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat brain. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2005; 15: 311–317.
Schumacher J, Jamra RA, Becker T, Ohlraun S, Klopp N, Binder EB et al. Evidence for a relationship between genetic variants at the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) locus and major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2005; 58: 307–314.
Hansen HH, Mikkelsen JD . Long-term effect on serotonin transporter mRNA expression of chronic neonatal exposure to a serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 1998; 352: 307–315.
Vazquez-Palacios G, Bonilla-Jaime H, Velazquez-Moctezuma J . Antidepressant effects of nicotine and fluoxetine in an animal model of depression induced by neonatal treatment with clomipramine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2005; 29: 39–46.
McNamara RK, Skelton RW . The neuropharmacological and neurochemical basis of place learning in the Morris water maze. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 1993; 18: 33–49.
Sun MK, Alon DL . Induced depressive behavior impairs learning and memory in rats. Neurosience 2004; 129: 129–139.
Sun MK, Alkon DL . Related Induced depressive behavior impairs learning and memory in rats. Neuroscience 2004; 129: 129–139.
Schramm NL, McDonald MP, Limbird LE . The alpha (2a)-adrenergic receptor plays a protective role in mouse behavioral models of depression and anxiety. J Neurosci 200; 21: 4875–4882.
Brennan K, Roberts DCS, Anisman H . Individual differences in sucrose consumption in the rat: motivational and neurochemical correlates of hedonia. Psychopharmacology 2001; 157: 269–276.
Licinio J, Wong ML . The role of inflammatory mediators in the biology of major depression: central nervous system cytokines modulate the biological substrate of depressive symptoms, regulate stress-responsive systems, and contribute to neurotoxicity and neuroprotection. Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 317–327.
Turrin NP, Rivest S . Innate immune reaction in response to seizures: implications for the neuropathology associated with epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 2004; 16: 321–334.
Sheline YI, Mittler BL, Mintun MA . The hippocampus and depression. Eur Psychiatry 2002; 17: 300–305.
Muller N, Riedel M, Schwarz MJ . Psychotropic effects of COX-2 inhibitors-a possible new approach for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Pharmacopsychiatry 2004; 37: 266–269.
Hu F, Wang X, Pace TW, Wu H, Miller AH . Inhibition of COX-2 by celecoxib enhances glucocorticoid receptor function. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 426–428.
Malberg JE, Duman RS . Cell proliferation in adult hippocampus is decreased by inescapable stress: reversal by fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003; 28: 1562–1571.
Popoli M, Gennarelli M, Racagni G . Modulation of synaptic plasticity by stress and antidepressants. Bipolar Disord 2002; 4: 166–182.
Malberg JE . Implications of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in antidepressant action. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2004; 29: 196–205.
Fuchs E, Czeh B, Kole MH, Michaelis T, Lucassen PJ . Alterations of neuroplasticity in depression: the hippocampus and beyond. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2004; 14: S481–S490.
Lee PR, Brady DL, Shapiro RA, Dorsa DM, Koenig JI . Social interaction deficits caused by chronic phencyclidine administration are reversed by oxytocin. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005; 30: 1883–1894.
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M . Validation of open: closed arm entries in an elevated mlus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. Neurosci Methods 1985; 14: 149–167.
Andreani R, Bacellar LF . The relationship between anxiety and depression in animal models: a study using the forced swimming test and elevated plus-maze. Braz J Med Biol Res 1999; 32: 1121–1126.
Day LB, Schalert T . Anticholinergic effects on acquisition of place learning in the Morris water task: spatial mapping deficit or inability to inhibit nonplace strategies? Behav neurosci 1998; 110: 998–1005.
Moser MB, Trommald M, Andersen P . An increase in dendritic spine density on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells followin spatial learning in adult rats suggests the formation of new synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1994; 91: 12673–12675.
Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F, Thiebot M, Poncelte M, Soubrie P et al. Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR 141416, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 1997; 132: 104–106.
Hansen HH, Sanchez C, Meier E . Neonatal administration of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor Lu 10-134-C increases forced swimming-induced immobility in adult rats: a putative animal model of depression? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997; 283: 1333–1341.
Meredith G, Arbuthnott G . IBRO Handbook Series: Methods in Neurosciences. Wiley: England, 1993 Volume 16: Morphological Investigation of Single Neurons in vitro. Wiley.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001; 25: 402–408.
Ausubel F . Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley: United States of America, 1998.
Primer of Biostatistics, 5th edn, Stanton Glantz: Mc Graw-Hill, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Duality of interest
By the present, we declare that we have no duality or conflict of interest. The present work was financed entirely by the Hospital Italiano of Buenos Aires, a ‘non profit’ organization.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cassano, P., Hidalgo, A., Burgos, V. et al. Hippocampal upregulation of the cyclooxygenase-2 gene following neonatal clomipramine treatment (a model of depression). Pharmacogenomics J 6, 381–387 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500385
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500385
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Biosensors, Recent Advances in Determination of BDNF and NfL
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
The Developing Brain as a Target for Experimental Treatments in Modeling Pathological Processes
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2020)
-
Increased in cyclooxygenase—2 immunoreactivity and DNA damage in hippocampus of rats infected by Trypanosoma evansi
Comparative Clinical Pathology (2016)
-
Vatairea macrocarpa Lectin (VML) Induces Depressive-like Behavior and Expression of Neuroinflammatory Markers in Mice
Neurochemical Research (2013)
-
Chronic escitalopram treatment restores spatial learning, monoamine levels, and hippocampal long-term potentiation in an animal model of depression
Psychopharmacology (2011)