Abstract
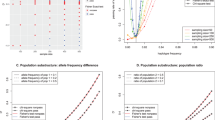
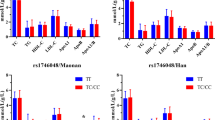
The major inflammatory cytokines interleukin(IL)1β, IL6 and tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) play a crucial role in infection, inflammation and stress responses. Previously, three coding genes were resequenced, identifying promoter polymorphisms that were used in association studies of neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders and cancer. These studies have produced intriguing but inconsistent results, potentially because the known functional variants: IL1B-511 C>T, IL6-174 G>C and TNF-308 G>A provided an incomplete picture of the total functional diversity at these genes. Therefore, we created marker panels for IL1B, IL6 and TNF/LTA that included the known functional marker but also other markers evenly spaced and with sufficient density to identify haplotype block structure and to maximize haplotype diversity. A total of 26 markers were genotyped in 96 US Caucasians and 96 African Americans. In both populations, a single block with little evidence of historical recombination was observed in IL1B, IL6 and TNF/LTA. For each gene, haplotypes captured the information content of each functional locus, even if that locus was not genotyped, and presumably haplotypes would capture the signal from unknown functional loci whose alleles are of moderate abundance. This study demonstrates the utility of using gene haplotype maps and marker panels as tools for linkage studies on related phenotypes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rothwell NJ . Functions and mechanisms of interleukin 1 in the brain. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1991; 12: 430–436.
McGeer PL, McGeer EG . Polymorphisms in inflammatory genes and the risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 2001; 58: 1790–1792.
Turnbull AV, Rivier C . Regulation of the HPA axis by cytokines. Brain Behav Immun 1995; 9: 253–275.
McGeer PL, McGeer EG . Innate immunity, local inflammation, and degenerative disease. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ 2002; 29: 3.
Jenny NS, Tracy RP, Ogg MS et al. In the elderly, interleukin-6 plasma levels and the −174G>C polymorphism are associated with the development of cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2002; 22: 2066–2071.
Anisman H, Merali Z . Cytokines, stress and depressive illness: brain-immune interactions. Ann Med 2003; 35: 2–11.
Molina PE, McClain C, Valla D et al. Molecular pathology and clinical aspects of alcohol-induced tissue injury. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2002; 26: 120–128.
Evseev VA, Igon'kina SI, Vetrile LA . Immunologic aspects of pathologic pain. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk 2003; 6: 12–16.
Ashford JW, Mortimer JA . Non-familial Alzheimer's disease is mainly due to genetic factors. J Alzheimers Dis 2002; 4: 169–177.
Flossmann E, Schulz UG, Rothwell PM . Systematic review of methods and results of studies of the genetic epidemiology of ischemic stroke. Stroke 2004; 35: 212–227.
Johansson C, Jansson M, Linner L et al. Genetics of affective disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2001; 11: 385–394.
Kreek MJ, Nielsen DA, LaForge KS . Genes associated with addiction: alcoholism, opiate, and cocaine addiction. Neuromolecular Med 2004; 5: 85–108.
Lariviere WR, Wilson SG, Laughlin TM et al. Heritability of nociception. III. Genetic relationships among commonly used assays of nociception and hypersensitivity. Pain 2002; 97: 75–86.
Pociot F, Molvig J, Wogensen L, Worsaae H, Nerup J . A TaqI polymorphism in the human interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) gene correlates with IL-1 beta secretion in vitro. Eur J Clin Invest 1992; 22: 396–402.
Zhang PA, Li Y, Xu P . Relationship of interleukin-1B and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms with chronic hepatitis B. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 2003; 20: 508–511.
Zeng ZR, Hu PJ, Hu S et al. Association of interleukin 1B gene polymorphism and gastric cancers in high and low prevalence regions in China. Gut 2003; 52: 1684–1689.
Ferri C, Sciacca FL, Grimaldi LE et al. Lack of association between IL-1A and IL-1B promoter polymorphisms and multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2000; 69: 564–565.
Grimaldi LM, Casadei VM, Ferri C et al. Association of early-onset Alzheimer's disease with an interleukin-1alpha gene polymorphism. Ann Neurol 2000; 47: 361–365.
Nishimura M, Mizuta I, Mizuta E et al. Influence of interleukin-1beta gene polymorphisms on age-at-onset of sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett 2000; 284: 73–76.
Vickers MA, Green FR, Terry C et al. Genotype at a promoter polymorphism of the interleukin-6 gene is associated with baseline levels of plasma C-reactive protein. Cardiovasc Res 2002; 53: 1029–1034.
Iakupova EV, Grinchuk OV, Kalimullina D et al. Molecular genetic analysis of the interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphisms in multiple myeloma. Mol Biol (Mosk) 2003; 37: 420–424.
Humphries SE, Luong LA, Ogg MS, Hawe E, Miller GJ . The interleukin-6 −174 G/C promoter polymorphism is associated with risk of coronary heart disease and systolic blood pressure in healthy men. Eur Heart J 2001; 22: 2243–2252.
Wieser F, Fabjani G, Tempfer C et al. Analysis of an interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism in women with endometriosis by pyrosequencing. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2003; 10: 32–36.
Hefler LA, Grimm C, Ackermann S et al. An interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism influences the biological phenotype of ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3066–3068.
Holla LI, Fassmann A, Stejskalova A et al. Analysis of the interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphisms in Czech patients with chronic periodontitis. J Periodontol 2004; 75: 30–36.
Lim CS, Zheng S, Kim YS et al. The −174 G to C polymorphism of interleukin-6 gene is very rare in koreans. Cytokine 2002; 19: 52–54.
Wilson AG, di Giovine FS, Duff GW . Genetics of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in autoimmune, infectious, and neoplastic diseases. J Inflamm 1995; 45: 1–12.
Kroeger KM, Carville KS, Abraham LJ . The −308 tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter polymorphism effects transcription. Mol Immunol 1997; 34: 391–399.
McGuire W, Hill AV, Allsopp CE, Greenwood BM, Kwiatkowski D . Variation in the TNF-alpha promoter region associated with susceptibility to cerebral malaria. Nature 1994; 371: 508–510.
Wilson AG, Clay FE, Crane AM, Cork MJ, Duff GW . Comparative genetic association of human leukocyte antigen class II and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with dermatitis herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol 1995; 104: 856–858.
Brinkman BM, Zuijdeest D, Kaijzel EL, Breedveld FC, Verweij CL . Relevance of the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) −308 promoter polymorphism in TNF alpha gene regulation. J Inflamm 1995; 46: 32–41.
Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 2002; 296: 2225–2229.
Ackerman H, Usen S, Mott R et al. Haplotypic analysis of the TNF locus by association efficiency and entropy. Genome Biol 2003; 4: R24.
Shi MM, Myrand SP, Bleavins MR, de la Iglesia FA . High throughput genotyping for the detection of a single nucleotide polymorphism in NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase (DT diaphorase) using TaqMan probes. Mol Pathol 1999; 52: 295–299.
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P . A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 68: 978–989.
Long JC, Williams RC, Urbanek M . An E-M algorithm and testing strategy for multiple-locus haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet 1995; 56: 799–810.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Alec Roy and Dr Mary-Anne Enoch for subsets of their population datasets, and to Longina Akhtar for assistance with cell culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by NIH Intramural Grants Z01 DE00366 and Z01 AA000301, and the Comprehensive Neuroscience Program Grant USUHS G192BR-C4 (Henry Jackson Foundation).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belfer, I., Buzas, B., Hipp, H. et al. Haplotype structure of inflammatory cytokines genes (IL1B, IL6 and TNF/LTA) in US Caucasians and African Americans. Genes Immun 5, 505–512 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364118
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364118
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neuro-inflammatory effects of photodegradative products of bilirubin
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Association of Lymphotoxin Alpha Polymorphism with Type 1 Diabetes in a Tunisian Population
Biochemical Genetics (2014)
-
Structure of tumor necrosis factor-alpha haploblocks in European populations
Immunogenetics (2013)
-
Lymphotoxin-alpha polymorphisms and presence of cancer in 1,536 consecutive autopsy cases
BMC Cancer (2008)
-
Genetic variation in tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin-alpha (TNF–LTA) and breast cancer risk
Human Genetics (2007)