Abstract
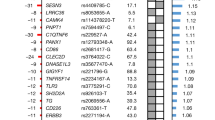
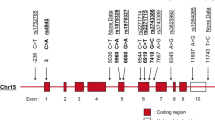
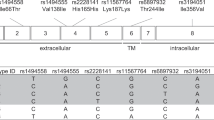
The interleukin-21 receptor (IL21R) was recently discovered as a novel member of the class-I-cytokine-receptor family and is selectively expressed in lymphoid tissues. IL21R shows strong sequence homologies to the interleukin-4 receptor α chain gene (IL4RA). In addition, both genes are adjacent and share structural similarity. We analyzed all the exons of the human IL21R gene and its 5′ flanking region for sequence variation. We identified four novel single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and genotyped 300 healthy blood donors. Total serum IgE levels were measured in all subjects and associated with IL21R SNPs. Results revealed a significant association of one IL21R polymorphism (T-83C) with elevated IgE levels (>100 kU/I) in females (OR=3.000, CI=[1.163;8.385], P=0.015, n=138). This was confirmed in a second prospectively collected group of female blood donors (OR=2.535, CI=[0.927;6.733], P=0.046, n=123). In contrast, no effects were observed in male subjects in either population. These findings identify IL21R as a possible novel target locus influencing IgE synthesis in female individuals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinzmann A, Deichmann KA . Genes for atopy and asthma. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2001; 1: 387–392.
Ober C . Susceptibility genes in asthma and allergy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2001; 1: 174–179.
Shirakawa I, Deichmann KA, Izuhara I, Mao I, Adra CN, Hopkin JM . Atopy and asthma: genetic variants of IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. Immunol Today 2000; 21: 60–64.
Ober C, Tsalenko A, Willadsen S et al. Genome-wide screen for atopy susceptibility alleles in the Hutterites. Clin Exp Allergy 1999; 29(Suppl 4): 11–15.
Deichmann KA, Heinzmann A, Forster J et al. Linkage and allelic association of atopy and markers flanking the IL4-receptor gene. Clin Exp Allergy 1998; 28: 151–155.
Ober C, Leavitt SA, Tsalenko A et al. Variation in the interleukin 4-receptor alpha gene confers susceptibility to asthma and atopy in ethnically diverse populations. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 66: 517–526.
Hackstein H, Hecker M, Kruse S et al. A novel polymorphism in the 5′ promoter region of the human interleukin-4 receptor alpha-chain gene is associated with decreased soluble interleukin-4 receptor protein levels. Immunogenetics 2001; 53: 264–269.
Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature 2000; 408: 57–63.
Ozaki K, Kikly K, Michalovich D, Young PR, Leonard WJ . Cloning of a type I cytokine receptor most related to the IL-2 receptor beta chain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000; 97: 11439–11444.
Kasaian MT, Whitters MJ, Carter LL et al. IL-21 limits NK cell responses and promotes antigen-specific T cell activation: a mediator of the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Immunity 2002; 16: 559–569.
Brenne AT, Baade Ro T, Waage A, Sundan A, Borset M, Hjorth-Hansen H . Interleukin-21 is a growth and survival factor for human myeloma cells. Blood 2002; 99: 3756–3762.
Jarvis D, Luczynska C, Chinn S, Burney P . The association of age, gender and smoking with total IgE and specific IgE. Clin Exp Allergy 1995; 25: 1083–1091.
Kerkhof M, Droste JH, de Monchy JG, Schouten JP, Rijcken B . Distribution of total serum IgE and specific IgE to common aeroallergens by sex and age, and their relationship to each other in a random sample of the Dutch general population aged 20–70 years. Dutch ECRHS Group, European Community Respiratory Health Study. Allergy 1996; 51: 770–776.
Webber MP, Carpiniello KE, Oruwariye T, Appel DK . Prevalence of asthma and asthma-like symptoms in inner-city elementary schoolchildren. Pediatr Pulmonol 2002; 34: 105–111.
Kurukulaaratchy RJ, Fenn M, Twiselton R, Matthews S, Arshad SH . The prevalence of asthma and wheezing illnesses among 10-year-old schoolchildren. Respir Med 2002; 96: 163–169.
Court CS, Cook DG, Strachan DP . The descriptive epidemiology of house dust mite-specific and total immunoglobin E in England using a nationally representative sample. Clin Exp Allergy 2002; 32: 1033–1041.
Hackstein H, Hofmann H, Bohnert A, Bein G . Definition of human interleukin-4 receptor alpha chain haplotypes and allelic association with atopy markers. Hum Immunol 1999; 60: 1119–1127.
Maniatis N, Collins A, Xu CF et al. The first linkage disequilibrium (LD) maps: delineation of hot and cold blocks by diplotype analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 2228–2233.
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L . Arlequin ver. 2000: A Software for Population Genetics Data Analysis. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, University of Geneva: Switzerland.
Acknowledgements
The excellent technical assistance of Ms Uta Schellenberg and Ms Angelika Nockher is gratefully acknowledged. We are grateful to Professor Katz and Dr Auch, Institute of Clinical Chemistry, University of Giessen, for measuring IgE levels.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, Germany (NGFN IE-S08T03). H Hackstein is supported by a scholarship of the Stiftung Hämotherapie-Forschung, Bonn, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hecker, M., Bohnert, A., König, I. et al. Novel genetic variation of human interleukin-21 receptor is associated with elevated IgE levels in females. Genes Immun 4, 228–233 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363954
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363954