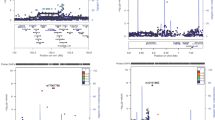
Abstract
In a large case-control study of Swedish incident type I diabetes patients and controls, 0–34 years of age, we tested the hypothesis that the GIMAP5 gene, a key genetic factor for lymphopenia in spontaneous BioBreeding rat diabetes, is associated with type I diabetes; with islet autoantibodies in incident type I diabetes patients or with age at clinical onset in incident type I diabetes patients. Initial scans of allelic association were followed by more detailed logistic regression modeling that adjusted for known type I diabetes risk factors and potential confounding variables. The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs6598, located in a polyadenylation signal of GIMAP5, was associated with the presence of significant levels of IA-2 autoantibodies in the type I diabetes patients. Patients with the minor allele A of rs6598 had an increased prevalence of IA-2 autoantibody levels compared to patients without the minor allele (OR=2.2; Bonferroni-corrected P=0.003), after adjusting for age at clinical onset (P=8.0 × 10−13) and the numbers of HLA-DQ A1*0501-B1*0201 haplotypes (P=2.4 × 10−5) and DQ A1*0301-B1*0302 haplotypes (P=0.002). GIMAP5 polymorphism was not associated with type I diabetes or with GAD65 or insulin autoantibodies, ICA, or age at clinical onset in patients. These data suggest that the GIMAP5 gene is associated with islet autoimmunity in type I diabetes and add to recent findings implicating the same SNP in another autoimmune disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Hirschhorn JN . Genetic epidemiology of type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2003; 4: 87–100.
Lorenzen T, Pociot F, Hougaard P, Nerup J . Long-term risk of IDDM in first-degree relatives of patients with IDDM. Diabetologia 1994; 37: 321–327.
Davis JA . Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in twins. Differences between monozygotic and dizygotic twins may need to be taken into account. BMJ 1996; 312: 313–314.
Dahlquist G, Blom L, Tuvemo T, Nyström L, Sandstrom A, Wall S . The Swedish childhood diabetes study—results from a nine year case register and a one year case-referent study indicating that type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus is associated with both type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and autoimmune disorders. Diabetologia 1989; 32: 2–6.
EURODIAB ACE Study Group. Variation and trends in incidence of childhood diabetes in Europe. Lancet 2000; 355: 873–876.
Mathis D, Vence L, Benoist C . Beta-cell death during progression to diabetes. Nature 2001; 414: 792–798.
Risch N . Genetics of IDDM: evidence for complex inheritance with HLA. Genet Epidemiol 1989; 6: 143–148.
Concannon P, Erlich HA, Julier C, Morahan G, Nerup J, Pociot F et al. Type 1 diabetes: evidence for susceptibility loci from four genome-wide linkage scans in 1435 multiplex families. Diabetes 2005; 54: 2995–3001.
Bell GI, Horita S, Karam JH . A polymorphic locus near the human insulin gene is associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1984; 33: 176–183.
Barratt BJ, Payne F, Lowe CE, Hermann R, Healy BC, Harold D et al. Remapping the insulin gene/IDDM2 locus in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1884–1889.
Nistico L, Buzzetti R, Pritchard LE, Van der Auwera B, Giovannini C, Bosi E et al. The CTLA-4 gene region of chromosome 2q33 is linked to, and associated with, type 1 diabetes. Belgian Diabetes Registry. Hum Mol Genet 1996; 5: 1075–1080.
Ueda H, Howson JM, Esposito L, Heward J, Snook H, Chamberlain G et al. Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature 2003; 423: 506–511.
Bottini N, Musumeci L, Alonso A, Rahmouni S, Nika K, Rostamkhani M et al. A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 337–338.
Roach JC, Deutsch K, Li S, Siegel AF, Bekris LM, Einhaus DC et al. Genetic mapping at 3-kilobase resolution reveals inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor 3 as a risk factor for type 1 diabetes in Sweden. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 79: 614–627.
Rich SS, Concannon P, Erlich H, Julier C, Morahan G, Nerup J et al. The type 1 diabetes genetics consortium. Ann NY Acad Sci 2006; 1079: 1–8.
Cox NJ, Wapelhorst B, Morrison VA, Johnson L, Pinchuk L, Spielman RS et al. Seven regions of the genome show evidence of linkage to type 1 diabetes in a consensus analysis of 767 multiplex families. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 69: 820–830.
Nerup J, Pociot F, European Consortium for IDDM Studies. A genomewide scan for type 1-diabetes susceptibility in Scandinavian families: identification of new loci with evidence of interactions. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 69: 1301–1313.
The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14 000 cases of seven common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 2007; 447: 661–678.
Notkins AL, Lernmark Å . Autoimmune type 1 diabetes: resolved and unresolved issues. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 1247–1252.
Wicker LS, Todd JA, Prins JB, Podolin PL, Renjilian RJ, Peterson LB . Resistance alleles at two non-major histocompatibility complex-linked insulin-dependent diabetes loci on chromosome 3, Idd3 and Idd10, protect nonobese diabetic mice from diabetes. J Exp Med 1994; 180: 1705–1713.
MacMurray AJ, Moralejo DH, Kwitek AE, Rutledge EA, Van Yserloo B, Gohlke P et al. Lymphopenia in the BB rat model of type 1 diabetes is due to a mutation in a novel immune-associated nucleotide (Ian)-related gene. Genome Res 2002; 12: 1029–1039.
Wicker LS, Chamberlain G, Hunter K, Rainbow D, Howlett S, Tiffen P et al. Fine mapping, gene content, comparative sequencing, and expression analyses support Ctla4 and Nramp1 as candidates for Idd5.1 and Idd5.2 in the nonobese diabetic mouse. J Immunol 2004; 173: 164–173.
Colle E, Guttmann RD, Seemayer T . Spontaneous diabetes mellitus syndrome in the rat. I. Association with the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med 1981; 154: 1237–1242.
Hornum L, Romer J, Markholst H . The diabetes-prone BB rat carries a frameshift mutation in Ian4, a positional candidate of Iddm1. Diabetes 2002; 51: 1972–1979.
Beaudoing E, Freier S, Wyatt JR, Claverie JM, Gautheret D . Patterns of variant polyadenylation signal usage in human genes. Genome Res 2000; 10: 1001–1010.
Harrell FE . Regression Modeling Strategies: with Applications to Linear Models, Logistic Regression, and Survival Analysis. Springer: New York, 2001.
Ott J . Association of genetic loci: replication or not, that is the question. Neurology 2004; 63: 955–958.
Wacholder S, Chanock S, Garcia-Closas M, El Ghormli L, Rothman N . Assessing the probability that a positive report is false: an approach for molecular epidemiology studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004; 96: 434–442.
Payne F, Smyth DJ, Pask R, Barratt B, Cooper J, Twells R et al. Haplotype tag single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of the human orthologues of the rat type 1 diabetes genes Ian4 (Lyp/Iddm1) and Cblb. Diabetes 2004; 53: 505–509.
Decochez K, Truyen I, van der Auwera B, Weets I, Vandemeulebroucke E, de Leeuw IH et al. Combined positivity for HLA DQ2/DQ8 and IA-2 antibodies defines population at high risk of developing type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 687–694.
Graham J, Hagopian WA, Kockum I, Li LS, Sanjeevi CB, Lowe RM et al. Genetic effects on age-dependent onset and islet cell autoantibody markers in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2002; 51: 1346–1355.
Hellquist A, Zucchelli M, Kivinen K, Saarialho-Kere U, Koskenmies S, Widen E et al. The human GIMAP5 gene has a common polyadenylation polymorphism increasing risk to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). J Med Genet 2007; 44: 314–321.
Edwalds-Gilbert G, Veraldi K, Milcarek C . Alternative poly(A) site selection in complex transcription units: means to an end? Nucl Acids Res 1997; 25: 2547–2561.
Conne B, Stutz A, Vassalli JD . The 3′ untranslated region of messenger RNA: a molecular ‘hotspot’ for pathology? Nat Med 2000; 6: 637–641.
Sandal T, Aumo L, Hedin L, Gjertsen BT, Doskeland SO . Irod/Ian5: an inhibitor of (gamma)-radiation- and okadaic acid-induced apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 2003; 14: 3292–3304.
Nitta T, Nasreen M, Seike T, Goji A, Ohigashi I, Miyazaki T et al. IAN family critically regulates survival and development of T lymphocytes. PLoS Biol 2006; 4: e103.
Dalberg U, Markholst H, Hornum L . Both Gimap5 and the diabetogenic BBDP allele of Gimap5 induce apoptosis in T cells. Int Immunol 2007; 19: 447–453.
Pihoker C, Gilliam LK, Hampe CS, Lernmark Å . Autoantibodies in diabetes. Diabetes 2005; 54 (Suppl 2): S52–S61.
Nitta T, Takahama Y . The lymphocyte guard-IANs: regulation of lymphocyte survival by IAN/GIMAP family proteins. Trends Immunol 2007; 28: 58–65.
Hermann R, Laine AP, Veijola R, Vahlberg T, Simell S, Lahde J et al. The effect of HLA class II, insulin and CTLA4 gene regions on the development of humoral beta cell autoimmunity. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 1766–1775.
Hermann R, Lipponen K, Kiviniemi M, Kakko T, Veijola R, Simell O et al. Lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase (LYP/PTPN22) Arg620Trp variant regulates insulin autoimmunity and progression to type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2006; 49: 1198–1208.
Landin-Olsson M, Karlsson FA, Lernmark Å, Sundkvist G . Islet cell and thyrogastric antibodies in 633 consecutive 15- to 34-yr-old patients in the diabetes incidence study in Sweden. Diabetes 1992; 41: 1022–1027.
Kockum I, Sanjeevi CB, Eastman S, Landin-Olsson M, Dahlquist G, Lernmark Å . Complex interaction between HLA DR and DQ in conferring risk for childhood type 1 diabetes. Eur J Immunogenet 1999; 26: 361–372.
Sanjeevi CB, Lybrand TP, DeWeese C, Landin-Olsson M, Kockum I, Dahlquist G et al. Polymorphic amino acid variations in HLA-DQ are associated with systematic physical property changes and occurrence of IDDM. Members of the Swedish Childhood Diabetes Study. Diabetes 1995; 44: 125–131.
Hubley R, Zitzler E, Siegel A, Roach J . Multiobjective genetic marker selection. Advances in Nature-Inspired Computation: The PPSN VII Workshops 2002; 7: 32–33.
Jurinke C, van den Boom D, Cantor CR, Koster H . Automated genotyping using the DNA MassArray technology. Methods Mol Biol 2002; 187: 179–192.
Palmer JP, Asplin CM, Clemons P, Lyen K, Tatpati O, Raghu PK et al. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science 1983; 222: 1337–1339.
Hagopian WA, Sanjeevi CB, Kockum I, Landin-Olsson M, Karlsen AE, Sundkvist G et al. Glutamate decarboxylase-, insulin-, and islet cell-antibodies and HLA typing to detect diabetes in a general population-based study of Swedish children. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 1505–1511.
Hagopian WA, Karlsen AE, Gottsater A, Landin-Olsson M, Grubin CE, Sundkvist G et al. Quantitative assay using recombinant human islet glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65) shows that 64 K autoantibody positivity at onset predicts diabetes type. J Clin Invest 1993; 91: 368–374.
Grubin CE, Daniels T, Toivola B, Landin-Olsson M, Hagopian WA, Li L et al. A novel radioligand binding assay to determine diagnostic accuracy of isoform-specific glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies in childhood IDDM. Diabetologia 1994; 37: 344–350.
Falorni A, Grubin CE, Takei I, Shimada A, Kasuga A, Maruyama T et al. Radioimmunoassay detects the frequent occurrence of autoantibodies to the Mr 65,000 isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase in Japanese insulin-dependent diabetes. Autoimmunity 1994; 19: 113–125.
Mire-Sluis AR, Gaines Das R, Lernmark Å . The World Health Organization International Collaborative Study for islet cell antibodies. Diabetologia 2000; 43: 1282–1292.
Lan MS, Lu J, Goto Y, Notkins AL . Molecular cloning and identification of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, IA-2, from human insulinoma. DNA Cell Biol 1994; 13: 505–514.
Rabin DU, Pleasic SM, Palmer-Crocker R, Shapiro JA . Cloning and expression of IDDM-specific human autoantigens. Diabetes 1992; 41: 183–186.
Kawasaki E, Eisenbarth GS, Wasmeier C, Hutton JC . Autoantibodies to protein tyrosine phosphatase-like proteins in type I diabetes. Overlapping specificities to phogrin and ICA512/IA-2. Diabetes 1996; 45: 1344–1349.
Olsson ML, Sundkvist G, Lernmark Å . Prolonged incubation in the two-colour immunofluorescence test increases the prevalence and titres of islet cell antibodies in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1987; 30: 327–332.
Bonifacio E, Lernmark Å, Dawkins RL . Serum exchange and use of dilutions have improved precision of measurement of islet cell antibodies. J Immunol Methods 1988; 106: 83–88.
R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2006, ISBN 3-900051-07-0, http://www.R-project.org.
Warnes G, Leisch F . Genetics: Population Genetics 2005; R package version 1.2.0.
Shin J-H, Blay S, McNeney B, Graham J . LDheatmap: an R function for graphical display of pairwise linkage disequilibria between single nucleotide polymorphisms. J Stat Soft 2006; 16: Code Snippet 3, http://www.jstatsoft.org/v16/c03/v16c03.pdf.
Pritchard JK, Przeworski M . Linkage disequilibrium in humans: models and data. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 69: 1–14.
Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS, Roskin KM, Pringle TH, Zahler AM et al. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 2002; 12: 996–1006.
Zhang H, Hu J, Recce M, Tian B . PolyA_DB: a database for mammalian mRNA polyadenylation. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33 (Database issue): D116–D120.
Acknowledgements
The MAGENTA study was funded by Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation International grant 1-2001-873 to ÅL. JS, BM and SB also received support from Canadian Institutes of Health Research grants NPG-64869 and ATF-66667, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada grants 213124-03 and 227972-00 and the Mathematics of Information Technology and Complex Systems, Canadian Networks of Centres of Excellence. JS and JG have fellowships from the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research. CBS is supported by a grant from the Swedish Medical Research Council (K2006-72X-14740-04-3). IK is supported by a career development award from the Juvenile Diabetes Foundation International (2-2000-570). We thank William Hagopian, Mona Landin-Olsson and Jerry Palmer for access to data on the autoantibody markers.
The following authors are from the Diabetes Incidence in Sweden Study Group: Hans Arnqvist, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Linköping, Linköping; Elisabeth Björck, Department of Medicine, University Hospital, Uppsala; Jan Eriksson, Department of Medicine, University of Umeå, Umeå; Lennarth Nyström, Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, University of Umeå, Umeå; Lars Olof Ohlson, Sahlgrenska Hospital, University of Göteborg, Göteborg; Bengt Scherstén, Department of Community Health Sciences, Dahlby, University of Lund, Lund; and Jan Östman, Center for Metabolism and Endocrinology, Huddinge University Hospital, Stockholm.
The following authors are from the Swedish Childhood Diabetes Study Group, all from Departments of Pediatrics: M Aili, Halmstad; LE Bååth, Östersund; E Carlsson, Kalmar; H Edenwall, Karlskrona; G Forsander, Falun; BW Granström, Gällivare; I Gustavsson, Skellefteå; R Hanås, Uddevalla; L Hellenberg, Nyköping; H Hellgren, Lidköping; E Holmberg, Umeå; H Hörnell, Hudiksvall; Sten-A Ivarsson, Malmö; C Johansson, Jönköping; G Jonsell, Karlstad; K Kockum, Ystad; B Lindblad, Mölndal; A Lindh, Borås; J Ludvigsson, Linköping; U Myrdal, Västerås; J Neiderud, Helsingborg; K Segnestam, Eskilstuna; S Sjöblad, Lund; L Skogsberg, Boden; L Strömberg, Norrköping; U Ståhle, Ängelholm; B Thalme, Huddinge; K Tullus, Danderyd; T Tuvemo, Uppsala; M Wallensteen, Stockholm; O Westphal, Göteborg; and J Åman, Örebro.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website (http://www.nature.com/gene)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, JH., Janer, M., McNeney, B. et al. IA-2 autoantibodies in incident type I diabetes patients are associated with a polyadenylation signal polymorphism in GIMAP5. Genes Immun 8, 503–512 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364413
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364413
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation in health and disease
Nature Reviews Genetics (2019)
-
Gimap5-dependent inactivation of GSK3β is required for CD4+ T cell homeostasis and prevention of immune pathology
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Tubulin‐ and actin‐associating GIMAP4 is required for IFN‐γ secretion during Th cell differentiation
Immunology & Cell Biology (2015)
-
Non-HLA type 1 diabetes genes modulate disease risk together with HLA-DQ and islet autoantibodies
Genes & Immunity (2015)
-
Temporal induction of immunoregulatory processes coincides with age-dependent resistance to viral-induced type 1 diabetes
Genes & Immunity (2013)