Abstract
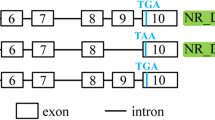
Previous studies have identified mRNA three isoforms encoding interleukin-15 (IL-15) that are produced through differential splicing and encode for the same mature IL-15 protein with two different signal peptides. Our analysis of mouse intestinal epithelial cells revealed two new IL-15 mRNA isoforms generated by different alternative splicing events. In one form (IL-15ΔE6), exon 6 is absent, and in the second form the first 48 nt of exon 7 are absent (IL-15ΔE7) through usage of an alternative 5′ splicing site within exon 7. These mRNA isoforms encoded in-frame IL-15 protein variants lacking either 15aa (IL-15ΔE6) or 16aa (IL-15ΔE7) both utilizing the normal long signal peptide. Significant structural changes were predicted for these new IL-15 isoforms. RNAse protection assays revealed the highest expression of isoform mRNA in the intestinal epithelium and functional analysis of recombinant IL-15 isoform proteins suggested possible regulatory functions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waldmann TA . T-cell receptors for cytokines: targets for immunotherapy of leukemia/lymphoma. Ann Oncol 2000; 11 (Suppl 1): 101–106.
Schluns KS, Stoklasek T, Lefrancois L . The roles of interleukin-15 receptor alpha: trans-presentation, receptor component, or both? Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2005; 37: 1567–1571.
Burton JD, Bamford RN, Peters C, Grant AJ, Kurys G, Goldman CK et al. A lymphokine, provisionally designated interleukin-T and produced by a human adult T-cell leukemia line, stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 4935–4939.
Bamford RN, Grant AJ, Burton JD, Peters C, Kurys G, Goldman CK et al. The interleukin (Il)-2 receptor-beta chain is shared by Il-2 and a cytokine, provisionally designated Il-T, that stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 4940–4944.
Carson WE, Giri JG, Lindemann MJ, Linett ML, Ahdieh M, Paxton R et al. Interleukin (IL) 15 is a novel cytokine that activates human natural killer cells via components of the IL-2 receptor. J Exp Med 1994; 180: 1395–1403.
Armitage RJ, Macduff BM, Eisenman J, Paxton R, Grabstein KH . IL-15 has stimulatory activity for the induction of B cell proliferation and differentiation. J Immunol 1995; 154: 483–490.
Koka R, Burkett PR, Chien M, Chai S, Chan F, Lodolce JP et al. Interleukin (IL)-15R[alpha]-deficient natural killer cells survive in normal but not IL-15R[alpha]-deficient mice. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 977–984.
Minagawa M, Watanabe H, Miyaji C, Tomiyama K, Shimura H, Ito A et al. Enforced expression of Bcl-2 restores the number of NK cells, but does not rescue the impaired development of NKT cells or intraepithelial lymphocytes, in IL-2/IL-15 receptor beta-chain-deficient mice. J Immunol 2002; 169: 4153–4160.
Ranson T, Vosshenrich CA, Corcuff E, Richard O, Laloux V, Lehuen A et al. IL-15 availability conditions homeostasis of peripheral natural killer T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 2663–2668.
Ranson T, Vosshenrich CA, Corcuff E, Richard O, Muller W, Di Santo JP . IL-15 is an essential mediator of peripheral NK-cell homeostasis. Blood 2003; 101: 4887–4893.
Prlic M, Blazar BR, Farrar MA, Jameson SC . In vivo survival and homeostatic proliferation of natural killer cells. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 967–976.
Schluns KS, Nowak EC, Cabrera-Hernandez A, Puddington L, Lefrancois L, Aguila HL . Distinct cell types control lymphoid subset development by means of IL-15 and IL-15 receptor alpha expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 5616–5621.
Zhang X, Sun S, Hwang I, Tough DF, Sprent J . Potent and selective stimulation of memory-phenotype CD8+ T cell in vivo by IL-15. Immunity 1998; 8: 591–599.
Kennedy MK, Glaccum M, Brown SN, Butz EA, Viney JL, Embers M et al. Reversible defects in natural killer and memory CD8T cell lineages in Interleukin-15-deficient mice. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 771–780.
Berard M, Brandt K, Paus SB, Tough DF . IL-15 promotes the survival of naive and memory phenotype CD8(+) T cells. J Immunol 2003; 170: 5018–5026.
Burkett PR, Koka R, Chien M, Chai S, Chan F, Ma A et al. IL-15Ralpha expression on CD8+ T cells is dispensable for T cell memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 4724–4729.
Schluns KS, Williams K, Ma A, Zheng XX, Lefrançois L . Cutting Edge: Requirement for IL-15 in the generation of primary and memory antigen-specific CD8 T cells. J Immunol 2002; 168: 4827–4831.
Yajima T, Nishimura H, Ishimitsu R, Watase T, Busch DH, Pamer EG et al. Overexpression of IL-15 in vivo increases antigen-driven memory CD8+ T cells following a microbe exposure. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1198–1203.
Dubois S, Mariner J, Waldmann TA, Tagaya Y . IL-15Ralpha recycles and presents IL-15 In trans to neighboring cells. Immunity 2002; 17: 537–547.
Sandau MM, Schluns KS, Lefrancois L, Jameson SC . Cutting edge: transpresentation of IL-15 by bone marrow-derived cells necessitates expression of IL-15 and IL-15R alpha by the same cells. J Immunol 2004; 173: 6537–6541.
Schluns KS, Klonowski KD, Lefrançois L . Trans-regulation of memory CD8 T cell prolferation by IL-15Rα+ bone marrow-derived cells. Blood 2004; 103: 988–994.
Figueras M, Busquets S, Carbo N, Barreiro E, Almendro V, Argiles JM et al. Interleukin-15 is able to suppress the increased DNA fragmentation associated with muscle wasting in tumour-bearing rats. FEBS Lett 2004; 569: 201–206.
Argiles JM, Lopez-Soriano J, Almendro V, Busquets S, Lopez-Soriano FJ . Cross-talk between skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: a link with obesity? Med Res Rev 2005; 25: 49–65.
Waldmann TA, Tagaya Y . The multifaceted regulation of interleukin-15 expression and the role of this cytokine in NK cell differentiation and host response to intracellular pathogens. Annu Rev Immunol 1999; 17: 19–49.
Lynch KW . Consequences of regulated pre-mRNA splicing in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2004; 4: 931–940.
Zav'yalov VP, Denesyuk AI, White B, Yurovsky VV, Atamas SP, Korpela T . Molecular model of an alternative splice variant of human IL-4, IL-4 delta 2, a naturally occurring inhibitor of IL-4-stimulated T cell proliferation. Immunol Lett 1997; 58: 149–152.
Denesyuk AI, Zav'yalov VP, Denessiouk KA, Korpela T . Molecular models of two competitive inhibitors, IL-2delta2 and IL-2delta3, generated by alternative splicing of human interleukin-2. Immunol Lett 1998; 60: 61–66.
Bihl MP, Heinimann K, Rudiger JJ, Eickelberg O, Perruchoud AP, Tamm M et al. Identification of a novel IL-6 isoform binding to the endogenous IL-6 receptor. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002; 27: 48–56.
Nishimura H, Washizu J, Nakamura N, Enomoto A, Yoshikai Y . Translational efficiency is up-regulated by alternative exon in murine IL-15 mRNA. J Immunol 1998; 160: 936–942.
Tagaya Y, Burton JD, Miyamoto Y, Waldmann TA . Identification of a novel receptor/signal transduction pathway for IL- 15/T in mast cells. EMBO J 1996; 15: 4928–4939.
Tagaya Y, Kurys G, Thies TA, Losi JM, Azimi N, Hanover JA et al. Generation of secretable and nonsecretable interleukin 15 isoforms through alternate usage of signal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 14444–14449.
Meazza R, Verdiani S, Biassoni R, Coppolecchia M, Gaggero A, Orengo AM et al. Identification of a novel interleukin-15 (IL-15) transcript isoform generated by alternative splicing in human small cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncogene 1996; 12: 2187–2192.
Anderson DM, Kumaki S, Ahdieh M, Bertles J, Tometsko M, Loomis A et al. Functional characterization of the human interleukin-15 receptor alpha chain and close linkage of IL15RA and IL2RA genes. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 29862–29869.
Tagaya Y, Kurys G, Thies TA, Losi JM, Azimi N, Hanover JA et al. Generation of secretable and nonsecretable interleukin 15 isoforms through alternate usage of signal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 14444–14449.
Meazza R, Gaggero A, Neglia F, Basso S, Sforzini S, Pereno R et al. Expression of two interleukin-15 mRNA isoforms in human tumors does not correlate with secretion: role of different signal peptides. Eur J Immunol 1997; 27: 1049–1054.
Reinecker HC, MacDermott RP, Mirau S, Dignass A, Podolsky DK . Intestinal epithelial cells both express and respond to interleukin 15. Gastroenterology 1996; 111: 1706–1713.
Hirose K, Suzuki H, Nishimura H, Mitani A, Washizu J, Matsuguchi T et al. Interleukin-15 may be responsible for early activation of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes after oral infection with Listeria monocytogenes in rats. Infect Immun 1998; 66: 5677–5683.
Hirose K, Nishimura H, Matsuguchi T, Yoshikai Y . Endogenous IL-15 might be responsible for early protection by natural killer cells against infection with an avirulent strain of Salmonella choleraesuis in mice. J Leukoc Biol 1999; 66: 382–390.
Tsytsikov VN, Yurovsky VV, Atamas SP, Alms WJ, White B . Identification and characterization of two alternative splice variants of human interleukin-2. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 23055–23060.
Bernard J, Harb C, Mortier E, Quemener A, Meloen RH, Vermot-Desroches C et al. Identification of an interleukin-15alpha receptor-binding site on human interleukin-15. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 24313–24322.
Bamford RN, DeFilippis AP, Azimi N, Kurys G, Waldmann TA . The 5′ untranslated region, signal peptide, and the coding sequence of the carboxyl terminus of IL-15 participate in its multifaceted translational control. J Immunol 1998; 160: 4418–4426.
Onu A, Pohl T, Krause H, Bulfone-Paus S . Regulation of IL-15 secretion via the leader peptide of two IL-15 isoforms. J Immunol 1997; 158: 255–262.
Gaggero A, Azzarone B, Andrei C, Mishal Z, Meazza R, Zappia E et al. Differential intracellular trafficking, secretion and endosomal localization of two IL-15 isoforms. Eur J Immunol 1999; 29: 1265–1274.
Giri JG, Kumaki S, Ahdieh M, Friend DJ, Loomis A, Shanebeck K et al. Identification and cloning of a novel IL-15 binding protein that is structurally related to the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor. EMBO J 1995; 14: 3654–3663.
Dubois S, Magrangeas F, Lehours P, Raher S, Bernard J, Boisteau O et al. Natural splicing of exon 2 of human interleukin-15 receptor alpha-chain mRNA results in a shortened form with a distinct pattern of expression. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 26978–26984.
Bulanova E, Budagian V, Orinska Z, Krause H, Paus R, Bulfone-Paus S . Mast cells express novel functional IL-15 receptor alpha isoforms. J Immunol 2003; 170: 5045–5055.
Ma A, Boone DL, Lodolce JP . The pleiotropic functions of interleukin 15: not so interleukin 2-like after all. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 753–756.
Zhao H, Nguyen H, Kang J . Interleukin 15 controls the generation of the restricted T cell receptor repertoire of gamma delta intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 1263–1271.
Ferrari-Lacraz S, Zanelli E, Neuberg M, Donskoy E, Kim YS, Zheng XX et al. Targeting IL-15 receptor-bearing cells with an antagonist mutant IL-15/Fc protein prevents disease development and progression in murine collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 2004; 173: 5818–5826.
Ruckert R, Brandt K, Braun A, Hoymann HG, Herz U, Budagian V et al. Blocking IL-15 prevents the induction of allergen-specific T cells and allergic inflammation in vivo. J Immunol 2005; 174: 5507–5515.
Yoshihara K, Yajima T, Kubo C, Yoshikai Y . Role of interleukin 15 in colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium in mice. Gut 2006; 55: 334–341.
Flint N, Cove FL, Evans GS . A low-temperature method for the isolation of small-intestinal epithelium along the crypt-villus axis. Biochem J 1991; 280: 331–334.
Stoye J . Multiple sequence alignment with the Divide-and-Conquer method. Gene 1998; 211: GC45–GC56.
Notredame C, Higgins DG, Heringa J . T-coffee: a novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J Mol Biol 2000; 302: 205–217.
Combet C, Blanchet C, Geourjon C, Deleage G . NPS@: network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem Sci 2000; 25: 147–150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, X., Lefrançois, L. Novel IL-15 isoforms generated by alternative splicing are expressed in the intestinal epithelium. Genes Immun 7, 407–416 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364314
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364314
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An activation-induced IL-15 isoform is a natural antagonist for IL-15 function
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
An Alternatively Spliced IL-15 Isoform Modulates Abrasion-Induced Keratinocyte Activation
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2015)
-
Interleukin-7 (IL-7) and IL-7 splice variants affect differentiation of human neural progenitor cells
Genes & Immunity (2010)
-
Expression analysis and functional activity of interleukin-7 splice variants
Genes & Immunity (2009)