ABSTRACT
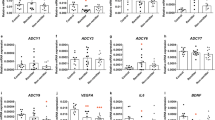
Chronic lithium treatment of B-lymphoblast cell lines (BLCLs) from bipolar-I disorder (BD-I) patients and healthy subjects ex vivo attenuates agonist- and thapsigargin-stimulated intracellular calcium (Ca2+) responses. As these findings suggest that chronic lithium treatment modifies receptor (ROCE) and/or store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) mechanisms, we determined whether chronic lithium treatment of BLCLs modified the expression of two members of the transient receptor potential channels (TRPC1 & 3), which participate in ROCE/SOCE. Chronic lithium treatment significantly reduced BLCL TRPC3 immunoreactivity (repeated-measures ANOVA, P=0.00005), with interaction effects of diagnosis (P=0.037) and sex (P=0.040). The lithium-induced decrease was greatest in BLCLs from female BD-I patients compared with those from healthy females (−27%) and with vehicle-treated BLCLs from female BD-I patients (−33%). However, lithium treatment did not affect TRPC1 and 3 mRNA levels, and TRPC1 immunoreactivity. Downregulation of TRPC3 may be an important mechanism by which lithium ameliorates pathophysiological Ca2+ disturbances as observed in BD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warsh JJ, Li PP . Second messenger systems and mood disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry 1996; 9: 23–29.
Manji HK, Moore GJ, Rajkowska G, Chen G . Neuroplasticity and cellular resilience in mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 578–593.
Mattson MP . Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2000; 1: 120–129.
Hara Y, Wakamori M, Ishii M, Maeno E, Nishida M, Yoshida T et al. LTRPC2 Ca2+-permeable channel activated by changes in redox status confers susceptibility to cell death. Mol Cell 2002; 9: 163–173.
Dubovsky SL, Murphy J, Thomas M, Rademacher J . Abnormal intracellular calcium ion concentration in platelets and lymphocytes of bipolar patients. Am J Psychiatry 1992; 149: 118–120.
Emamghoreishi M, Schlichter L, Li PP, Parikh S, Sen J, Kamble A et al. High intracellular calcium concentrations in transformed lymphoblasts from subjects with bipolar I disorder. Am J Psychiatry 1997; 154: 976–982.
Wasserman MJ, Warsh JJ, Li PP, Pennefather P, Sibony D . Hyperactive intracellular calcium mobilization in B lymphoblasts from patients with bipolar I disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2003; 53: 79S.
Hough C, Lu S-J, Davis CL, Chuang D-M, Post RM . Elevated basal and thapsigargin-stimulated intracellular calcium of platelets and lymphocytes from bipolar affective disorder patients measured by a fluorometric microassay. Biol Psychiatry 1999; 46: 247–255.
Wasserman MJ, Corson TW, Sibony D, Cooke RG, Parikh SV, Pennefather P et al. Chronic lithium treatment attentuates intracellular calcium mobilization. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004; 29: 759–769.
Kato T, Ishiwata M, Mori K, Washizuka S, Tajima O, Akiyama T et al. Mechanisms of altered Ca2+ signalling in transformed lymphoblastoid cells from patients with bipolar disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2003; 6: 379–389.
Nonaka S, Hough CJ, Chuang DM . Chronic lithium treatment robustly protects neurons in the central nervous system against excitotoxicity by inhibiting N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated calcium influx. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 2642–2647.
Chen Y, Hertz L . Inhibition of noradrenaline stimulated increase in [Ca2+]i in cultured astrocytes by chronic treatment with a therapeutically relevant lithium concentration. Brain Res 1996; 711: 245–248.
Yamaji T, Kagaya A, Uchitomi Y, Yokota N, Yamawaki S . Chronic treatment with antidepressants, verapamil, or lithium inhibits the serotonin-induced intracellular calcium response in individual C6 rat glioma cells. Life Sci 1997; 60: 817–823.
Varney MA, Godfrey PP, Drummond AH, Watson SP . Chronic lithium treatment inhibits basal and agonist-stimulated responses in rat cerebral cortex and GH3 pituitary cells. Mol Pharmacol 1992; 42: 671–678.
Dubovsky SL, Lee C, Christiano J, Murphy J . Lithium decreases platelet intracellular calcium concentration in bipolar patients. Lithium 1991; 2: 167–174.
Hashimoto R, Hough C, Nakazawa T, Yamamoto T, Chuang DM . Lithium protection against glutamate excitotoxicity in rat cerebral cortical neurons: involvement of NMDA receptor inhibition possibly by decreasing NR2B tyrosine phosphorylation. J Neurochem 2002; 80: 589–597.
Rajkowska G . Cell pathology in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 2002; 4: 105–116.
Tkachev D, Mimmack ML, Ryan MM, Wayland M, Freeman T, Jones PB et al. Oligodendrocyte dysfunction in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Lancet 2003; 362: 798–805.
Verkhratsky A, Orkand RK, Kettenmann H . Glial calcium: homeostasis and signaling function. Physiol Rev 1998; 78: 99–141.
Yoon IS, Li PP, Siu KP, Kennedy JL, Macciardi F, Cooke RG et al. Altered TRPC7 gene expression in bipolar-I disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2001; 50: 620–626.
Nishida M, Sugimoto K, Hara Y, Mori E, Morii T, Kurosaki T et al. Amplification of receptor signalling by Ca2+ entry-mediated translocation and activation of PLCγ2 in B lymphocytes. EMBO J 2003; 22: 4677–4688.
Rosado JA, Sage SO . Activation of store-mediated calcium entry by secretion-like coupling between the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type II and human transient receptor potential (hTrp1) channels in human platelets. Biochem J 2001; 356: 191–198.
Vazquez G, Wedel BJ, Trebak M, St John BG, Putney Jr JW . Expression level of the canonical transient receptor potential 3 (TRPC3) channel determines its mechanism of activation. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 21649–21654.
Vennekens R, Voets T, Bindels RJ, Droogmans G, Nilius B . Current understanding of mammalian TRP homologues. Cell Calcium 2002; 31: 253–264.
Zitt C, Zobel A, Obukhov AG, Harteneck C, Kalkbrenner F, Luckhoff A et al. Cloning and functional expression of a human Ca2+-permeable cation channel activated by calcium store depletion. Neuron 1996; 16: 1189–1196.
Ginzinger DG . Gene quantification using real-time quantitative PCR: an emerging technology hits the mainstream. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 503–512.
Ong HL, Chen J, Chataway T, Brereton H, Zhang L, Downs T et al. Specific detection of the endogenous transient receptor potential (TRP)-1 protein in liver and airway smooth muscle cells using immunoprecipitation and Western-blot analysis. Biochem J 2002; 364: 641–648.
den Dekker E, Molin DG, Breikers G, van Oerle R, Akkerman JW, van Eys GJ et al. Expression of transient receptor potential mRNA isoforms and Ca(2+) influx in differentiating human stem cells and platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001; 1539: 243–255.
Riccio A, Medhurst AD, Mattei C, Kelsell RE, Calver AR, Randall AD et al. mRNA distribution analysis of human TRPC family in CNS and peripheral tissues. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2002; 109: 95–104.
Garcia RL, Schilling WP . Differential expression of mammalian TRP homologues across tissues and cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997; 239: 279–283.
Emamghoreishi M, Li PP, Schlichter L, Parikh SV, Cooke RG, Warsh JJ et al. Associated disturbances in calcium homeostasis and G protein-mediated cAMP signaling in bipolar I disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 48: 665–673.
Alfonso J, Pollevick GD, Castensoon A, Jazin E, Frasch AC . Analysis of gene expression in the rat hippocampus using real time PCR reveals high inter-individual variation in mRNA expression levels. J Neurosci Res 2002; 67: 225–234.
Bustin SA . Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 2000; 25: 169–193.
Cheung VG, Conlin LK, Weber TM, Arcaro M, Jen KY, Morley M, Spielman R . Natural variation in human gene expression assessed in lymphoblastoid cells. Nat Genet 2003; 33: 422–425.
Tan CH, Javors MA, Seleshi E, Lowrimore PA, Bowden CL . Effects of lithium on platelet ionic intracellular calcium concentration in patients with bipolar (manic-depressive) disorder and healthy controls. Life Sci 1990; 46: 1175–1180.
Berk M, Bodemer W, Oudenhove TV, Butkow N . The platelet intracellular calcium response to serotonin is augmented in bipolar manic and depressed patients. Hum Psychopharmacol 1995; 10: 189–193.
Yoon IS, Li PP, Siu KP, Kennedy JL, Cooke RG, Parikh SV et al. Altered IMPA2 gene expression and calcium homeostasis in bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2001; 6: 678–683.
Winer J, Jung CK, Shackel I, Williams PM . Development and validation of real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for monitoring gene expression in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Anal Biochem 1999; 270: 41–49.
Bradford MM . A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976; 72: 248–254.
Gardner RC . Psychological Statistics Using SPSS for Windows. Prentice-Hall Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ 2001; pp. 146–153.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-12851, JJW, and MOP-53323, JJW and PPL), the Ontario Mental Health Foundation (JJW), and a CAMH Postdoctoral Fellowship award (SA). We gratefully acknowledge the contributions of the physicians and research staff of the Mood and Anxiety Programs of the Clarke Institute, Center for Addiction and Mental Health, and University of Toronto who referred potential patient subjects for participation in the studies from which the cell repository was established. Kin Po Siu contributed essential technical assistance in the growth and maintenance of cell lines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
DUALITY OF INTEREST
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreopoulos, S., Wasserman, M., Woo, K. et al. Chronic lithium treatment of B lymphoblasts from bipolar disorder patients reduces transient receptor potential channel 3 levels. Pharmacogenomics J 4, 365–373 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500266
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500266
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Investigation of genetic loci shared between bipolar disorder and risk-taking propensity: potential implications for pharmacological interventions
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)
-
Mood stabilizing drugs regulate transcription of immune, neuronal and metabolic pathway genes in Drosophila
Psychopharmacology (2016)
-
TRPC Channels: Prominent Candidates of Underlying Mechanism in Neuropsychiatric Diseases
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)
-
Permeation, regulation and control of expression of TRP channels by trace metal ions
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2015)
-
Lithium and bipolar mood disorder: the inositol-depletion hypothesis revisited
Molecular Psychiatry (2005)